A post route is a delivery or transportation path designed to efficiently distribute mail, packages, or goods within a specific area. Optimizing a post route improves speed, reduces fuel consumption, and enhances overall service quality. Discover how refining your post route can streamline operations in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
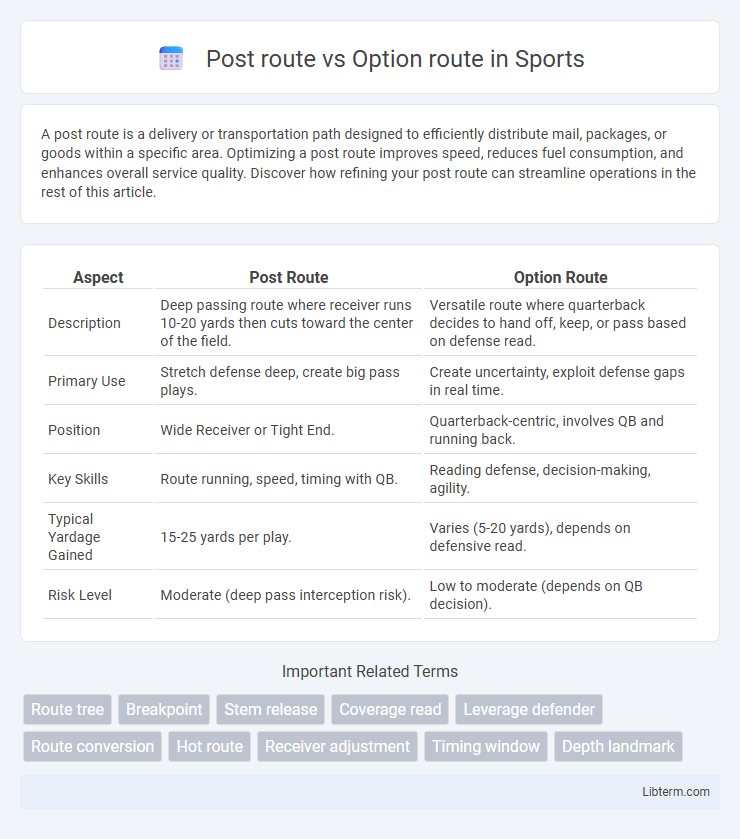
| Aspect | Post Route | Option Route |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Deep passing route where receiver runs 10-20 yards then cuts toward the center of the field. | Versatile route where quarterback decides to hand off, keep, or pass based on defense read. |
| Primary Use | Stretch defense deep, create big pass plays. | Create uncertainty, exploit defense gaps in real time. |
| Position | Wide Receiver or Tight End. | Quarterback-centric, involves QB and running back. |
| Key Skills | Route running, speed, timing with QB. | Reading defense, decision-making, agility. |
| Typical Yardage Gained | 15-25 yards per play. | Varies (5-20 yards), depends on defensive read. |
| Risk Level | Moderate (deep pass interception risk). | Low to moderate (depends on QB decision). |
Understanding Post Routes and Option Routes
Post routes use the POST HTTP method to submit data to a server for processing, commonly employed in form submissions or API calls that modify server state. Option routes refer to the HTTP OPTIONS method, which allows a client to discover allowed HTTP methods on a server resource, facilitating CORS preflight requests and API interaction validation. Understanding POST routes is essential for handling data input securely, while OPTIONS routes provide essential metadata for API communication and cross-origin request handling.
Key Differences Between Post and Option Routes
Post routes primarily involve vertical route patterns where the receiver runs straight downfield and then angles toward the center to exploit deep middle zones, optimizing yardage gains on long passing plays. Option routes offer dynamic flexibility, allowing the receiver to adjust their path based on defensive coverage, typically choosing either an inside or outside route, which enhances adaptability during the play. The key difference lies in predictability: post routes follow a predetermined pattern aimed at fixed deep targets, while option routes rely on real-time decision-making to maximize offensive advantage against various coverages.
Route Patterns: Post vs. Option
Post route patterns handle client data submissions typically using fixed paths aligned with form actions or API endpoints, ensuring secure data transmission and state changes on the server. Option route patterns serve preflight CORS requests by responding to HTTP OPTIONS methods, matching broad route patterns that allow browsers to confirm permitted methods and headers before actual requests. Post routes usually demand exact pattern matches for processing data, whereas Option routes implement flexible pattern matching to accommodate various cross-origin requests efficiently.
When to Use a Post Route
Post routes are essential for handling form submissions, uploading files, or any scenario requiring data to be sent securely to the server for processing. They are used when the action changes server state, such as creating or updating resources, unlike Options routes which are primarily used for CORS preflight requests to determine allowed HTTP methods. Choose a Post route when the client needs to send sensitive or large amounts of data that should not be exposed in URLs.
When to Use an Option Route
Option routes are primarily used in HTTP to determine server-supported communication options for a specific resource before sending the actual request, which helps optimize client-server interactions and reduce unnecessary data transfer. They are ideal for discovering allowed HTTP methods, supported content types, or authentication schemes without modifying the resource state, making them essential in CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) preflight requests. Post routes, in contrast, are designed to submit data to be processed by the server, commonly used for creating or updating resources, not for capability discovery or negotiation.
Advantages of Post Routes in Passing Attacks
Post routes offer greater unpredictability in passing attacks by allowing receivers to break vertically past defenders, creating deep opportunities for yardage gains. The design of post routes exploits the middle of the field, forcing safeties to cover large zones and opening up passing lanes for quarterbacks. This leverage against defensive coverage enhances the effectiveness of vertical passing plays compared to option routes, which rely more on route adjustments and reads than on explosive separation.
Benefits of Option Routes for Receivers
Option routes provide receivers with increased flexibility by allowing them to choose the most efficient or cost-effective shipping path, reducing delays and minimizing transportation costs. These routes enhance supply chain resilience through alternative delivery options, improving reliability and adaptability during disruptions. Receivers benefit from optimized transit times and potentially lower freight charges by leveraging multiple routing choices tailored to their specific needs.
Impact on Defensive Coverage
Post routes create deep vertical threats that stretch the defense, often pulling safeties and deep coverage away from underneath zones, which can open up space for intermediate routes. Option routes provide receivers with the flexibility to read the defense and adjust their route in real-time, effectively exploiting soft spots in man or zone coverages and causing confusion among defenders. Defensive coverage faces increased complexity with option routes, as defenders must anticipate multiple potential receiver paths, while post routes primarily challenge the secondary's ability to maintain deep coverage integrity.
Coaching Tips for Teaching Post and Option Routes
Coaching tips for teaching post and option routes emphasize precise footwork and timing to maximize route effectiveness against various coverages. For the post route, instruct receivers to break sharply towards the middle of the field at a 45-degree angle while maintaining close proximity to the defender. When running option routes, develop receivers' ability to read defensive cues in real-time and adjust their routes dynamically, enhancing offensive adaptability and exploiting coverage weaknesses.
Choosing the Right Route for Your Offensive Strategy
Choosing the right route for your offensive strategy involves understanding the key differences between Post and Option routes. Post routes, which target deep middle areas of the field, are ideal for quick, decisive yardage gains and exploiting defensive backfield weaknesses, especially against zones. Option routes provide flexibility, allowing the receiver to adjust their pattern based on the defender's coverage, making them effective in creating mismatches and maximizing yards after catch.
Post route Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com