Isolation play in basketball focuses on creating one-on-one opportunities where a player exploits a matchup advantage to score or facilitate. This strategy relies heavily on individual skill, spacing, and reading the defense to maximize offensive efficiency. Discover how mastering isolation play can elevate your game by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
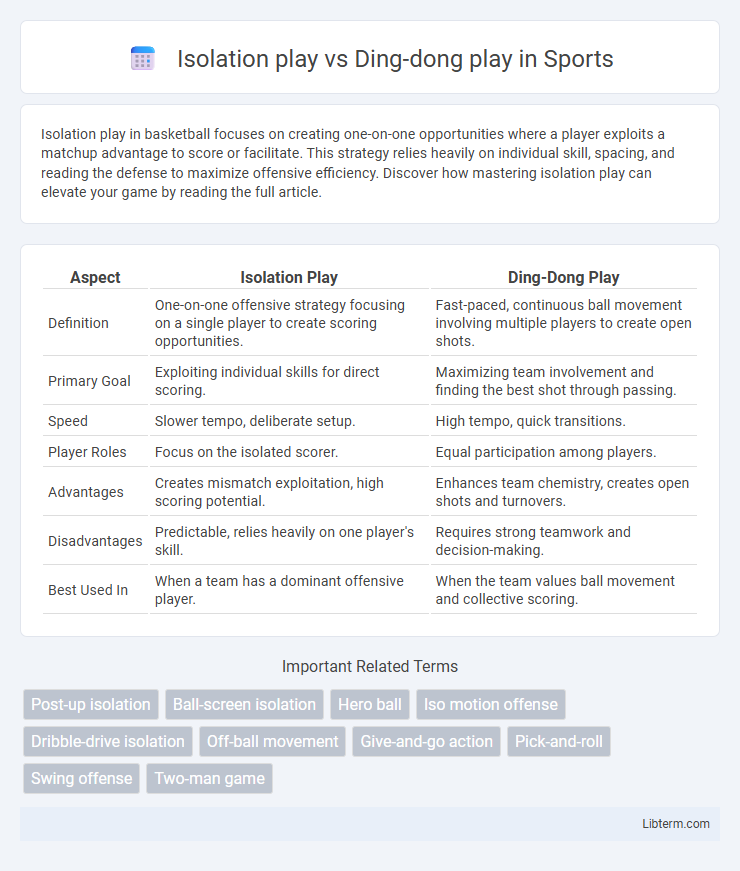
| Aspect | Isolation Play | Ding-Dong Play |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One-on-one offensive strategy focusing on a single player to create scoring opportunities. | Fast-paced, continuous ball movement involving multiple players to create open shots. |
| Primary Goal | Exploiting individual skills for direct scoring. | Maximizing team involvement and finding the best shot through passing. |
| Speed | Slower tempo, deliberate setup. | High tempo, quick transitions. |
| Player Roles | Focus on the isolated scorer. | Equal participation among players. |
| Advantages | Creates mismatch exploitation, high scoring potential. | Enhances team chemistry, creates open shots and turnovers. |
| Disadvantages | Predictable, relies heavily on one player's skill. | Requires strong teamwork and decision-making. |
| Best Used In | When a team has a dominant offensive player. | When the team values ball movement and collective scoring. |
Introduction to Isolation Play and Ding-dong Play
Isolation play centers on creating one-on-one matchups by clearing space for a specific player to exploit defensive weaknesses, emphasizing individual skill and spacing. Ding-dong play relies on rapid ball movement and continuous passing among teammates to disrupt defenses and generate open shots through team coordination. Both strategies offer distinct tactical advantages in basketball, targeting different aspects of offensive execution.
Definitions and Key Characteristics
Isolation play involves creating one-on-one matchups by spacing the floor and allowing a single player to exploit their scoring ability against a defender, emphasizing individual skill and decision-making. Ding-dong play refers to a rapid ball movement strategy where players pass quickly around the perimeter or inside, aiming to find the best shot opportunity through team coordination and spacing. Both strategies highlight contrasting offensive philosophies: isolation prioritizes individual talent while ding-dong focuses on collective ball circulation and shot creation.
Developmental Benefits of Isolation Play
Isolation play fosters individual creativity and self-awareness by allowing children to explore materials and ideas without social influence, which supports cognitive and emotional development. This form of play encourages problem-solving skills and concentration as children engage deeply with their environment, promoting independence and intrinsic motivation. In contrast to ding-dong play, which emphasizes interaction, isolation play offers a vital foundation for building personal identity and self-regulation.
Developmental Benefits of Ding-dong Play
Ding-dong play fosters social interaction, language development, and cooperative problem-solving skills by encouraging children to engage with peers in dynamic, reciprocal exchanges. This play style enhances emotional regulation and empathy through shared experiences, contrasting with isolation play, which predominantly supports independent exploration and self-soothing. The developmental benefits of ding-dong play contribute significantly to a child's ability to build relationships and navigate social contexts effectively.
Social Interaction Differences
Isolation play involves a child playing alone with minimal social interaction, emphasizing solitary exploration and self-entertainment. In contrast, ding-dong play encourages active social engagement, where children take turns and respond to each other's actions, fostering cooperative skills and communication. These differences highlight how isolation play promotes independent development, while ding-dong play enhances social bonding and interpersonal learning.
Cognitive and Emotional Impact
Isolation play fosters focused attention and problem-solving skills by minimizing distractions, enhancing cognitive development and emotional regulation. Ding-dong play, characterized by rapid back-and-forth interactions, stimulates social cognition and emotional responsiveness by encouraging turn-taking and empathy. Both play styles contribute uniquely to a child's cognitive flexibility and emotional intelligence through different mechanisms of engagement.
Age Appropriateness and Stages
Isolation play typically emerges in toddlers aged 12 to 24 months, marking an early developmental stage where children explore objects independently, fostering sensory and motor skills. Ding-dong play, often observed in children aged 2 to 4 years, involves repetitive actions with toys or objects that produce sound, supporting auditory development and cause-effect understanding. Both play types align with distinct cognitive and developmental milestones critical for age-appropriate learning progression.
Real-life Examples and Scenarios
Isolation play in basketball involves creating one-on-one opportunities for a skilled scorer, often seen in the NBA with players like Kevin Durant utilizing isolation to exploit mismatches in late-game scenarios. In contrast, ding-dong play emphasizes continuous ball movement and rapid passes, exemplified by teams like the Golden State Warriors, who use this strategy to increase open shot opportunities and keep defenses off balance. Real-life scenarios highlight isolation plays dominating in clutch moments where individual skill is crucial, whereas ding-dong play thrives in fast-paced, team-oriented offenses aiming for high-percentage shots.
Expert Insights on Play Styles
Expert analysis reveals that Isolation play emphasizes one-on-one offensive matchups to exploit individual skill advantages, frequently utilized by elite scorers to create high-percentage shots. Ding-dong play integrates continuous ball movement and player rotations, optimizing team spacing and collective scoring opportunities through rapid passes and off-ball cuts. Coaches prioritize Isolation in late-game clutch situations for isolation scoring, while favoring Ding-dong strategies in regular flow to enhance offensive efficiency and defensive disruption.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Play Approach
Isolation play emphasizes creating one-on-one matchups to exploit individual offensive skills, while ding-dong play relies on continuous ball movement and team coordination to generate scoring opportunities. Teams with strong individual scorers benefit from isolation strategies, whereas those with balanced talent and high basketball IQ thrive in ding-dong systems. Selecting the right play approach depends on roster composition, player strengths, and coaching philosophy aligned with maximizing offensive efficiency.
Isolation play Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com