Go route provides an efficient way to navigate HTTP requests using URL patterns in web applications. Leveraging this feature streamlines the process of handling different endpoints, improving your app's performance and maintainability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Go route enhances routing functionality for your projects.
Table of Comparison
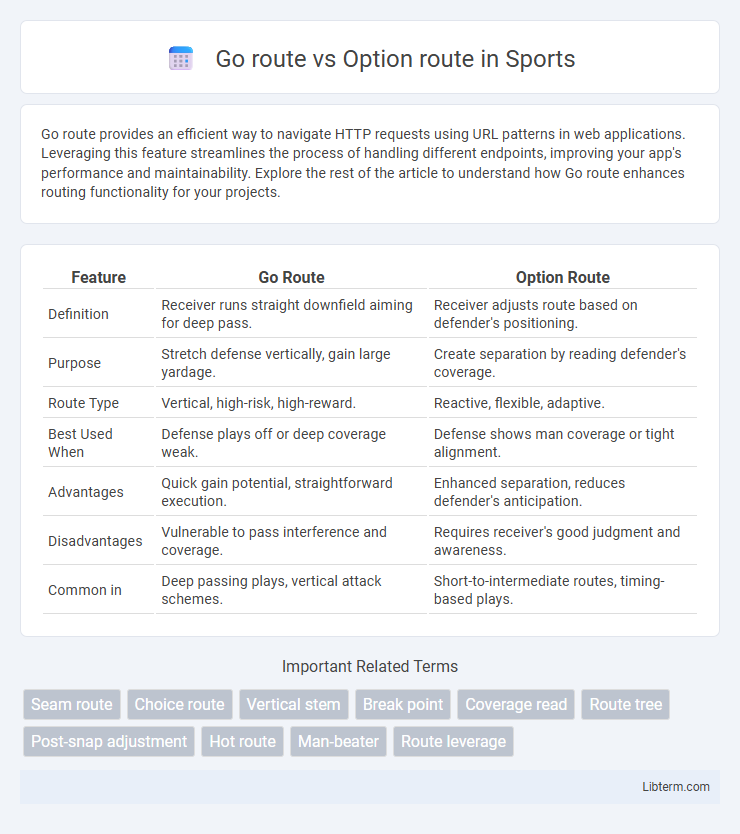
| Feature | Go Route | Option Route |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Receiver runs straight downfield aiming for deep pass. | Receiver adjusts route based on defender's positioning. |
| Purpose | Stretch defense vertically, gain large yardage. | Create separation by reading defender's coverage. |
| Route Type | Vertical, high-risk, high-reward. | Reactive, flexible, adaptive. |
| Best Used When | Defense plays off or deep coverage weak. | Defense shows man coverage or tight alignment. |
| Advantages | Quick gain potential, straightforward execution. | Enhanced separation, reduces defender's anticipation. |
| Disadvantages | Vulnerable to pass interference and coverage. | Requires receiver's good judgment and awareness. |
| Common in | Deep passing plays, vertical attack schemes. | Short-to-intermediate routes, timing-based plays. |
Introduction to Go Route and Option Route
Go route is a predefined navigation path within an application framework designed to streamline user flow and improve app responsiveness. Option route allows dynamic decision-making at runtime, offering flexibility by enabling developers to select navigation paths based on user input or application state. Both routes enhance user experience by optimizing navigation efficiency and adaptability within complex app architectures.
Defining the Go Route
The Go route is a fundamental passing concept in football where the receiver runs straight down the field aiming to outrun defenders for a deep pass. This route maximizes speed and timing, relying on the quarterback's ability to deliver the ball accurately before defensive coverage tightens. Unlike option routes that adjust based on defensive reads, the Go route maintains a consistent trajectory, emphasizing vertical stretch of the defense.
Explaining the Option Route
Option Route in Go offers a flexible approach for scheduling and executing functions or methods with dynamic conditions and parameters. Unlike traditional Go routines that run tasks concurrently without structured control, Option Route enables developers to define specific execution paths controlled by configuration options, enhancing modularity and reusability. This pattern improves code maintainability by allowing selective activation of routes based on runtime criteria, promoting efficient resource management in concurrent applications.
Key Differences Between Go Route and Option Route
Go route prioritizes speed and vertical separation by having the receiver sprint straight downfield, aiming to outrun defenders for a deep pass, while option route relies on the receiver making real-time decisions based on defensive alignment, adjusting their path to exploit coverage weaknesses. The go route demands precise timing and a strong arm from the quarterback to connect on quick, long-range throws, whereas option routes require advanced reading skills and adaptability from both quarterback and receiver to dynamically select the best attacking angle. In terms of usage, go routes are typically used to stretch the defense and create big-play opportunities, whereas option routes serve to maintain possession and methodically advance the ball through tailored route choices.
Situational Usage: When to Run Each Route
Go routes are ideal for deep passes when the quarterback needs to stretch the defense vertically and create big-play opportunities, especially against zone coverage or when the defense is playing off the line. Option routes offer flexibility based on the defender's positioning, making them effective in man coverage or mixed coverages where the receiver reads the defense and adjusts the route accordingly to find open space. Use Go routes in clear, aggressive downfield situations and Option routes in scenarios requiring adaptability and quick decision-making from the receiver.
Advantages of the Go Route
The Go route offers significant advantages in football, allowing the receiver to sprint straight downfield, maximizing yards after catch opportunities and exploiting defensive weaknesses in deep coverage. This route is effective for creating separation quickly, leveraging the receiver's speed to stretch the defense vertically and open up the field for big plays. Quarterbacks benefit from the Go route's simplicity and timing, as the route provides a clear target for quick decisions under pressure.
Benefits of the Option Route
Option routes in Go provide greater flexibility by enabling developers to define clear, self-contained route options that improve code readability and maintainability. These routes facilitate easier middleware integration and dynamic route handling, allowing for granular control over route behaviors. By using option routes, applications can achieve optimized performance through selective processing and cleaner separation of concerns.
Challenges and Risks of Each Route
Go Route presents risks including potential misalignment with long-term strategic goals and increased costs from rapid implementation without thorough analysis. Option Route challenges involve complexity in decision-making due to multiple possible outcomes, which can lead to analysis paralysis and delayed action. Both routes require careful risk management to balance flexibility and decisiveness in project execution.
Impact on Offensive Strategy
Go routes accelerate a receiver's sprint downfield, forcing defensive backs into deep coverage and creating vertical stretching of the defense, which opens opportunities for deep passes or intermediate routes underneath. Option routes provide receivers the flexibility to adjust their path based on coverage, allowing quarterbacks to read defenders and exploit weaknesses dynamically, enhancing adaptability and unpredictability within the offensive scheme. Utilizing a combination of Go and Option routes diversifies offensive threats by balancing high-speed vertical attacks with strategic decision-making, ultimately optimizing yardage gains and clock management.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Route for Success
Choosing the right routing approach impacts application efficiency and maintainability significantly. Go route excels in concurrent task management with lightweight goroutines, ideal for high-performance, scalable applications, while Option route enhances flexibility through explicit routing configurations suited for complex, condition-based navigation. Evaluating project requirements, concurrency needs, and code maintainability guides the optimal selection between Go route and Option route for successful software development.
Go route Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com