Natural turn techniques enhance driving safety by encouraging smooth, controlled steering movements that align with the road's curvature. Employing these methods reduces tire wear and improves vehicle handling under various road conditions. Discover how mastering natural turns can transform your driving experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
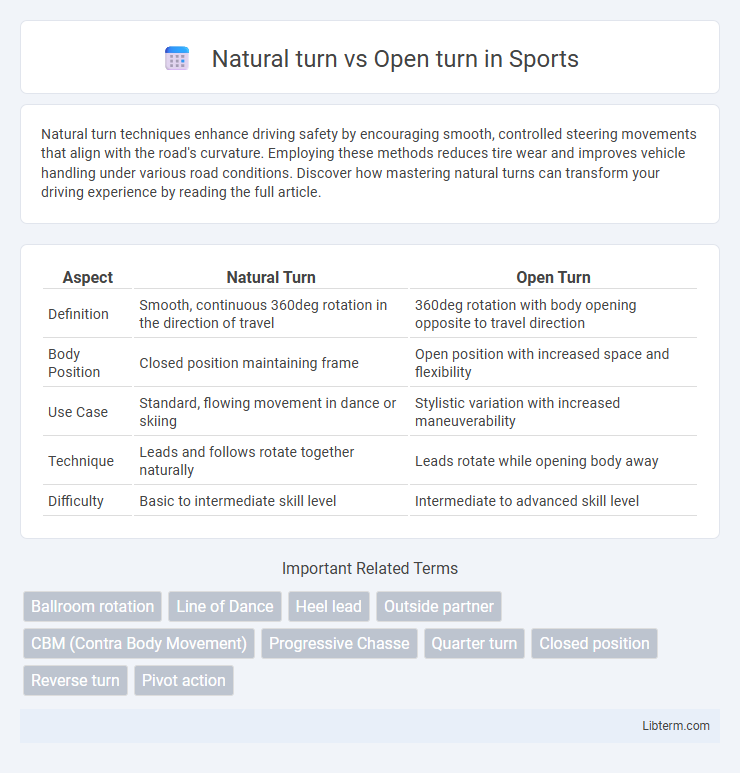
| Aspect | Natural Turn | Open Turn |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Smooth, continuous 360deg rotation in the direction of travel | 360deg rotation with body opening opposite to travel direction |
| Body Position | Closed position maintaining frame | Open position with increased space and flexibility |
| Use Case | Standard, flowing movement in dance or skiing | Stylistic variation with increased maneuverability |
| Technique | Leads and follows rotate together naturally | Leads rotate while opening body away |
| Difficulty | Basic to intermediate skill level | Intermediate to advanced skill level |
Introduction to Ballroom Dance Turns
Natural turns and open turns are fundamental techniques in ballroom dance, essential for smooth partner coordination and fluid movement across the floor. The natural turn, typically a rightward or clockwise rotation, creates momentum and allows dancers to progress along the line of dance efficiently. Open turns involve a more open position and are used to change direction or create visual dynamics, enhancing the expressive quality of ballroom routines.
Defining Natural Turn and Open Turn
Natural turn occurs when both speakers intuitively pause and switch roles in conversation without explicit cues, allowing the dialogue to flow spontaneously. Open turn refers to moments when a speaker's turn is intentionally prolonged or left incomplete to signal that others may enter or take over the conversation. Understanding these mechanisms highlights how conversational participants manage turn-taking dynamically through implicit timing and explicit signaling.
Historical Origins of Natural and Open Turns
Natural turns and open turns trace their origins to traditional ballroom dance styles prominent in the early 20th century, with natural turns emerging from the waltz's counter-clockwise rotational patterns. Open turns developed alongside Latin dances like the rumba and cha-cha, emphasizing outward-facing steps and greater spatial freedom between partners. Historical dance manuals from the 1920s and 1930s document these variations as foundational elements shaping modern ballroom techniques.
Basic Technique: Natural Turn
The Natural Turn is a fundamental ballroom dance move where the lead gently rotates the follower clockwise over six beats, creating smooth and continuous motion. This technique emphasizes maintaining a firm frame, consistent rise and fall, and precise foot placement to ensure balance and flow. Mastery of the Natural Turn provides a strong foundation for complex patterns and enhances overall dance fluidity.
Basic Technique: Open Turn
The Open Turn is a fundamental dance technique characterized by a wide, sweeping rotation where the dancer's body faces outward, promoting smooth transitions and fluid movement. This technique requires precise foot placement and controlled momentum to maintain balance and grace. Mastery of the Open Turn enhances overall dance performance by enabling clearer directional changes and increased stylistic expression.
Key Differences Between Natural and Open Turns
Natural turns occur spontaneously during conversation to manage speaker changes without explicit cues, relying on intonation, pauses, and body language. Open turns invite responses through questions or prompts, signaling clear opportunities for listeners to contribute. The key difference lies in the intentionality and explicitness of turn-taking cues, with natural turns being implicit and fluid, whereas open turns are deliberate and structurally designed for interaction.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common mistakes in natural turn include failing to recognize subtle conversational cues, leading to interruptions or awkward pauses. In open turn scenarios, speakers often dominate the conversation without allowing others to contribute, causing imbalance and miscommunication. To avoid these errors, focus on active listening, observe nonverbal signals carefully, and practice equitable turn-taking by encouraging quieter participants to share their thoughts.
Tips for Mastering Both Turns
Mastering natural turns requires maintaining smooth body alignment and using subtle weight shifts to guide direction changes, while open turns demand precise edge control and deliberate upper body rotation to execute wide, flowing curves. Practicing balance exercises and edge drills enhances stability and responsiveness for both turns. Consistent on-ice repetition and video analysis help refine technique, ensuring seamless transition between natural and open turns.
When to Use Natural vs. Open Turn in Dance
Natural turns are ideal for traditional ballroom dances like the waltz and foxtrot, where maintaining a smooth, continuous motion in a clockwise direction is essential. Open turns suit Latin and social dances such as salsa and cha-cha, providing space for arm styling and facilitating directional changes without the strict frame of closed position. Selecting between natural and open turns depends on the dance style's character, partner connection, and the desired flow of movement.
Conclusion: Enhancing Your Dance with Proper Turns
Mastering natural turns and open turns significantly improves your dance fluidity, balance, and style, making each movement more expressive and controlled. Proper execution of natural turns utilizes body alignment and momentum for smooth transitions, while open turns emphasize precise footwork and space awareness. Incorporating both techniques into your practice enhances overall dance performance and allows for greater versatility across various dance styles.
Natural turn Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com