A reverse turn is a fundamental dance move that involves changing direction smoothly, often used in ballet and ballroom dancing to add elegance and flow to your performance. Mastering the reverse turn enhances balance, coordination, and control, making your movements appear seamless and graceful. Discover step-by-step techniques and tips to perfect your reverse turn in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
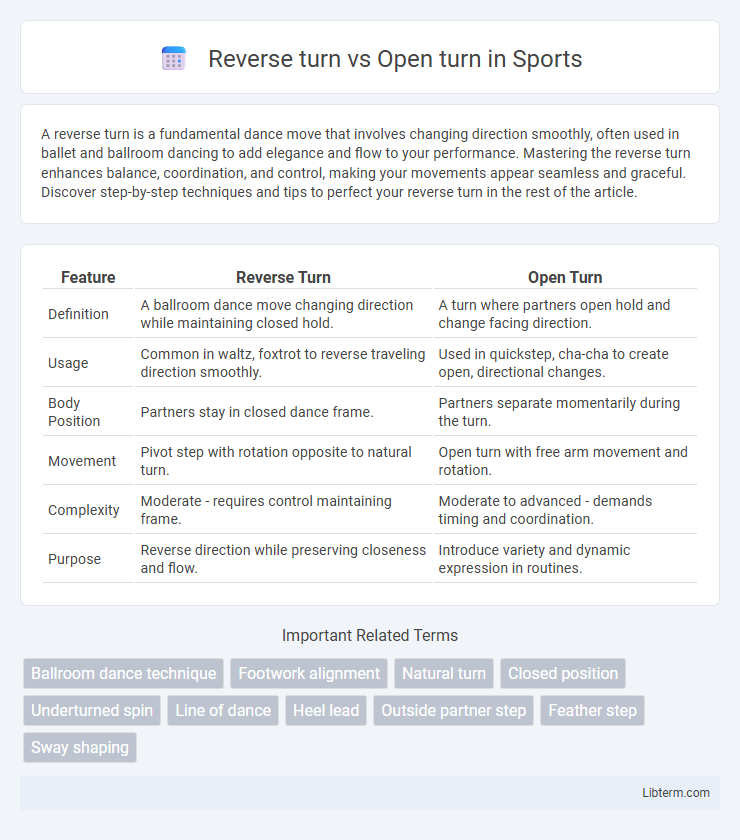
| Feature | Reverse Turn | Open Turn |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A ballroom dance move changing direction while maintaining closed hold. | A turn where partners open hold and change facing direction. |
| Usage | Common in waltz, foxtrot to reverse traveling direction smoothly. | Used in quickstep, cha-cha to create open, directional changes. |
| Body Position | Partners stay in closed dance frame. | Partners separate momentarily during the turn. |
| Movement | Pivot step with rotation opposite to natural turn. | Open turn with free arm movement and rotation. |
| Complexity | Moderate - requires control maintaining frame. | Moderate to advanced - demands timing and coordination. |
| Purpose | Reverse direction while preserving closeness and flow. | Introduce variety and dynamic expression in routines. |
Introduction to Reverse Turn and Open Turn
Reverse turn and open turn are fundamental dance moves in ballroom styles like the waltz and foxtrot, distinguished by their directional patterns and body positioning. A reverse turn involves a counterclockwise rotation, allowing dancers to elegantly change direction while maintaining close hold, emphasizing smoothness and fluidity. In contrast, an open turn opens the dance frame, enabling partners to move apart slightly for a clockwise or counterclockwise rotation, adding dynamic variation and expanding movement possibilities.
Defining Reverse Turn: Technique and Purpose
The reverse turn in dance involves a pivoting movement where the leader and follower rotate in opposite directions, creating a smooth, inward spiral that alters the line of dance. This technique enhances fluidity and control, allowing dancers to navigate crowded spaces or transition seamlessly between patterns. Its primary purpose is to maintain connection and flow while changing direction with precision and elegance.
Understanding Open Turn: Key Characteristics
Open turns in dance emphasize expanded arm movements and a wide, sweeping motion, creating a dynamic and expressive style distinct from the more compact Reverse turn. These turns involve stepping away from the partner with a clear extension of the body, enhancing visual space and energy. Understanding open turn mechanics improves dancers' ability to execute fluid transitions and maintain posture during choreography.
Key Differences Between Reverse Turn and Open Turn
The key differences between the reverse turn and open turn lie in their execution and direction; the reverse turn rotates dancers clockwise with a six-step pattern, while the open turn involves anti-clockwise rotation with a four-step pattern. In ballroom dances such as the foxtrot or quickstep, the reverse turn typically initiates with a backward step on the right foot, and the open turn begins with a forward step on the left foot, affecting the line of dance and partner positioning. Timing and technique variations also distinguish these turns, with reverse turns emphasizing smooth continuous rotation and open turns focusing on a more open hold and transitional movement.
Footwork Analysis: Reverse vs Open Turn
Reverse turns involve crossing the feet during the pivot, creating a compact and swift rotational movement essential in dances like Waltz and Foxtrot. Open turns maintain a more linear foot placement with minimal crossing, allowing for extended movement and fluid transitions ideal in dances such as Cha-Cha and Rumba. Footwork analysis reveals that reverse turns demand precise heel-to-toe positioning to maintain balance, while open turns rely on toe-to-ball weight shifts for smoother directional changes.
Body Alignment and Movement Dynamics
Reverse turns emphasize inward body rotation and compact movement, requiring dancers to maintain a closer frame and initiate turns using core muscles for controlled momentum. Open turns rely on outward body alignment with extended arms and greater spatial freedom, allowing for more expansive, flowing motion through the hips and legs. Proper body alignment in reverse turns enhances balance and precision, while open turns prioritize fluidity and dynamic range of motion in the lower body.
Common Mistakes in Reverse and Open Turns
Common mistakes in reverse turns include improper foot placement that disrupts balance, insufficient rotation leading to a stiff movement, and failure to maintain smooth contact with the partner, which causes a loss of fluidity. In open turns, errors often involve over-rotating, incorrect timing with the music or partner, and weak frame connection that results in awkward positioning and reduced control. Addressing these issues enhances overall dance technique and partner synchronization in both reverse and open turns.
Choosing the Right Turn: Dance Styles and Contexts
Choosing the right turn in dance depends on style and context, with reverse turns offering smooth, controlled rotation ideal for ballroom dances like the waltz and foxtrot. Open turns provide a more expansive, expressive movement suited to Latin dances such as salsa or cha-cha, allowing greater freedom of motion. Understanding the rhythmic structure and partner positioning in each dance helps determine whether a reverse or open turn enhances the performance.
Tips for Mastering Both Reverse and Open Turns
Mastering both reverse and open turns requires precise foot placement and controlled body rotation to maintain balance and fluidity. In reverse turns, focus on initiating the step with a smooth heel lead and maintaining a strong frame to execute the backward movement cleanly. For open turns, emphasize a wide step and gradual arm extension to create space and direction while keeping the pivot sharp and controlled.
Conclusion: Enhancing Dance Performance with Proper Turns
Mastering reverse turns and open turns significantly enhances dance performance by improving fluidity and precision in movement. Reverse turns offer controlled balance and spatial awareness, while open turns add dynamic expansion and stylistic variability. Integrating both turn types optimizes technique, contributing to a polished and adaptable dance repertoire.
Reverse turn Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com