Zone defense strategically positions players to cover specific areas on the court or field, effectively limiting opponent scoring opportunities by forcing difficult shots. This tactic emphasizes teamwork and communication, requiring players to maintain awareness of opponents entering their zones. Discover how mastering zone defense can elevate your game by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
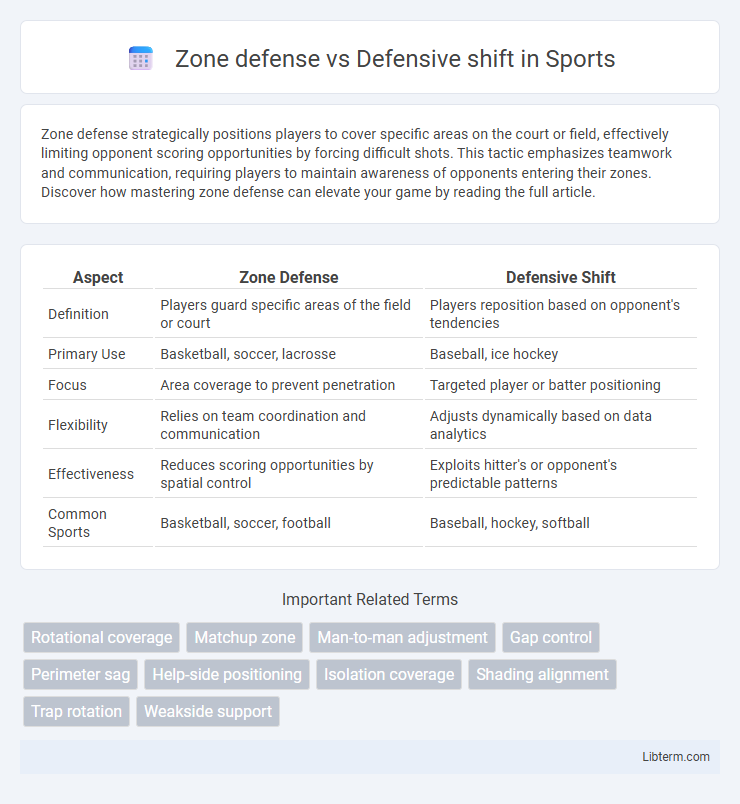
| Aspect | Zone Defense | Defensive Shift |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Players guard specific areas of the field or court | Players reposition based on opponent's tendencies |
| Primary Use | Basketball, soccer, lacrosse | Baseball, ice hockey |
| Focus | Area coverage to prevent penetration | Targeted player or batter positioning |
| Flexibility | Relies on team coordination and communication | Adjusts dynamically based on data analytics |
| Effectiveness | Reduces scoring opportunities by spatial control | Exploits hitter's or opponent's predictable patterns |
| Common Sports | Basketball, soccer, football | Baseball, hockey, softball |
Introduction to Zone Defense and Defensive Shift
Zone defense assigns players to guard specific areas of the court, optimizing team coverage by reducing gaps and forcing opponents into low-percentage shots. Defensive shift involves repositioning defenders based on opponents' tendencies and situational data, enhancing adaptability and disrupting offensive plays. Both strategies emphasize spatial control but differ in execution, with zone defense prioritizing area coverage and defensive shift focusing on dynamic adjustments.
Key Differences Between Zone Defense and Defensive Shift
Zone defense assigns players to defend specific areas on the field or court, emphasizing coverage and spatial control to limit opponents' scoring opportunities. Defensive shift, often used in baseball, involves repositioning fielders based on the batter's hitting tendencies to increase the chances of fielding batted balls effectively. Key differences include the fixed-area responsibility in zone defense versus the dynamic, batter-specific realignment in defensive shifts.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Zone defense originated in basketball during the 1940s as a strategic method to guard areas rather than individual players, evolving through rule changes to limit its use but regaining popularity in the 21st century due to its flexibility in team defense. Defensive shift, especially prominent in baseball since the early 2000s, developed as a response to data analytics identifying hitters' tendencies, allowing teams to reposition fielders strategically to increase ground ball outs. Both defensive strategies reflect an evolution driven by changing game dynamics and advancements in performance analysis, fundamentally shifting how teams approach defense.
Tactical Objectives of Each Strategy
Zone defense aims to protect specific areas on the field by positioning players to cover zones, minimizing opponents' scoring opportunities through spatial control and teamwork. Defensive shift focuses on adjusting player alignment dynamically based on hitters' tendencies, increasing the likelihood of fielding batted balls in high-frequency zones. Both strategies optimize defensive efficiency but differ in tactical objectives: zone defense emphasizes area coverage and balance, while defensive shift targets strategic realignment to exploit opponent weaknesses.
Advantages of Zone Defense
Zone defense offers strategic advantages by assigning players to guard specific areas, reducing individual mismatches and enhancing team coordination. This method confuses opponents by limiting easy passes and exploiting shooting angles, leading to lower shooting percentages. Zone defense also conserves player energy by minimizing constant switching and intensive one-on-one coverage, maintaining defensive intensity throughout the game.
Benefits of the Defensive Shift
The Defensive Shift enhances infield coverage by aligning players based on hitter tendencies, increasing the likelihood of ground ball outs and reducing opponent batting averages. This strategic realignment allows teams to anticipate and counteract predictable hitting patterns, resulting in higher defensive efficiency. By concentrating defenders on high-probability hit zones, the Defensive Shift minimizes gaps and optimizes player positioning for better run prevention.
Common Sports Utilizing Each Strategy
Zone defense commonly appears in basketball and soccer, where players cover specific areas of the field or court to prevent scoring opportunities. Defensive shifts dominate in baseball, with infielders repositioning based on hitters' tendencies to increase the likelihood of outs. Both strategies enhance team defense by optimizing player positioning relative to opponent behavior and game dynamics.
Situational Effectiveness and Limitations
Zone defense effectively limits passing lanes and protects high-percentage scoring areas, making it ideal in situations with strong perimeter shooters or when guarding slower players. Defensive shift adjusts player positioning based on batter tendencies, enhancing effectiveness against predictable hitters but often exposing gaps to unexpected plays. Both strategies face limitations: zone defense can be vulnerable to quick ball movement and offensive penetration, while defensive shifts may reduce coverage flexibility and increase susceptibility to bunt or off-speed hits.
Player Roles and Responsibilities
Zone defense assigns players to specific areas on the field, requiring them to guard any opponent entering their designated zone, emphasizing spatial awareness and teamwork. Defensive shift involves repositioning players to counteract hitters' tendencies, demanding adaptability and precise communication to cover altered areas effectively. Both strategies rely on player roles evolving dynamically, with zone focusing on collective coverage and shifts targeting individual batter profiles to optimize defensive efficiency.
Choosing the Right Defense for Your Team
Zone defense provides structured coverage by assigning players to specific areas, enhancing team coordination against perimeter threats. Defensive shift involves repositioning players dynamically based on hitter tendencies, maximizing infield and outfield effectiveness for ground balls and line drives. Choosing the right defense depends on analyzing opponent strengths, team speed, and situational data to optimize defensive alignment and improve overall run prevention.
Zone defense Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com