A topspin serve generates forward spin on the ball, causing it to dip sharply and bounce higher, making it challenging for your opponent to return. Mastering this technique enhances your control and adds a strategic edge to your tennis or table tennis game. Discover the secrets to perfecting your topspin serve in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
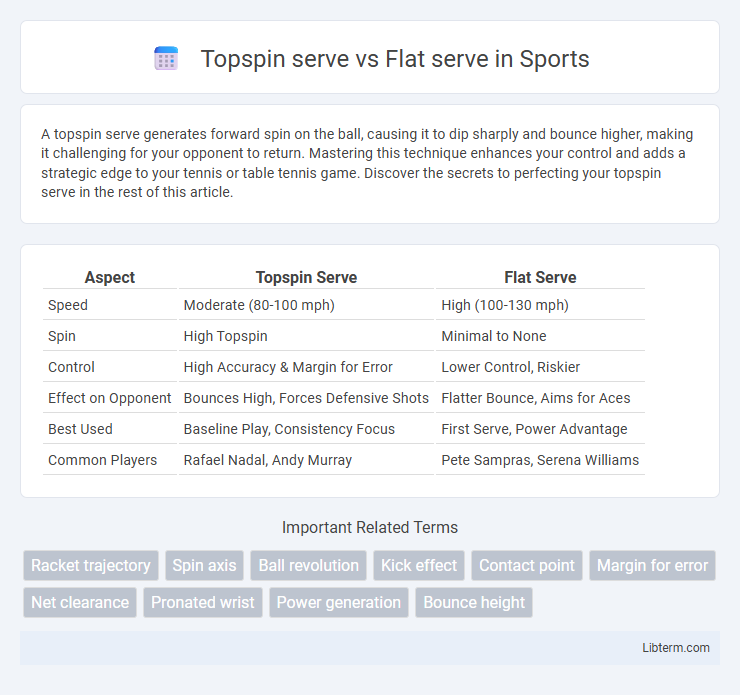
| Aspect | Topspin Serve | Flat Serve |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Moderate (80-100 mph) | High (100-130 mph) |
| Spin | High Topspin | Minimal to None |
| Control | High Accuracy & Margin for Error | Lower Control, Riskier |
| Effect on Opponent | Bounces High, Forces Defensive Shots | Flatter Bounce, Aims for Aces |
| Best Used | Baseline Play, Consistency Focus | First Serve, Power Advantage |
| Common Players | Rafael Nadal, Andy Murray | Pete Sampras, Serena Williams |
Introduction to Topspin and Flat Serves
Topspin serves generate a high-rotation ball that dips quickly, making it difficult for opponents to return due to the downward motion and increased bounce. Flat serves deliver a fast, low-trajectory ball with minimal spin, maximizing speed and power to overpower the receiver. Both serving techniques are essential in tennis, offering strategic options based on player style and match conditions.
Key Differences Between Topspin and Flat Serves
Topspin serves generate a forward spin that causes the ball to dip quickly and bounce higher, enhancing control and consistency, especially on second serves. Flat serves hit the ball with minimal spin, resulting in faster speeds and a more direct, powerful trajectory that aims to overpower the opponent. The key difference lies in the trade-off between speed and control: topspin offers greater margin for error and consistency, while flat serves prioritize velocity and aggressive point initiation.
Mechanics of the Topspin Serve
The mechanics of the topspin serve involve a brushing motion that imparts forward spin on the ball, causing it to dip sharply and bounce higher upon landing. This spin is generated through wrist snap and racquet acceleration upward and forward at contact, contrasting with the flat serve's linear, high-velocity trajectory. Mastery of the topspin serve enhances control and margin for error while making the ball's bounce unpredictable for the opponent.
Mechanics of the Flat Serve
The flat serve relies on a precise, linear racket path combined with a firm wrist snap to produce maximum ball speed and minimal spin, resulting in a fast, straight trajectory. Key mechanics include a high toss slightly in front of the body and a fully extended arm to generate optimal power transfer from the kinetic chain. This serve demands strong shoulder rotation and explosive leg drive to enhance velocity, making it ideal for aggressive serving on fast surfaces.
Advantages of Using a Topspin Serve
The topspin serve generates higher ball rotation, causing the ball to dip sharply and bounce unpredictably, making it difficult for the opponent to return effectively. This increased spin enhances control and consistency, reducing unforced errors compared to a flat serve's faster but less controllable trajectory. Players using a topspin serve benefit from tactical versatility and improved placement, allowing strategic targeting of opponents' weaker shots.
Benefits of the Flat Serve in Tennis
The flat serve in tennis offers maximum speed and power, making it a formidable weapon for scoring aces and putting opponents on the defensive early in the point. With its minimal spin, the flat serve travels faster and maintains a straighter trajectory, reducing reaction time for the receiver. This serve type is particularly effective on faster surfaces like grass and hard courts, where its high velocity can dominate play and enhance the server's offensive advantage.
Situational Effectiveness: When to Use Each Serve
Topspin serves generate a high bounce and heavy spin, making them ideal for baseline rallies and forcing opponents into defensive positions on slower court surfaces. Flat serves deliver maximum speed and minimal spin, proving most effective during first serves or on faster courts where skidding the ball reduces reaction time. Choosing between topspin and flat serves depends on match context, opponent's weaknesses, and court surface to optimize point construction and serve placement.
Common Mistakes with Topspin and Flat Serves
Topspin serves often suffer from common mistakes such as improper racket angle and insufficient wrist snap, reducing spin effectiveness and ball control. Flat serves frequently encounter errors like overhitting and lack of placement accuracy, leading to faults and easier returns. Mastering racket positioning and consistent toss height improves the reliability and power of both serve types.
Tips for Improving Both Serve Types
To improve a topspin serve, focus on brushing up the ball with a high racket speed and a relaxed wrist to generate maximum spin and consistent net clearance. For a flat serve, emphasize explosive power and precise ball toss placement slightly in front and to the right for right-handed players to maximize velocity and accuracy. Consistent practice of stance, grip, and follow-through mechanics enhances control and effectiveness for both serve types on various court surfaces.
Topspin Serve vs Flat Serve: Which Is Better for Your Game?
Topspin serves generate higher ball rotation, causing a deeper, higher-bouncing bounce that is harder for opponents to attack, making them ideal for baseline play and defensive strategies. Flat serves, characterized by minimal spin and maximum speed, provide greater power and ace potential, often used to dominate points quickly with aggressive serve-and-volley tactics. Choosing between topspin and flat serves depends on your playing style, court surface, and ability to control spin versus power for consistent serve effectiveness.
Topspin serve Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com