A common foul in sports occurs when a player breaks the rules of fair play, such as making illegal contact or handling the ball incorrectly. This penalty often results in the opposing team gaining possession or receiving a free throw or penalty kick. Discover how common fouls impact the flow of the game and what you need to know to stay on the winning side.
Table of Comparison
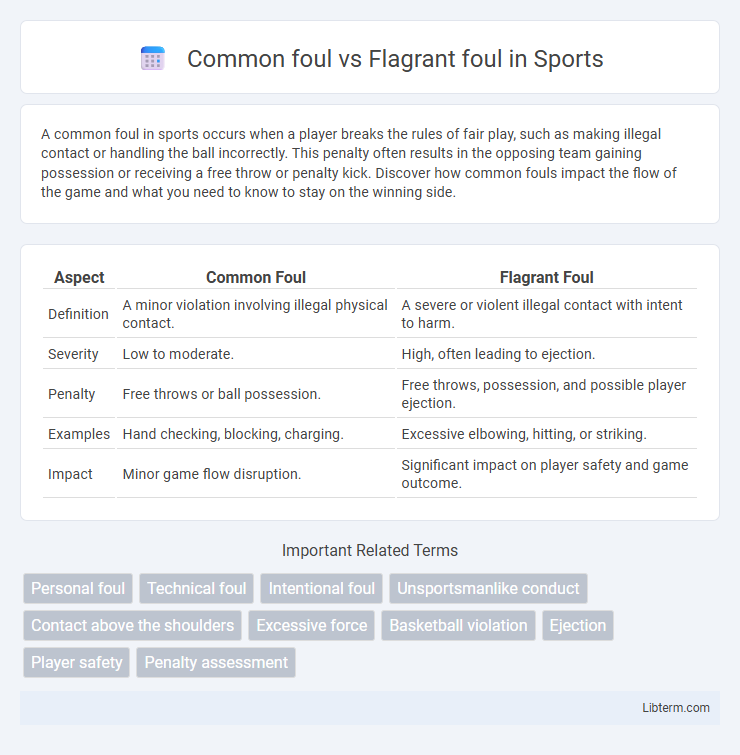
| Aspect | Common Foul | Flagrant Foul |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A minor violation involving illegal physical contact. | A severe or violent illegal contact with intent to harm. |
| Severity | Low to moderate. | High, often leading to ejection. |
| Penalty | Free throws or ball possession. | Free throws, possession, and possible player ejection. |
| Examples | Hand checking, blocking, charging. | Excessive elbowing, hitting, or striking. |
| Impact | Minor game flow disruption. | Significant impact on player safety and game outcome. |
Understanding Fouls in Basketball
Common fouls in basketball refer to minor personal fouls such as illegal hand-checking or blocking that result in free throws only when the opposing team is in the bonus. Flagrant fouls are severe infractions involving excessive or violent contact, categorized into Flagrant 1 and Flagrant 2, with the latter leading to player ejection. Understanding these fouls is crucial for players and referees to maintain fair play and player safety during games.
Definition of a Common Foul
A common foul in basketball is defined as a defensive or offensive infraction involving illegal physical contact with an opponent during play, which results in a stoppage of the game and potentially awards free throws if the team fouled is in the bonus. Unlike a flagrant foul, which involves excessive or violent contact that risks player safety and carries harsher penalties such as ejection, a common foul is typically less severe and penalizes standard breaches of the rules. The key distinction lies in the severity and intent of the contact, with common fouls addressing routine rule violations without flagrant intent.
What Constitutes a Flagrant Foul
A flagrant foul constitutes severe or violent contact that poses a significant risk of injury to an opponent, exceeding the boundaries of a common foul, which typically involves minor infractions such as incidental contact or fouls during routine play. The NBA defines a flagrant foul as unnecessary or excessive contact, categorized as Flagrant 1 (unnecessary) or Flagrant 2 (unnecessary and excessive), often resulting in automatic ejection for the latter. Referees assess factors like intent, impact, and potential to cause harm when determining if a foul warrants flagrant classification, influencing penalties and game dynamics.
Key Differences Between Common and Flagrant Fouls
Common fouls involve minor infractions like reaching or blocking with minimal contact, often resulting in free throws if the team is in a penalty situation. Flagrant fouls are severe violations characterized by excessive or violent contact, which poses a risk of injury and typically lead to player ejection and free throws awarded to the opposing team. The key difference lies in the severity and intent of the contact, with flagrant fouls penalized more harshly to maintain player safety and game integrity.
Examples of Common Fouls
Common fouls in basketball include actions such as blocking, charging, holding, and reaching in, which occur during normal defensive or offensive play. Examples of common fouls are a defender illegally using their body to impede an offensive player's movement or an offensive player pushing off to gain an advantage. These fouls result in free throws only when the fouled team is in the bonus situation, differentiating them from flagrant fouls that involve excessive or violent contact.
Recognizing Flagrant Foul Situations
Flagrant fouls involve excessive or violent contact that risks player injury and are recognized by aggressive behavior such as deliberate hitting, elbowing, or pushing an opponent with severe force. Common fouls typically involve minor infractions like reaching in or hand-checking without harmful intent, resulting in free throws or possession changes without severe penalties. Officials identify flagrant fouls through observation of player actions exceeding normal physical play, emphasizing intent, severity, and potential for injury to enforce stricter penalties.
Penalties for Common Fouls
Common fouls in basketball result in the opposing team receiving possession of the ball or free throws if the foul occurs during a shooting attempt, with penalties varying based on the number of team fouls accumulated in a quarter. Typically, once a team commits a certain number of common fouls (such as five per quarter in the NBA), the opposing team is awarded bonus free throws, often one-and-one or two-shot opportunities. Unlike flagrant fouls, common fouls do not involve additional penalties such as player ejection or free throws plus possession benefits.
Consequences of Flagrant Fouls
Flagrant fouls in basketball result in immediate free throws and possession awarded to the opposing team, significantly impacting game momentum. These fouls often lead to player ejections, fines, and potential suspensions due to their severe nature and intent to harm. The consequences emphasize player safety and maintain fair play standards across professional leagues like the NBA and NCAA.
Referees’ Role in Determining Foul Type
Referees assess intent, severity, and impact on the game to differentiate between common and flagrant fouls, using criteria such as the level of contact and potential harm to the opponent. Common fouls result from routine gameplay infractions, whereas flagrant fouls involve excessive or violent contact warranting stricter penalties. Referees rely on established league guidelines and real-time judgment to ensure fair play and player safety during foul determination.
Impact of Fouls on Game Outcomes
Common fouls typically result in possession changes or free throws, minimally affecting team momentum, whereas flagrant fouls significantly alter game dynamics by allowing free throws, possession retention, and increased player penalties. Flagrant fouls often lead to player ejections, impacting team rotations and defensive strategies more drastically than common fouls. The increased severity of flagrant fouls can shift momentum, increase scoring opportunities, and potentially determine close game outcomes in basketball.
Common foul Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com