Infield refers to the area within the diamond in baseball or softball where the bases are located, including positions such as first base, second base, shortstop, and third base. Mastering infield strategies and skills is crucial for defensive plays and overall team success. Explore the rest of the article to enhance your understanding of infield techniques and positioning.
Table of Comparison
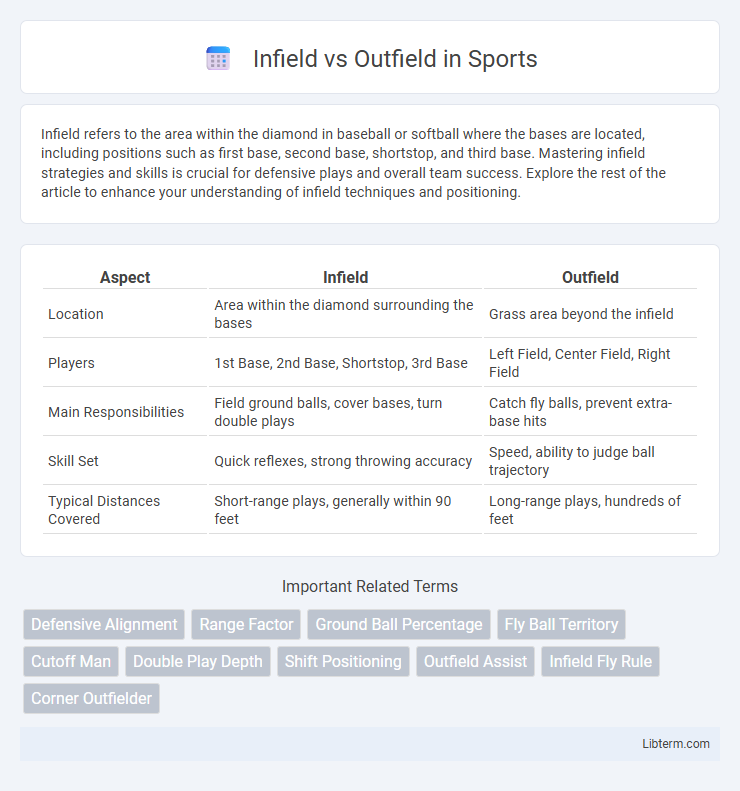
| Aspect | Infield | Outfield |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Area within the diamond surrounding the bases | Grass area beyond the infield |
| Players | 1st Base, 2nd Base, Shortstop, 3rd Base | Left Field, Center Field, Right Field |
| Main Responsibilities | Field ground balls, cover bases, turn double plays | Catch fly balls, prevent extra-base hits |
| Skill Set | Quick reflexes, strong throwing accuracy | Speed, ability to judge ball trajectory |
| Typical Distances Covered | Short-range plays, generally within 90 feet | Long-range plays, hundreds of feet |
Introduction to Infield and Outfield
The infield in baseball comprises the area within the four bases, including the positions of first baseman, second baseman, shortstop, and third baseman, focusing on quick defensive plays and ground ball handling. The outfield extends beyond the infield, covering left field, center field, and right field, where players capture fly balls and cover large ground to prevent extra-base hits. Both zones require specialized skills, with the infield emphasizing agility and reaction time, while the outfield demands speed and strong throwing arms.
Key Differences Between Infield and Outfield
Infield and outfield differ mainly in player positioning and field dimensions, with the infield comprising the area within the four bases and the outfield extending beyond the infield. Infielders, including positions like shortstop and second baseman, specialize in quick reflexes and ground ball defense, while outfielders focus on catching fly balls and covering larger distances. The tactics and skills required for each area reflect these variations, influencing how teams strategize defensive play in baseball or softball.
Roles and Responsibilities of Infielders
Infielders primarily focus on fielding ground balls, turning double plays, and covering bases to prevent runners from advancing, with specific roles assigned to first base, second base, shortstop, and third base positions. Their responsibilities include quick reaction times, strong throwing arms, and precise coordination to execute plays within the infield area. Effective communication and situational awareness are essential for infielders to support pitchers and outfielders in controlling the game's pace and preventing scoring opportunities.
Roles and Responsibilities of Outfielders
Outfielders are primarily responsible for catching fly balls, preventing extra-base hits, and backing up infielders on ground balls. They require speed and strong throwing arms to cover large areas and throw accurately to infield bases to prevent runners from advancing. Outfielders also communicate constantly to avoid collisions and ensure efficient coverage during dynamic game situations.
Skills Required for Infield Positions
Infield positions demand quick reflexes, precise hand-eye coordination, and strong throwing accuracy to effectively field ground balls and execute double plays. Players must excel in strategic decision-making to anticipate plays and position themselves optimally, especially at shortstop and second base. Agile footwork and the ability to react instantly to sharply hit balls are essential skills distinguishing infielders from outfielders.
Skills Required for Outfield Positions
Outfield positions demand exceptional speed and agility to cover vast areas of the field and track fly balls efficiently. Strong throwing accuracy and arm strength are essential for making long, precise throws to infield bases, preventing runners from advancing. Sharp situational awareness and quick reaction times enable outfielders to anticipate plays and support team defense effectively.
Common Infield Positions Explained
Common infield positions include first base, second base, shortstop, and third base, each responsible for fielding ground balls and making quick throws to get runners out. The shortstop typically covers the most ground between second and third base, while the first baseman often fields throws to complete outs. Second baseman supports double plays and covers the right side of the infield, contributing to overall defensive strategy.
Common Outfield Positions Explained
Common outfield positions include left field, center field, and right field, each requiring speed, strong throwing arms, and keen situational awareness to cover large areas of the baseball field. Center fielders typically have the most ground to cover and are often the fastest outfielders, responsible for backing up plays and communicating with corner outfielders. Left and right fielders handle line drives, fly balls, and prevent extra-base hits, with right fielders often needing the strongest arm to make long throws to third base and home plate.
How Playing Surface Affects Infield vs Outfield Play
The playing surface significantly impacts both infield and outfield performance, with infielders relying on firm, smooth dirt or synthetic turf for precise ground ball control and quick throws. Outfielders benefit from well-maintained grass or artificial turf that allows consistent ball roll and reduces unpredictable bounces, aiding in accurate fly ball tracking and fielding. Variations in surface texture and firmness alter player speed, reaction times, and ball behavior, making maintenance crucial for optimal infield and outfield play.
Choosing Between Infield and Outfield: Which Suits You?
Choosing between infield and outfield depends on your skills, speed, and game awareness. Infielders must have quick reflexes, strong throwing arms, and excellent hand-eye coordination to handle fast ground balls and make rapid plays. Outfielders benefit from speed, good judgment on fly balls, and the ability to cover large areas, making the choice crucial to matching your strengths with positional demands.
Infield Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com