Serve your customers with excellence by understanding their needs and delivering prompt, personalized service that exceeds expectations. Quality service builds trust, encourages repeat business, and enhances your brand reputation. Discover practical strategies to elevate your customer service experience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
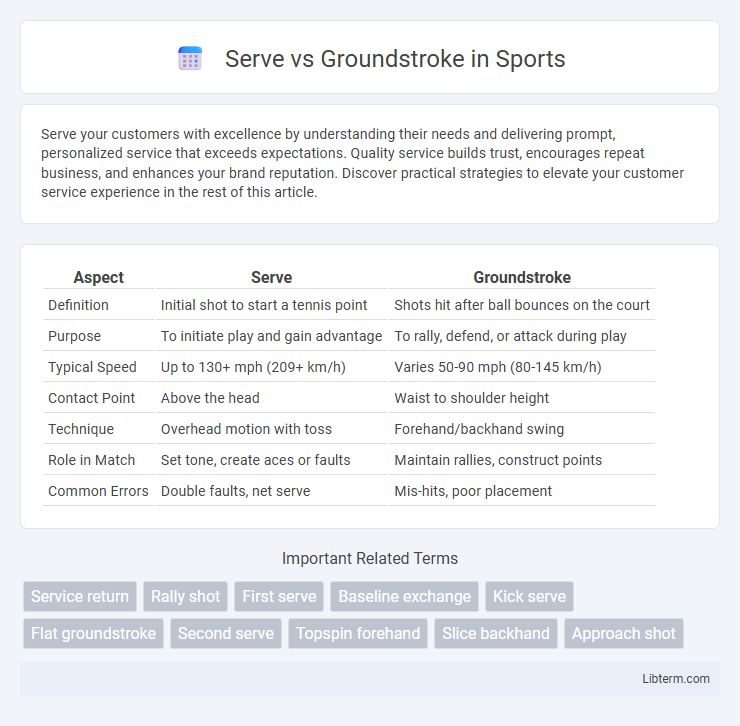
| Aspect | Serve | Groundstroke |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Initial shot to start a tennis point | Shots hit after ball bounces on the court |
| Purpose | To initiate play and gain advantage | To rally, defend, or attack during play |
| Typical Speed | Up to 130+ mph (209+ km/h) | Varies 50-90 mph (80-145 km/h) |
| Contact Point | Above the head | Waist to shoulder height |
| Technique | Overhead motion with toss | Forehand/backhand swing |
| Role in Match | Set tone, create aces or faults | Maintain rallies, construct points |
| Common Errors | Double faults, net serve | Mis-hits, poor placement |
Understanding the Difference: Serve vs Groundstroke
A serve is the initial shot in tennis used to start a point, characterized by an overhead motion that propels the ball into the opponent's service box with power and precision. Groundstrokes are subsequent shots executed after the ball has bounced, typically involving forehand or backhand swings aimed at maintaining pressure and positioning during rallies. Understanding the difference between serve and groundstroke highlights their distinct roles: the serve initiates play with control and advantage, while groundstrokes drive the point forward through consistent baseline exchanges.
Key Techniques: Mastering the Serve
Mastering the serve involves precise ball toss, consistent contact point, and optimal body rotation to generate power and accuracy. Effective grip choices like the continental grip facilitate control and variety, while proper weight transfer from the back foot to the front foot enhances momentum. Incorporating fluid wrist snap and follow-through ensures spin and placement, making the serve a formidable weapon in tennis.
Fundamental Skills: Building a Solid Groundstroke
Developing a solid groundstroke requires precise timing, consistent ball contact, and proper footwork to control rallies from the baseline. Unlike the serve, which emphasizes power and placement to start the point, groundstrokes demand sustained accuracy and varied spins to maintain pressure on opponents. Mastering fundamental skills like grip, stroke mechanics, and positioning enhances shot reliability and strategic play during long exchanges.
When to Use: Serve vs Groundstroke in Match Play
Use the serve to initiate points with power and precision, aiming to gain an immediate advantage through placement and spin. Groundstrokes become essential during rallies, where consistency and positioning determine shot selection to control the baseline and create openings. Strategic use of serve sets up opportunities for aggressive groundstrokes, making timing and match context critical for effective play.
Importance of Stance and Footwork
Effective serve execution demands a stable, balanced stance with precise foot positioning to maximize power and control while minimizing injury risk. Groundstrokes require dynamic footwork, including quick lateral movements and proper weight transfer, to maintain optimal positioning for shot accuracy and consistency. Mastery of stance and footwork enhances overall performance by enabling fluid transitions between serving and groundstroke phases during rallies.
Power Generation: Serve vs Groundstroke Mechanics
Power generation in serves relies heavily on explosive leg drive, shoulder rotation, and a kinetic chain that transfers energy from the legs through the torso to the racquet, producing maximum racket head speed. Groundstroke power derives from weight transfer, hip rotation, and timing, emphasizing a stable base and fluid motion to generate force consistently during rallies. The serve mechanics prioritize vertical leap and pronation for acceleration, while groundstroke mechanics focus on horizontal body rotation and balance for sustained power.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common mistakes in serving include improper toss height, poor body alignment, and lack of follow-through, leading to inconsistent power and accuracy. Groundstroke errors often involve incorrect foot positioning, inadequate racket preparation, and failure to generate topspin, resulting in weak or off-target shots. To avoid these issues, players should practice consistent toss mechanics for serves, maintain balanced stances during groundstrokes, and focus on smooth, accelerated swings to enhance control and effectiveness.
Drills to Improve Serve and Groundstroke
Targeted drills like the toss-and-hit serve practice enhance consistency and power in serving by focusing on ball placement and racket speed. Groundstroke improvement benefits from multi-ball rally drills that emphasize footwork, timing, and stroke mechanics for both forehand and backhand shots. Incorporating shadow swings and resistance band exercises strengthens muscle memory and overall stroke precision.
Tactical Strategies for Each Stroke
Serve strategies emphasize placement and power to control point initiation and exploit opponent weaknesses, often aiming for aces or forcing weak returns. Groundstroke tactics focus on consistency, depth, and spin variations to construct rallies, apply pressure, and create openings in the opponent's court positioning. Combining aggressive serves with precise groundstrokes enhances overall tactical versatility, enabling players to dictate play and adapt to different match situations.
Choosing the Right Shot: Serve or Groundstroke?
Choosing the right shot between serve and groundstroke depends on positioning and match strategy. Serves initiate play with power and precision, setting the tone with a controlled advantage, while groundstrokes sustain rallies using consistent topspin and placement to maneuver opponents. Evaluating court dynamics, player strengths, and opponent weaknesses helps determine when to serve aggressively or rely on reliable groundstroke responses.
Serve Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com