A well-designed helmet offers essential protection by absorbing impact energy and reducing the risk of head injuries during accidents. Choosing a helmet that fits comfortably and meets safety standards can significantly enhance your overall safety while cycling, motorcycling, or engaging in other sports. Discover how to select the perfect helmet to safeguard your head by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
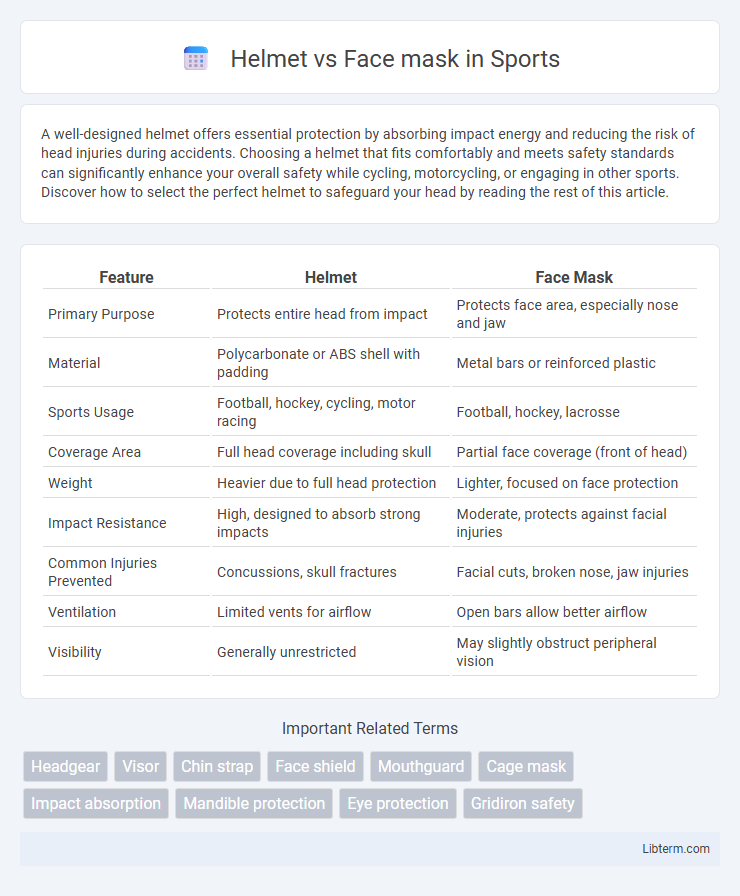
| Feature | Helmet | Face Mask |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Protects entire head from impact | Protects face area, especially nose and jaw |
| Material | Polycarbonate or ABS shell with padding | Metal bars or reinforced plastic |
| Sports Usage | Football, hockey, cycling, motor racing | Football, hockey, lacrosse |
| Coverage Area | Full head coverage including skull | Partial face coverage (front of head) |
| Weight | Heavier due to full head protection | Lighter, focused on face protection |
| Impact Resistance | High, designed to absorb strong impacts | Moderate, protects against facial injuries |
| Common Injuries Prevented | Concussions, skull fractures | Facial cuts, broken nose, jaw injuries |
| Ventilation | Limited vents for airflow | Open bars allow better airflow |
| Visibility | Generally unrestricted | May slightly obstruct peripheral vision |
Introduction: Helmet vs Face Mask
Helmets and face masks serve distinct protective functions in sports and safety gear, with helmets designed to shield the entire head from impact, while face masks primarily protect the facial region. Helmets are constructed using hard outer shells and cushioning to absorb shock, significantly reducing the risk of traumatic brain injuries. Face masks, often made from metal or polycarbonate materials, guard against facial fractures, ocular injuries, and respiratory harm during physical activities or hazardous environments.
Historical Background of Head and Face Protection
Early forms of head and face protection date back to ancient civilizations where warriors used helmets crafted from bronze and iron to shield against weapons. The evolution of helmets and face masks continued through medieval times with the introduction of visored helmets and full-face guards designed to enhance defense during combat. Modern advancements have focused on materials science and ergonomic design to improve protection in sports, military, and industrial settings.
Key Differences Between Helmets and Face Masks
Helmets provide full head coverage with a hard outer shell designed to absorb impact, while face masks primarily protect the facial area with a combination of bars or shields to prevent injuries from direct hits. Helmets often include padding and ventilation systems for comfort and safety, whereas face masks are lightweight and focus on visibility and breathability. The key difference lies in the scope of protection: helmets safeguard the entire head, impacting brain injury prevention, while face masks specifically shield the nose, mouth, and eyes against facial trauma.
Types of Helmets and Their Uses
Full-face helmets provide maximum protection by covering the entire head and face, making them ideal for high-speed motorcycling and racing. Modular helmets offer versatility with a flip-up chin bar, suitable for touring riders who value convenience without sacrificing safety. Open-face helmets prioritize comfort and visibility, commonly used in urban or low-speed environments where less coverage is sufficient.
Types of Face Masks and Their Uses
Face masks come in various types, including surgical masks, N95 respirators, cloth masks, and face shields, each designed for specific protection levels and uses. Surgical masks primarily prevent droplet transmission in medical settings, while N95 respirators filter airborne particles for enhanced respiratory protection, especially in hazardous environments. Cloth masks offer reusable protection for everyday use, and face shields provide a barrier against splashes and large droplets, often used alongside masks for comprehensive coverage.
Safety Standards and Effectiveness Comparison
Helmets and face masks both adhere to specific safety standards tailored to their protective functions, with helmets meeting rigorous impact resistance criteria such as DOT, ECE, or Snell certifications, while face masks comply with filtration efficiency standards like NIOSH N95 or ASTM F2100. Helmets offer superior protection against head injuries by absorbing and dissipating impact forces, whereas face masks primarily reduce the transmission of airborne particles and pathogens, ensuring respiratory safety. Effectiveness varies by use case: helmets are essential for high-impact scenarios like motorcycling or sports, and face masks are critical in environments requiring infection control or pollution reduction.
Comfort and Usability: Helmet vs Face Mask
Helmets provide superior overall protection but can feel bulky and heavy, impacting comfort during extended use. Face masks offer greater breathability and lighter weight, enhancing usability for longer wear and ease of communication. Choosing between helmet and face mask depends on balancing protection needs with comfort preferences and activity type.
Application in Sports, Construction, and Healthcare
Helmets provide comprehensive head protection and are essential in high-impact sports like football, construction sites for preventing traumatic injuries, and healthcare settings to shield against physical hazards during emergency responses. Face masks primarily protect the respiratory system by filtering airborne particles and are crucial in healthcare environments to reduce infection transmission, as well as in construction for dust and chemical exposure. Sports applications favor helmets for head safety, while face masks serve as respiratory protection in environments with airborne contaminants.
Cost Analysis: Which is More Economical?
Helmets generally cost more upfront, ranging from $50 to $300 depending on materials and technology, while face masks typically cost between $10 and $50. However, helmets offer better long-term value due to their durability and enhanced protection, reducing potential medical expenses associated with head injuries. Face masks may require more frequent replacement, leading to higher cumulative costs over time despite the lower initial investment.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Protection
Selecting the appropriate protection between a helmet and a face mask depends on the specific activity and associated risks; helmets provide comprehensive head impact protection ideal for sports and construction, while face masks excel in guarding against airborne particles and facial injuries. Prioritize helmets for high-impact scenarios requiring skull and brain safety, and face masks for environments with respiratory hazards or minor facial trauma risks. Understanding the distinct protective features ensures optimal safety and comfort tailored to each use case.
Helmet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com