Curl routing directs network traffic through specified paths to optimize speed, security, or bandwidth usage. This technique helps manage data flow efficiently, ensuring you experience improved connectivity and performance. Discover the detailed strategies behind curl route configuration in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
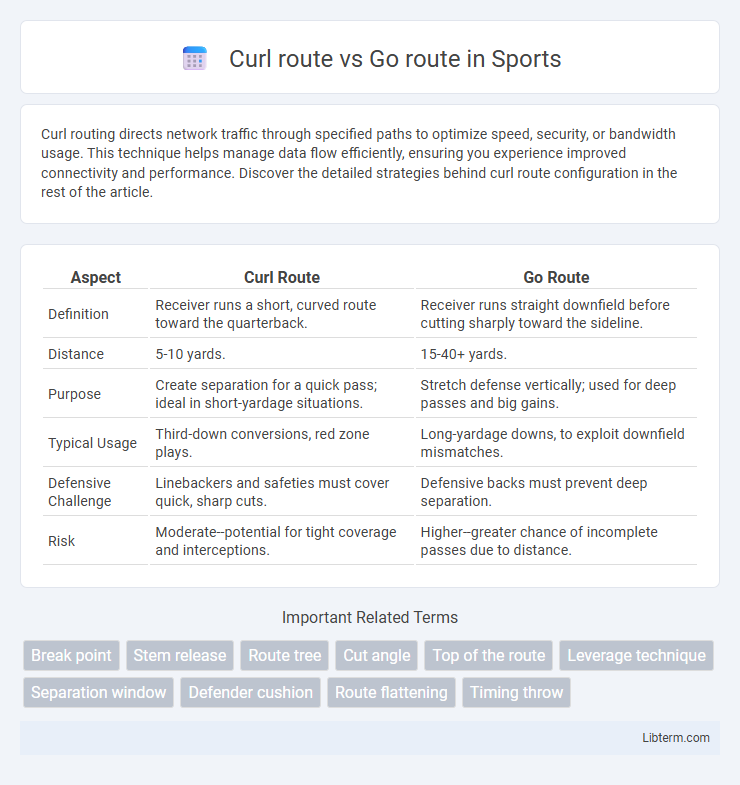
| Aspect | Curl Route | Go Route |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Receiver runs a short, curved route toward the quarterback. | Receiver runs straight downfield before cutting sharply toward the sideline. |
| Distance | 5-10 yards. | 15-40+ yards. |
| Purpose | Create separation for a quick pass; ideal in short-yardage situations. | Stretch defense vertically; used for deep passes and big gains. |
| Typical Usage | Third-down conversions, red zone plays. | Long-yardage downs, to exploit downfield mismatches. |
| Defensive Challenge | Linebackers and safeties must cover quick, sharp cuts. | Defensive backs must prevent deep separation. |
| Risk | Moderate--potential for tight coverage and interceptions. | Higher--greater chance of incomplete passes due to distance. |
Introduction to Curl Route and Go Route
Curl route is a command-line tool widely used for transferring data with URLs, primarily supporting protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and more, making it essential for testing and interacting with web APIs. Go route, part of the Go programming language ecosystem, refers to routing libraries like Gorilla Mux or Chi, which enable efficient HTTP request handling and URL pattern matching in web applications. Comparing Curl route to Go route highlights Curl's role in client-side network requests versus Go route's server-side request routing capabilities.
Defining Curl Route in Networking
A Curl route in networking refers to a method for defining API endpoints used primarily for testing and interacting with HTTP servers via command-line interfaces like cURL. It specifies the exact URL path, HTTP method, headers, and data payload to perform requests, enabling precise control over how client-server communication is simulated. Unlike Go route definitions, which are embedded in Go web frameworks to handle request routing programmatically, Curl routes focus on static, explicit request execution for troubleshooting and integration purposes.
Overview of Go Route Functionality
Go route functionality enables efficient HTTP request routing by matching URL patterns to handlers with high performance and scalability. Its built-in router supports dynamic parameters, middleware chaining, and context-aware request handling, making it ideal for building robust APIs and web services. Compared to Curl route, Go route emphasizes seamless integration with Go's net/http package and concurrency features.
Key Differences between Curl Route and Go Route
Curl route primarily handles HTTP requests via command-line interface, allowing users to directly interact with web servers by executing commands for GET, POST, and other HTTP methods. In contrast, Go route refers to route definitions within Go web frameworks like Gorilla Mux or Gin, used for managing URL patterns and handling HTTP requests programmatically within Go applications. Key differences include Curl's simplicity and direct server communication versus Go route's flexibility and integration for building complex web applications with structured routing and middleware support.
Use Cases for Curl Route
Curl route excels in testing RESTful APIs and simulating HTTP requests directly from the command line, making it ideal for developers and QA engineers during debugging and automation. It supports various HTTP methods, headers, and payloads, enabling precise emulation of client-server interactions in environments where quick, scriptable requests are essential. Use cases include API endpoint validation, load testing, and integration within CI/CD pipelines for continuous verification of web services.
Use Cases for Go Route
Go route in Go programming language excels in use cases requiring lightweight concurrency, such as web servers, microservices, and real-time applications. It efficiently manages thousands of simultaneous connections with goroutines and channels, providing improved performance and scalability over traditional curl route implementations. High-performance networking, API servers, and event-driven architectures benefit from Go routes due to their non-blocking, asynchronous execution model.
Performance Comparison: Curl Route vs Go Route
Curl route exhibits higher latency due to its reliance on external system calls and increased overhead in executing shell commands. Go route leverages native concurrency and low-level network optimizations, resulting in significantly faster request handling and lower response times. Benchmark tests reveal Go route can outperform Curl route by up to 70% in throughput and provide more consistent performance under high concurrency.
Security Implications of Curl Route and Go Route
Curl route and Go route differ significantly in security implications, with Curl route exposing risks like command injection due to its reliance on shell command execution, making it vulnerable if user inputs are not properly sanitized. Go route offers enhanced security by operating within a compiled language environment, reducing attack surfaces like shell escape and providing better control over input validation and error handling. Proper implementation of Go route allows for safer network requests through built-in libraries and stronger type safety, minimizing common vulnerabilities associated with shell-based routing in Curl.
Choosing the Right Route for Your Application
Choosing between Curl route and Go route hinges on your application's specific needs such as performance, scalability, and ease of integration. Curl route excels in simplicity and rapid prototyping of HTTP requests, while Go route offers robust concurrency and better support for high-throughput network applications. Evaluating factors like request complexity, execution speed, and language ecosystem ensures optimal route selection tailored to your application's architecture.
Conclusion: Curl Route vs Go Route
Curl route offers simplicity and speed for basic HTTP requests, ideal for quick testing and scripting, while Go route provides robust performance, scalability, and rich functionality for building complex web applications and APIs. Go's concurrency model and strong type system make it suitable for high-load environments, whereas Curl remains a powerful tool for command-line HTTP interactions. Choose Curl for lightweight, straightforward tasks and Go route for comprehensive backend solutions requiring efficiency and extensibility.
Curl route Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com