Double faults occur when a player serves two consecutive faults, resulting in the loss of a point, which can significantly impact the momentum of a tennis match. Understanding the causes of double faults, such as poor technique or mental pressure, helps you improve your serve consistency and overall performance on the court. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for reducing double faults and enhancing your game.
Table of Comparison
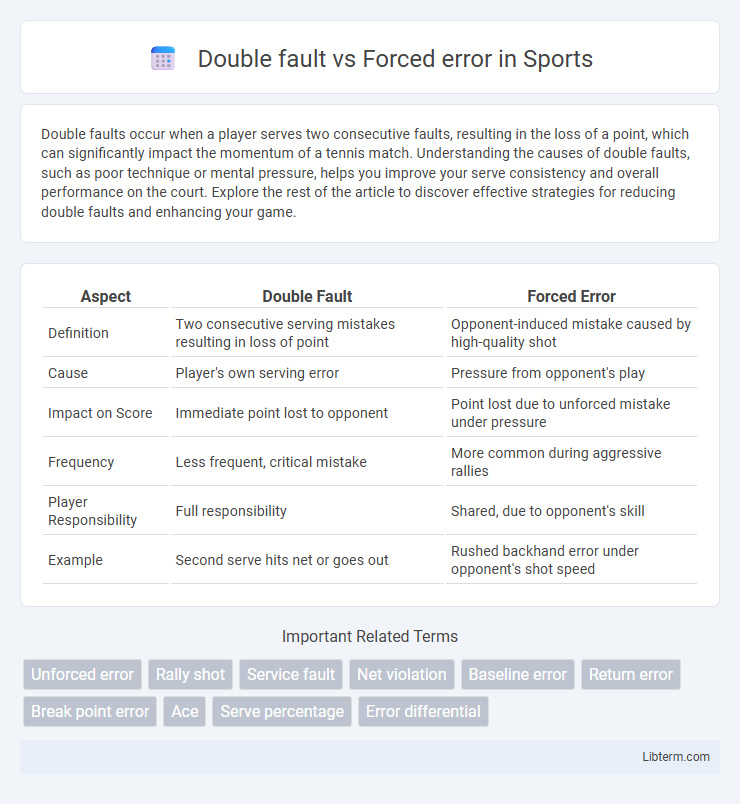
| Aspect | Double Fault | Forced Error |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two consecutive serving mistakes resulting in loss of point | Opponent-induced mistake caused by high-quality shot |
| Cause | Player's own serving error | Pressure from opponent's play |
| Impact on Score | Immediate point lost to opponent | Point lost due to unforced mistake under pressure |
| Frequency | Less frequent, critical mistake | More common during aggressive rallies |
| Player Responsibility | Full responsibility | Shared, due to opponent's skill |
| Example | Second serve hits net or goes out | Rushed backhand error under opponent's shot speed |
Understanding Double Faults in Tennis
Double faults occur when a player fails to deliver a legal serve twice consecutively, resulting in an immediate loss of the point. Unlike forced errors, which happen due to pressure from the opponent's shot quality or placement, double faults stem solely from service execution errors, highlighting the critical importance of consistent serving technique. Monitoring double fault ratios in professional matches provides insight into a player's mental resilience and serving reliability under pressure.
Defining Forced Errors: A Key Concept
Forced errors occur when a player makes a mistake due to the opponent's skillful shot that puts them under pressure, leading to unforced mistakes beyond their control. This contrasts with double faults, which happen when a player fails to successfully serve both attempts, resulting directly in lost points. Understanding forced errors highlights the impact of opponent tactics and shot placement on match dynamics and player performance.
Double Fault vs Forced Error: What’s the Difference?
A double fault occurs in tennis when a player serves two consecutive faults, resulting in an immediate loss of the point, reflecting a critical serving error under pressure. A forced error happens when an opponent's skillful shot or play causes a player to make a mistake, highlighting the impact of defensive prowess and shot difficulty. Understanding the difference between double faults and forced errors is essential for analyzing player performance and match dynamics in professional tennis.
Common Causes of Double Faults
Common causes of double faults include inconsistent toss motion, lack of proper grip pressure, and rushing the serve without adequate preparation. Physical fatigue and mental pressure often lead to timing disruptions, increasing the likelihood of double faults during critical points. Improper stance and insufficient practice of the toss-release coordination also contribute significantly to repeated double faults.
Factors Leading to Forced Errors
Forced errors in tennis occur when defensive shots are compelled by aggressive play, often resulting from high-speed serves, deep returns, and strategic ball placement that push players out of their comfort zones. Factors leading to forced errors include opponent pressure through consistent pace, spin variation, and exploiting court positioning to reduce reaction time and shot accuracy. Unlike double faults, which stem from serving mistakes, forced errors reflect a player's response to external challenges during rallies.
Impact on Match Outcomes
Double faults significantly increase the likelihood of losing games by handing unearned points to opponents, often shifting momentum and increasing pressure on the server. Forced errors, while reducing shot accuracy, result from opponents' aggressive play and can be strategically managed to minimize damage and create counter-attacking opportunities. Analyzing match statistics reveals that players with lower double fault rates generally sustain higher service hold percentages, directly influencing match outcomes more negatively than forced errors.
Psychological Aspects of Double Faults and Forced Errors
Double faults often trigger intense psychological pressure as players confront the fear of directly conceding points, leading to heightened anxiety and diminished confidence. Forced errors, while frustrating, typically result from aggressive opponent play, causing mental stress related to maintaining focus and managing frustration rather than self-blame. Understanding the distinct psychological impacts of double faults and forced errors can help athletes develop targeted mental resilience strategies to improve performance under pressure.
Strategies to Reduce Double Faults
Reducing double faults requires focused serve technique improvements, including consistent ball toss placement and optimized racket angle at contact to enhance accuracy and control. Implementing targeted serve practice routines and mental conditioning can decrease pressure-induced errors and improve first serve percentage. Employing video analysis to identify mechanical flaws and adapting pre-serve routines enhances muscle memory and reduces the risk of double faults.
Techniques for Minimizing Forced Errors
Minimizing forced errors in tennis requires consistent technique refinement, including maintaining a stable base, precise footwork, and controlled swing mechanics. Emphasizing proper grip adjustments and practicing drills that simulate match conditions enhance players' ability to anticipate and react effectively, reducing unforced mistakes. Integrating mental focus strategies with physical training helps maintain shot accuracy under pressure, thereby lowering the incidence of forced errors compared to double faults.
Training Tips for Improving Serve and Defense
Focusing on training techniques to reduce double faults and forced errors enhances overall serve and defensive performance. Practicing consistent toss mechanics and targeted serve placement drills can minimize double faults, while improving footwork and reaction time drills sharpens defensive returns. Incorporating video analysis and pressure simulation reinforces proper technique and decision-making under match conditions.
Double fault Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com