Tight Ends play a crucial role in both the passing and running game, combining the skills of a receiver and offensive lineman to create versatile offensive strategies. Their ability to catch important passes while effectively blocking defenders makes them indispensable on the football field. Discover more about how mastering the Tight End position can elevate Your team's performance by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
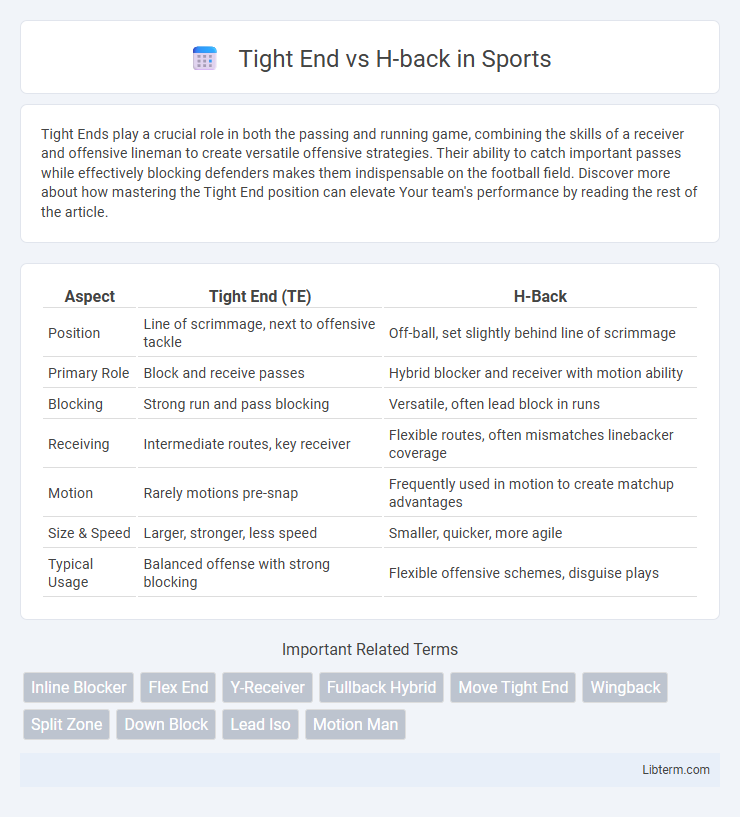
| Aspect | Tight End (TE) | H-Back |
|---|---|---|
| Position | Line of scrimmage, next to offensive tackle | Off-ball, set slightly behind line of scrimmage |
| Primary Role | Block and receive passes | Hybrid blocker and receiver with motion ability |
| Blocking | Strong run and pass blocking | Versatile, often lead block in runs |
| Receiving | Intermediate routes, key receiver | Flexible routes, often mismatches linebacker coverage |
| Motion | Rarely motions pre-snap | Frequently used in motion to create matchup advantages |
| Size & Speed | Larger, stronger, less speed | Smaller, quicker, more agile |
| Typical Usage | Balanced offense with strong blocking | Flexible offensive schemes, disguise plays |
Understanding the Roles: Tight End vs H-back
The Tight End primarily serves as a dual-threat player, positioned on the line of scrimmage to block effectively and catch passes, blending the skills of an offensive lineman and a wide receiver. The H-back operates slightly off the line, often motioning before the snap to provide flexible blocking, route running, and occasionally rushing duties, enhancing offensive versatility. Understanding the distinct positioning and responsibilities of Tight Ends and H-backs is crucial for optimizing offensive schemes and exploiting defensive matchups.
Historical Origins of Tight Ends and H-backs
The tight end position originated in early 20th-century football as a hybrid role combining blocking and receiving duties, evolving from the traditional end position on offense. The H-back emerged later as an innovation in offensive schemes, designed to create versatility by positioning a player off the line of scrimmage, blending fullback power with tight end agility. This strategic shift in the 1980s and 1990s allowed offenses to diversify formations and confuse defenses, as the H-back could shift between blocking and pass-catching roles more fluidly than a conventional tight end.
Position Alignment on the Field
Tight ends primarily line up on the line of scrimmage next to the offensive tackle, serving dual roles as blockers and receivers in the offensive formation. H-backs align slightly off the line, often positioned a step back from the tight end spot or in the backfield, allowing greater motion flexibility and varied route options. This difference in alignment impacts their use in offensive schemes, with tight ends more involved in traditional line blocking and H-backs utilized for versatile playmaking and mismatches.
Key Responsibilities and Assignments
Tight ends primarily serve as versatile players combining blocking duties with pass-catching roles, lining up on the offensive line to support both the run and pass game. H-backs operate in a more flexible position, often starting off the line of scrimmage to perform lead blocking, motioning for misdirection plays, and serving as short-yardage receivers. Both positions require strong blocking skills, but tight ends are more involved in traditional pass routes while H-backs excel in creating mismatches through movement and varied alignments.
Differences in Blocking Techniques
Tight ends typically engage in traditional inline blocking, using power to seal the edge against defensive ends or linebackers in both run and pass plays. H-backs employ more versatile and dynamic blocking techniques, often moving from the backfield or slot position to lead block on outside runs or chip blitzing defenders in pass protection. The tight end's blocking demands strength at the point of attack, while the H-back relies on agility and positional flexibility to adapt to multiple blocking assignments.
Route Running and Receiving Duties
Tight ends primarily run intermediate routes such as curls, outs, and seams, leveraging their size to create mismatches against linebackers and safeties in the receiving game. H-backs exhibit more versatility in route running, often lining up in the backfield or slot to execute a mix of short routes, flats, and angle patterns, capitalizing on their agility to find open space. Receiving duties for tight ends emphasize red zone targets and chain-moving receptions, while H-backs focus on quick releases and options in short to intermediate areas to sustain drives.
Impact on Offensive Schemes
The Tight End primarily serves as a versatile blocker and receiver on the offensive line, creating mismatches through size and route-running, which enhances both the running and passing games. The H-back, positioned off the line, combines the roles of fullback and tight end, adding dynamic motion and flexibility that complicates defensive reads and opens up play-action opportunities. Incorporating an H-back allows offenses to vary formations and exploit linebacker coverage, while Tight Ends anchor blocking schemes and stretch the field vertically.
Physical and Skill Set Requirements
Tight ends require a blend of size, strength, and blocking ability, often standing between 6'3" and 6'6" with 240-260 pounds to effectively engage defensive linemen and linebackers. H-backs prioritize agility, route-running precision, and versatility, frequently weighing slightly less at 230-250 pounds to excel in motion and mismatches against linebackers and safeties. Both positions demand reliable hands and spatial awareness but differ in their emphasis on physical dominance versus dynamic movement within offensive schemes.
Famous Tight Ends and H-backs in Football History
Famous tight ends such as Tony Gonzalez and Rob Gronkowski revolutionized the position with their receiving skills and blocking prowess, becoming central figures in offensive schemes. In contrast, renowned H-backs like Mike Vrabel and Pete Metzelaars blended tight end and fullback roles, excelling in versatile blocking and pass-catching duties. Both positions have shaped football history by enhancing offensive flexibility and exploiting mismatches against defensive coverage.
Choosing Between a Tight End and an H-back in Modern Offenses
Choosing between a Tight End and an H-back depends on the offensive scheme and player versatility. Tight Ends primarily serve as blockers and reliable pass-catchers on the line of scrimmage, excelling in traditional power-running formations and red-zone situations. H-backs combine the roles of fullback and tight end, offering increased mobility and flexibility, ideal for offenses that emphasize motion, misdirection, and varied route concepts.
Tight End Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com