Pace bowling relies on speed and accuracy to challenge batsmen and exploit pitch conditions. Fast bowlers use seam movement, swing, and bounce variations to unsettle opponents and take crucial wickets. Discover how mastering pace bowling can elevate your cricket game by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
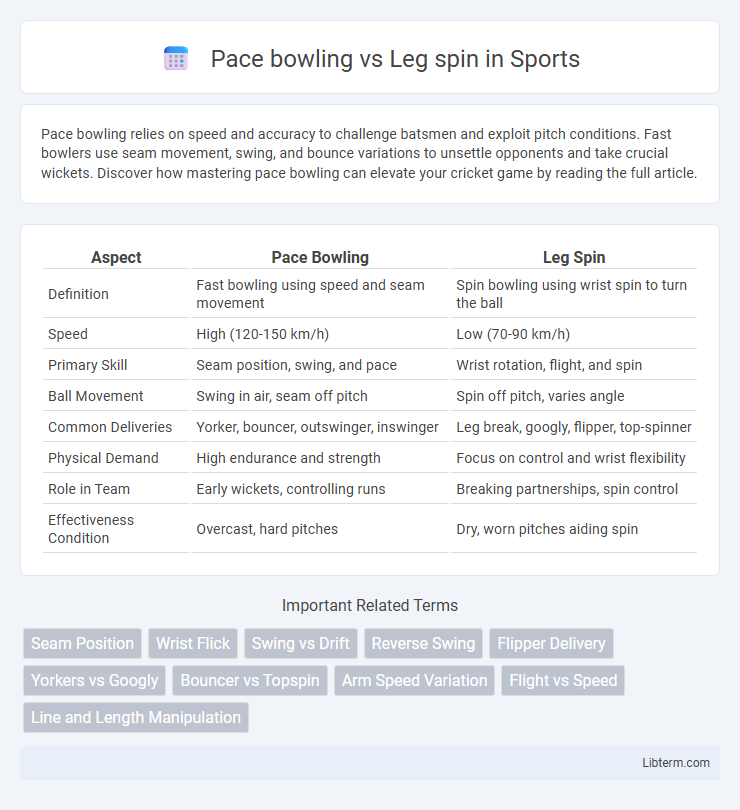
| Aspect | Pace Bowling | Leg Spin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fast bowling using speed and seam movement | Spin bowling using wrist spin to turn the ball |
| Speed | High (120-150 km/h) | Low (70-90 km/h) |
| Primary Skill | Seam position, swing, and pace | Wrist rotation, flight, and spin |
| Ball Movement | Swing in air, seam off pitch | Spin off pitch, varies angle |
| Common Deliveries | Yorker, bouncer, outswinger, inswinger | Leg break, googly, flipper, top-spinner |
| Physical Demand | High endurance and strength | Focus on control and wrist flexibility |
| Role in Team | Early wickets, controlling runs | Breaking partnerships, spin control |
| Effectiveness Condition | Overcast, hard pitches | Dry, worn pitches aiding spin |
Introduction to Pace Bowling and Leg Spin
Pace bowling relies on speed and seam movement to challenge batsmen by exploiting pitch conditions and generating bounce, typically delivering balls over 85 mph. Leg spin involves imparting wrist spin to the ball, causing it to turn sharply from the leg to off side, making it difficult for batsmen to predict and play accurately. Both techniques require distinct skills and strategies, with pace bowling emphasizing physical endurance and speed, while leg spin demands precision and variation in spin and flight.
Key Differences Between Pace and Leg Spin
Pace bowling relies on high-speed deliveries, typically exceeding 85 mph, to challenge batsmen with sheer velocity and bounce, while leg spin uses slower, spinning balls that turn sharply away from right-handed batsmen to induce false shots. The biomechanics differ significantly: pace bowlers generate momentum through a long run-up and fast arm action, whereas leg spinners depend on wrist rotation and finger flicks for imparting spin. In cricket strategy, pace bowling often aims to exploit pitch conditions for seam and swing movement, whereas leg spin thrives on variations in flight, turn, and deception.
