Jab is a quick, straight punching technique essential in boxing and martial arts for maintaining distance and setting up combinations. Mastering the jab can improve your offense and defense by disrupting your opponent's rhythm and creating openings. Discover how refining your jab can transform your fighting skills by reading the full article.
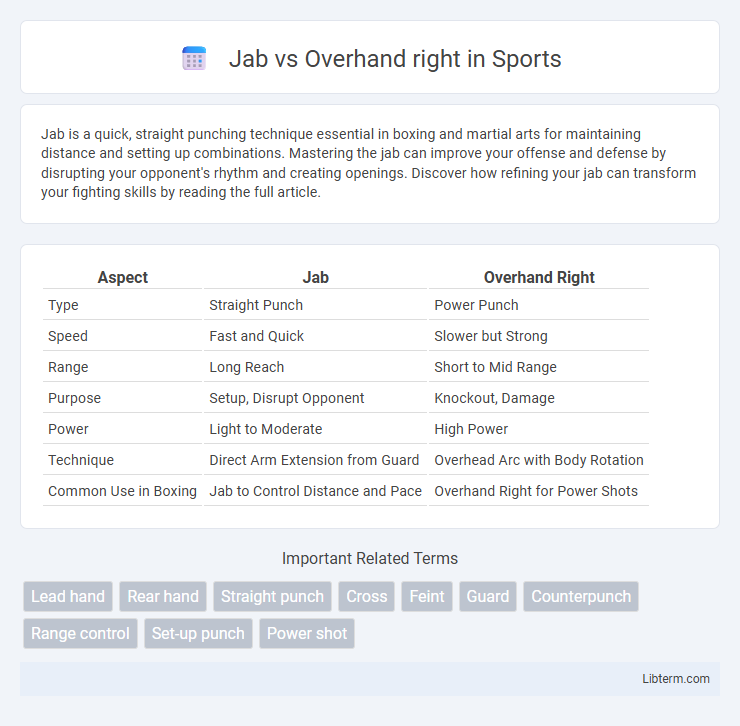
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Jab | Overhand Right |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Straight Punch | Power Punch |
| Speed | Fast and Quick | Slower but Strong |
| Range | Long Reach | Short to Mid Range |
| Purpose | Setup, Disrupt Opponent | Knockout, Damage |
| Power | Light to Moderate | High Power |
| Technique | Direct Arm Extension from Guard | Overhead Arc with Body Rotation |
| Common Use in Boxing | Jab to Control Distance and Pace | Overhand Right for Power Shots |
Understanding the Jab and Overhand Right
The jab is a quick, straight punch thrown with the lead hand, primarily used to control distance, disrupt an opponent's rhythm, and set up combinations. The overhand right is a powerful, looping punch delivered with the rear hand, designed to penetrate an opponent's guard and deliver knockout power by leveraging body rotation and downward trajectory. Understanding the biomechanical differences and strategic applications of the jab and overhand right enhances both offensive versatility and defensive effectiveness in boxing.
Key Differences Between Jab and Overhand Right
The jab is a quick, straight punch thrown with the lead hand, primarily used for range-finding, setting up combinations, and controlling distance, while the overhand right is a powerful, looping punch delivered with the rear hand designed to generate knockout power. Key differences include the jab's speed and precision versus the overhand right's emphasis on power and trajectory, as well as their distinct roles in boxing strategy; the jab disrupts an opponent's rhythm, whereas the overhand right targets openings created by defensive lapses. Biomechanically, the jab relies on linear extension and minimal body rotation, whereas the overhand right involves significant torso rotation and weight transfer to maximize impact force.
Proper Technique for Throwing a Jab
The jab requires precise alignment of the shoulder, wrist, and fist, ensuring the punch is straight and quick to maximize reach and impact. Proper technique involves pivoting the lead foot slightly while extending the arm fully without locking the elbow, maintaining balance and readiness for defense. Engaging core muscles and snapping the jab back immediately after ensures speed, control, and effective setup for subsequent strikes like the overhand right.
Proper Technique for Throwing an Overhand Right
Proper technique for throwing an overhand right involves rotating the hips and shoulders while maintaining a tight guard to generate maximum power and accuracy. The non-punching hand should stay up to protect the chin, with the elbow positioned slightly down to create a straight path for the punch. Foot placement is crucial; the rear foot pivots on the ball to transfer force effectively through the kinetic chain from legs to fist.
Situations Best Suited for the Jab
The jab is best suited for creating distance, setting up combinations, and maintaining control of the fight's tempo. It excels in situations where precision, speed, and quick counters are essential, helping to disrupt the opponent's rhythm. Fighters often use the jab to gauge range and create openings for more powerful strikes like the overhand right.
When to Use the Overhand Right
The overhand right is most effective when targeting an opponent who maintains a low guard or exposes their head after jabbing, allowing for a powerful, arcing punch that can bypass a straight defense. This punch is ideal in close-to-mid range combat where precision and timing can exploit openings created by an opponent's aggressive forward movement. Fighters often use the overhand right to capitalize on a momentary lapse in their opponent's defense, especially after dodging or slipping a jab.
Defensive Strategies Against the Jab
Effective defensive strategies against the jab include maintaining a tight guard, employing subtle head movement to slip punches, and using footwork to control distance. Parrying the jab with the rear hand or using a shoulder roll can disrupt the opponent's rhythm and create counterpunching opportunities. Consistent monitoring of the opponent's jab patterns enables precise timing for blocks and counters, minimizing exposure to strikes.
Defensive Strategies Against the Overhand Right
Defensive strategies against the overhand right prioritize head movement, such as slipping and weaving, to evade the powerful downward punch. Employing a high guard with tight elbow positioning helps absorb or deflect the overhand right's force, minimizing damage. Efficient footwork, including lateral pivots and controlled retreats, creates angles that reduce the punch's effectiveness and set up counterattacks like the jab.
Common Mistakes With Jab and Overhand Right
Common mistakes with the jab include dropping the lead hand, telegraphing the punch, and failing to snap the punch back quickly, which compromises defense and speed. Overhand right errors often involve improper weight transfer, over-rotation, and poor timing, leading to loss of balance and ineffective power generation. Mastering proper mechanics and maintaining defensive awareness are crucial to maximizing the effectiveness of both punches.
Training Drills to Improve Jab and Overhand Right
Effective training drills to improve the jab and overhand right include shadowboxing with resistance bands to enhance speed and precision, and heavy bag work focusing on proper technique and power generation. Double-end bag drills help develop timing and accuracy for both punches, while partner mitt drills simulate real-fight scenarios to refine defense and counterpunching skills. Incorporating plyometric exercises boosts explosive strength necessary for delivering sharp jabs and powerful overhand rights consistently.
Jab Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com