A crossover blends elements from two or more different genres, universes, or storylines, creating a unique narrative that appeals to diverse audiences. This technique allows characters or themes from separate franchises to interact, expanding the storytelling possibilities and enriching the overall experience. Discover how crossovers can transform your favorite stories by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
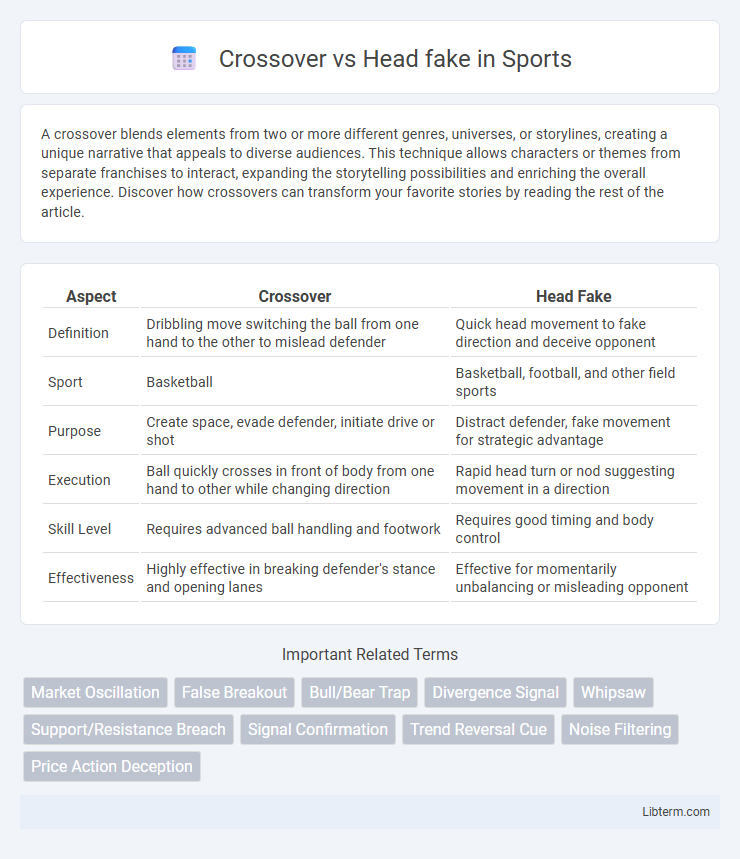
| Aspect | Crossover | Head Fake |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dribbling move switching the ball from one hand to the other to mislead defender | Quick head movement to fake direction and deceive opponent |
| Sport | Basketball | Basketball, football, and other field sports |
| Purpose | Create space, evade defender, initiate drive or shot | Distract defender, fake movement for strategic advantage |
| Execution | Ball quickly crosses in front of body from one hand to other while changing direction | Rapid head turn or nod suggesting movement in a direction |
| Skill Level | Requires advanced ball handling and footwork | Requires good timing and body control |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective in breaking defender's stance and opening lanes | Effective for momentarily unbalancing or misleading opponent |
Understanding Crossovers in Trading
Crossovers in trading occur when a short-term moving average crosses above or below a long-term moving average, signaling potential buy or sell opportunities based on momentum shifts. Understanding these crossovers helps traders identify trend reversals and market entry or exit points with greater precision. Differentiating a genuine crossover from a head fake, which is a false signal leading to potential losses, is crucial for effective trading strategies.
What is a Head Fake?
A head fake in trading is a misleading price movement that tricks traders into believing a trend is starting or reversing, only for the price to move in the opposite direction. Unlike a crossover, which signals a potential trend change based on moving average intersections, a head fake often causes false breakouts and triggers stop losses. Recognizing a head fake requires analyzing volume, price action, and market context to avoid premature trades.
Key Differences: Crossover vs Head Fake
The key difference between a crossover and a head fake lies in their execution and purpose: a crossover involves dribbling the basketball quickly from one hand to the other to deceive the defender about the player's direction, while a head fake uses only head movement to mislead the opponent about the next move without altering the ball's position. Crossovers typically require advanced ball-handling skills and are more effective in close defensive situations, whereas head fakes serve as subtle deception techniques to create space or an advantage. Understanding these distinctive strategies helps players enhance offensive versatility during gameplay.
Identifying Crossovers on Price Charts
Crossovers on price charts occur when a short-term moving average intersects a long-term moving average, signaling potential trend reversals or confirmations, while a head fake represents a false breakout that quickly reverses direction, trapping traders. Identifying crossovers involves observing moving average lines such as the 50-day and 200-day, where a bullish crossover (golden cross) suggests upward momentum and a bearish crossover (death cross) indicates downward pressure. Recognizing genuine crossovers requires confirming volume increases and the candlestick pattern context to avoid mistaking head fakes for authentic trend changes.
Spotting Head Fakes: Common Indicators
Spotting head fakes involves identifying false signals where price action suggests a movement in one direction before reversing sharply. Common indicators include sudden volume spikes without corresponding price continuation, candlestick patterns such as doji or spinning tops signaling indecision, and divergence between price and momentum indicators like RSI or MACD. Traders often confirm head fakes by monitoring support and resistance levels for quick rejections following apparent breakouts or crossovers.
Psychological Traps in Head Fakes
Head fakes exploit psychological traps by misleading the observer into anticipating a false outcome, triggering cognitive biases such as expectation bias and confirmation bias. This misdirection leverages the brain's tendency to predict patterns, causing traders or investors to prematurely commit to decisions based on perceived market signals. Understanding these traps is crucial for distinguishing genuine crossover signals from deceptive head fakes in technical analysis.
Technical Analysis Tools for Crossovers
Technical analysis tools for crossovers primarily include moving averages, such as the simple moving average (SMA) and exponential moving average (EMA), which identify trend reversals when short-term averages cross long-term averages. The crossover signals a potential buy or sell opportunity by highlighting momentum shifts, while head fakes occur when the price briefly breaks a key level or moving average but then reverses, triggering false signals. Traders often combine crossovers with volume analysis and oscillators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to confirm the validity of signals and reduce the risk of being misled by head fakes.
Risk Management: Avoiding Head Fakes
Effective risk management in trading involves distinguishing between genuine crossovers and deceptive head fakes to prevent false signals. Traders rely on confirmation tools such as volume analysis, moving averages alignment, and momentum indicators to validate crossover legitimacy. Implementing stop-loss orders and setting clear entry criteria minimizes losses caused by head fakes, enhancing overall portfolio protection.
Real-World Examples: Crossover and Head Fake Scenarios
The crossover pattern in stock trading often signals a trend reversal, as seen when Apple Inc.'s 50-day moving average crossed above its 200-day moving average in early 2023, indicating bullish momentum. Conversely, a head fake occurs when initial price movement misleads traders, like Tesla's price surge in mid-2022 that reversed sharply, trapping momentum traders. By analyzing these real-world examples, investors can better distinguish genuine breakouts from deceptive price actions and refine their trading strategies.
Best Practices for Trading Crossovers and Avoiding Head Fakes
Effective trading crossovers involves confirming signals with volume and trend strength indicators to reduce false entries. Best practices recommend using moving average crossovers alongside support and resistance analysis to validate breakout legitimacy. Avoiding head fakes requires patience and waiting for price confirmation to prevent premature trades triggered by deceptive market moves.
Crossover Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com