The V-sit is a powerful core exercise that strengthens abdominal muscles and improves balance by engaging both the upper and lower body simultaneously. This move helps enhance your posture and coordination, making it a key addition to any fitness routine. Discover how to master the V-sit and maximize its benefits by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
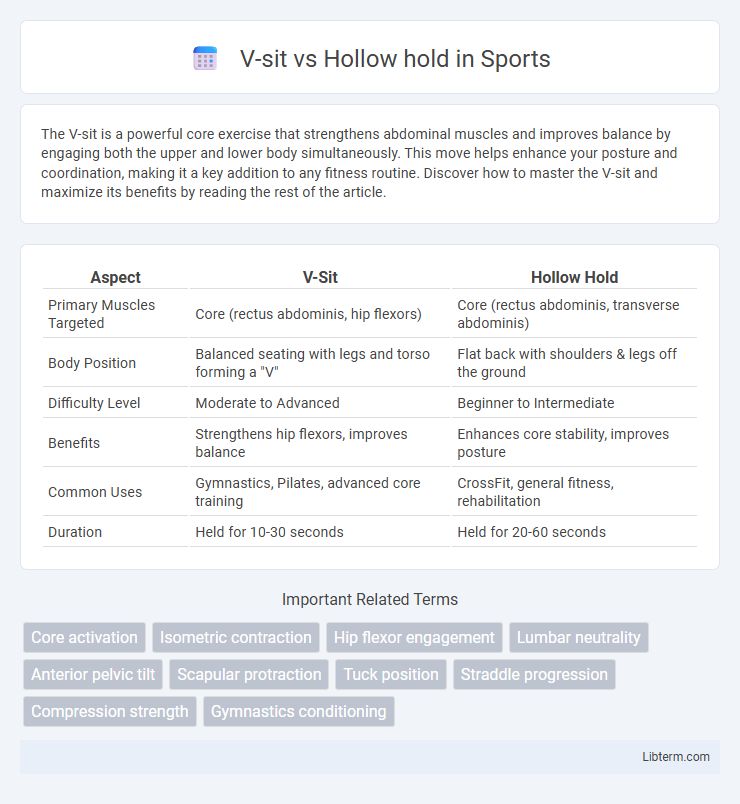
| Aspect | V-Sit | Hollow Hold |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Muscles Targeted | Core (rectus abdominis, hip flexors) | Core (rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis) |
| Body Position | Balanced seating with legs and torso forming a "V" | Flat back with shoulders & legs off the ground |
| Difficulty Level | Moderate to Advanced | Beginner to Intermediate |
| Benefits | Strengthens hip flexors, improves balance | Enhances core stability, improves posture |
| Common Uses | Gymnastics, Pilates, advanced core training | CrossFit, general fitness, rehabilitation |
| Duration | Held for 10-30 seconds | Held for 20-60 seconds |
Introduction to Core Strength Exercises
The V-sit and hollow hold are foundational core strength exercises that target deep abdominal muscles, enhancing overall stability and posture. The V-sit primarily engages the rectus abdominis and hip flexors by requiring balance in a seated "V" shape, while the hollow hold emphasizes isometric contraction of the transverse abdominis and obliques through a flat-back position. Incorporating both exercises into a workout routine promotes comprehensive core development, improving athletic performance and reducing injury risk.
What is the V-Sit?
The V-Sit is a core exercise that targets the abdominal muscles by requiring the individual to balance on their glutes while extending both legs and reaching their arms forward, forming a "V" shape with the body. This move enhances core strength, stability, and flexibility by engaging the hip flexors, lower abs, and lower back muscles. Compared to the Hollow Hold, the V-Sit demands greater balance and mobility, making it effective for improving overall core endurance and control.
Understanding the Hollow Hold
The hollow hold is a core exercise that emphasizes maintaining a posterior pelvic tilt while engaging the entire abdominal wall, which maximizes core stability and strength. Unlike the V-sit, which focuses on sitting upright with legs and torso forming a "V" shape, the hollow hold requires keeping the lower back pressed into the floor to prevent lumbar arching. Mastering the hollow hold enhances neuromuscular control and builds a foundation for more advanced gymnastic and calisthenic movements.
Key Muscle Groups Activated
The V-sit primarily targets the rectus abdominis and hip flexors, emphasizing core strength and balance. In contrast, the hollow hold activates the transverse abdominis, rectus abdominis, and lower back muscles, promoting overall core stability and endurance. Both exercises engage the obliques, but the hollow hold places greater emphasis on maintaining spinal alignment and a hollow body position.
Benefits of the V-Sit
The V-sit targets the rectus abdominis and hip flexors, enhancing core strength and stability more dynamically than the hollow hold. This exercise improves balance and coordination by engaging multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Increased core endurance from V-sits supports athletic performance and daily functional movements.
Advantages of the Hollow Hold
The Hollow Hold offers superior core stabilization by engaging both the rectus abdominis and transverse abdominis, leading to enhanced overall core strength and endurance. It promotes improved spinal alignment and posture due to its emphasis on maintaining a tucked pelvis and flat lower back. This exercise also effectively activates the lower abdominal muscles, making it highly beneficial for building foundational core stability.
Technique Comparison: V-Sit vs Hollow Hold
The V-sit requires balancing on the sit bones while keeping legs and torso elevated in a V shape, engaging the hip flexors and lower abs intensely. The hollow hold emphasizes a flattened lower back against the floor with arms and legs extended, targeting the entire core musculature and promoting spinal stability. Proper form in the V-sit demands hip flexor strength and balance, whereas the hollow hold focuses on maintaining a rigid, hollowed body position for maximal core activation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Common mistakes in the V-sit include arching the lower back and using momentum instead of core strength, which reduce exercise effectiveness. In the Hollow hold, a frequent error is lifting the head too high or not engaging the lower abdominal muscles fully, compromising form and core activation. Maintaining proper spinal alignment and controlled breathing is essential for both exercises to maximize core engagement and prevent injury.
Which Exercise Is Right for You?
Choosing between the V-sit and hollow hold depends on your fitness goals and core strength level. The V-sit targets the lower and upper abs with a dynamic hold, enhancing balance and flexibility, while the hollow hold emphasizes static core stabilization, crucial for overall body control and posture. Beginners may find the hollow hold more accessible, whereas advanced athletes benefit from the increased challenge and muscle engagement of the V-sit.
Conclusion: Optimizing Your Core Routine
Incorporate both V-sits and hollow holds to maximize core strength and stability, as V-sits target the rectus abdominis while hollow holds engage the entire core including the transverse abdominis and lower abs. Balancing these exercises enhances muscular endurance and improves functional movement efficiency. Tailoring your routine with these complementary moves accelerates progress toward a defined, resilient midsection.
V-sit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com