Techniques Involved in Pace Bowling
Pace bowling relies on a combination of fast arm action, strong wrist position, and seamless body momentum to generate speed and bounce. Key techniques include the run-up, which builds momentum; a high-arm action for accurate seam position; and a strong follow-through to maintain pace and control. Mastery of rhythm, balance, and wrist snap enhances swing and seam movement, distinguishing pace bowlers from leg spinners who rely primarily on spin and flight.
Fundamentals of Leg Spin Bowling
Leg spin bowling relies on precise wrist position and finger movement to impart significant spin on the cricket ball, causing unpredictable turn and bounce off the pitch. This technique demands consistent control over grip and release, enabling variations such as the googly and flipper to deceive batsmen. Mastery of leg spin fundamentals creates effective wicket-taking opportunities against pace bowling through variation in speed and trajectory.
Impact on Match Strategy
Pace bowling exerts pressure through speed variations and bounce, disrupting batsmen's timing and enabling aggressive field settings that aim for early wickets. Leg spin introduces deception with drifting, turn, and flight, forcing batsmen to take risks, often leading to crucial breakthroughs in middle overs. Combining pace and leg spin diversifies attack angles, complicating the batting side's strategy and enhancing overall tactical flexibility.
Conditions Favoring Pace or Leg Spin
Pace bowling thrives in conditions with overcast weather, green pitches, and hard surfaces that offer seam movement and bounce, enhancing the bowler's speed and swing. Leg spin excels on dry, dusty, and deteriorating pitches where rough areas assist grip and turn, allowing bowlers to generate sharp spin and unpredictable bounce. Understanding pitch characteristics and weather patterns is crucial for selecting between pace bowling and leg spin tactics.
Famous Pace Bowlers and Leg Spinners
Famous pace bowlers like Glenn McGrath and Dale Steyn are celebrated for their speed, accuracy, and ability to exploit seam movement, often intimidating batsmen with sheer pace and bounce. In contrast, legendary leg spinners such as Shane Warne and Anil Kumble mastered the art of turn, deception, and variation, using wrist spin to confuse batsmen and generate wickets through flight and spin. Both styles of bowling have defined eras in cricket, with pace bowlers dominating with speed and aggression, while leg spinners rely on guile and skillful variations to outthink opponents.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Style
Pace bowling excels in generating high speed and intimidating bounce, exploiting seam movement and swing to unsettle batsmen, but it often requires physical stamina and can be less effective on flat pitches. Leg spin offers deceptive turn and variations like googlies and flippers, making it difficult for batsmen to predict, though it risks being punished if not executed with precision in line and length. Mastery of pace bowling is suited for exploiting early pitch conditions, while leg spin thrives in dry, turning wickets where flight and spin dominate play.
Pace vs Leg Spin in Different Formats
Pace bowling dominates in Test cricket by exploiting pitch variations and sustained speed to induce edges and lbw dismissals, while leg spin thrives in limited-overs formats due to its unpredictability and ability to generate wickets through deception and flight. In ODIs and T20s, leg spinners often disrupt batting rhythms with variations like googlies and flippers, making scoring difficult under pressure, whereas pace bowlers rely on yorkers and slower bouncers to contain runs and take key wickets. The strategic utilization of pace versus leg spin varies significantly across formats, reflecting differences in match duration, pitch behavior, and batting aggression.
Future of Pace Bowling and Leg Spin in Cricket
Pace bowling continues to evolve with advancements in biomechanics and sports science, enhancing speed, swing, and accuracy, which are crucial for breaking through modern batting line-ups. Leg spin remains a valuable strategic weapon in limited-overs formats due to its ability to generate deception and wickets, especially with variations like the googly and flipper gaining prominence. The future of cricket will likely see a balanced blend where pace bowling dominates in conditions favoring seam movement, while leg spin thrives on subcontinental pitches and in formats prioritizing tactical bowling innovations.
Pace bowling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com