Albatrosses are remarkable seabirds known for their impressive wingspans, which can exceed 11 feet, enabling them to glide effortlessly over oceans for hours without flapping. These birds play a crucial role in marine ecosystems by feeding on squid, fish, and crustaceans while often traveling thousands of miles between feeding grounds and breeding sites. Discover more about the fascinating behaviors and conservation efforts surrounding albatrosses in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
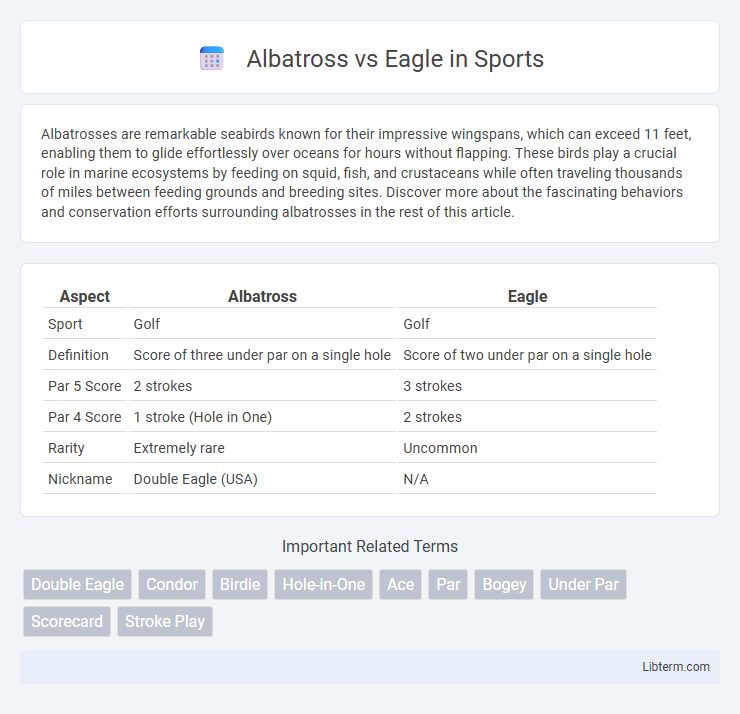
| Aspect | Albatross | Eagle |
|---|---|---|
| Sport | Golf | Golf |
| Definition | Score of three under par on a single hole | Score of two under par on a single hole |
| Par 5 Score | 2 strokes | 3 strokes |
| Par 4 Score | 1 stroke (Hole in One) | 2 strokes |
| Rarity | Extremely rare | Uncommon |
| Nickname | Double Eagle (USA) | N/A |
Introduction: Albatross vs Eagle
The albatross is renowned for its extraordinary wingspan, reaching up to 11 feet, enabling effortless gliding over oceans, while eagles exhibit powerful flight with broad, muscular wings designed for agility and hunting. Albatrosses primarily inhabit open sea environments, relying on wind currents for long-distance travel, contrasting with eagles' preference for diverse habitats including forests and mountains where they hunt prey. Both birds symbolize strength and freedom but differ significantly in flight mechanics, habitat, and hunting strategies.
Taxonomy and Classification
The albatross belongs to the family Diomedeidae within the order Procellariiformes, characterized by large seabirds with long wings adapted for dynamic soaring. In contrast, the eagle is part of the family Accipitridae in the order Accipitriformes, comprising powerful birds of prey with keen eyesight and strong talons. Both species occupy distinct taxonomic classes, reflecting their evolutionary divergence and differing ecological roles.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
The albatross boasts an impressive wingspan ranging from 6.5 to 11 feet, making it one of the largest flying birds, while the eagle's wingspan typically measures between 6 and 7.5 feet. Albatrosses have long, narrow wings adapted for dynamic soaring over oceans, contrasting with the broader, more robust wings of eagles designed for powerful flight and maneuverability. The body weight of an albatross varies from 6 to 20 pounds, depending on the species, whereas eagles weigh between 6.5 to 15 pounds, with differences in size and strength reflecting their predatory lifestyle compared to the albatross's oceanic soar.
Distribution and Habitat
Albatrosses primarily inhabit the Southern Ocean and North Pacific, favoring open ocean environments with vast expanses of cold water where they can glide effortlessly over long distances. Eagles are distributed across diverse habitats worldwide, ranging from forests and mountains to wetlands and grasslands, adapting to various climates and terrains. The albatross's pelagic lifestyle contrasts with the eagle's preference for terrestrial or near-water habitats, reflecting their distinct ecological niches.
Wingspan and Flight Abilities
The albatross boasts the longest wingspan among birds, measuring up to 11 feet, enabling it to glide effortlessly over oceans with minimal energy expenditure. Eagles have shorter wingspans, typically around 6 to 7.5 feet, but their powerful flight muscles allow for rapid acceleration and agile maneuvering in mountainous and forested environments. While albatrosses excel in dynamic soaring and long-distance gliding, eagles are masters of soaring combined with swift, precise dives to capture prey.
Feeding Habits and Diet
Albatrosses primarily feed on squid, fish, and krill, often scavenging from the ocean surface or diving shallowly to catch prey. Eagles have a more varied diet consisting of fish, small mammals, birds, and carrion, utilizing powerful talons to hunt and capture live prey. Both species exhibit opportunistic feeding behaviors, adapting their diets based on available resources in their environments.
Mating Rituals and Lifespan
Albatrosses exhibit elaborate mating rituals that include long courtship dances and mutual preening, often forming lifelong pair bonds lasting over 50 years. Eagles engage in aerial displays and nest-building as part of their courtship, with pair bonds generally lasting multiple breeding seasons, sometimes up to 20 years. Lifespan differs significantly, with albatrosses living up to 60 years in the wild, whereas eagles typically live around 20-30 years depending on the species.
Role in Culture and Symbolism
Albatross symbolizes endurance, freedom, and navigation in maritime folklore, often representing a good omen for sailors. Eagles embody strength, courage, and vision, serving as national emblems and spiritual icons across various cultures worldwide. Both birds hold profound symbolic significance, reflecting human values and natural majesty in mythology and art.
Conservation Status and Threats
The albatross species, particularly those in the genus Diomedea, face critical threats from longline fishing, habitat degradation, and invasive predators, leading to several species being classified as vulnerable or endangered on the IUCN Red List. Eagles, such as the Bald Eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus) and the Golden Eagle (Aquila chrysaetos), generally have more stable populations but remain threatened by habitat loss, pollution, and human disturbances in certain regions. Conservation efforts for albatrosses emphasize bycatch reduction and habitat protection, while eagle conservation focuses on legal protection, habitat restoration, and pollution control.
Key Differences: Albatross vs Eagle
The albatross is known for its exceptional wingspan, reaching up to 11 feet, enabling it to glide effortlessly over oceans for thousands of miles, while eagles typically have a wingspan of 6 to 7 feet and are powerful hunters with excellent vision. Albatrosses primarily feed on squid and fish by surface seizing or diving, whereas eagles hunt a diverse range of prey including mammals, birds, and reptiles using their sharp talons. Habitat differences are notable: albatrosses are pelagic seabirds found mainly in the Southern Ocean, whereas eagles inhabit a variety of terrestrial environments from forests to mountains.
Albatross Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com