A substitute fielder plays a crucial role in cricket by temporarily replacing an on-field player who may be injured, off the field, or otherwise unavailable. While they cannot bowl, bat, or act as captain, substitute fielders help maintain the team's defensive strength and fielding efficiency. Explore the rest of the article to understand the rules and strategic importance of substitute fielders in your game.
Table of Comparison
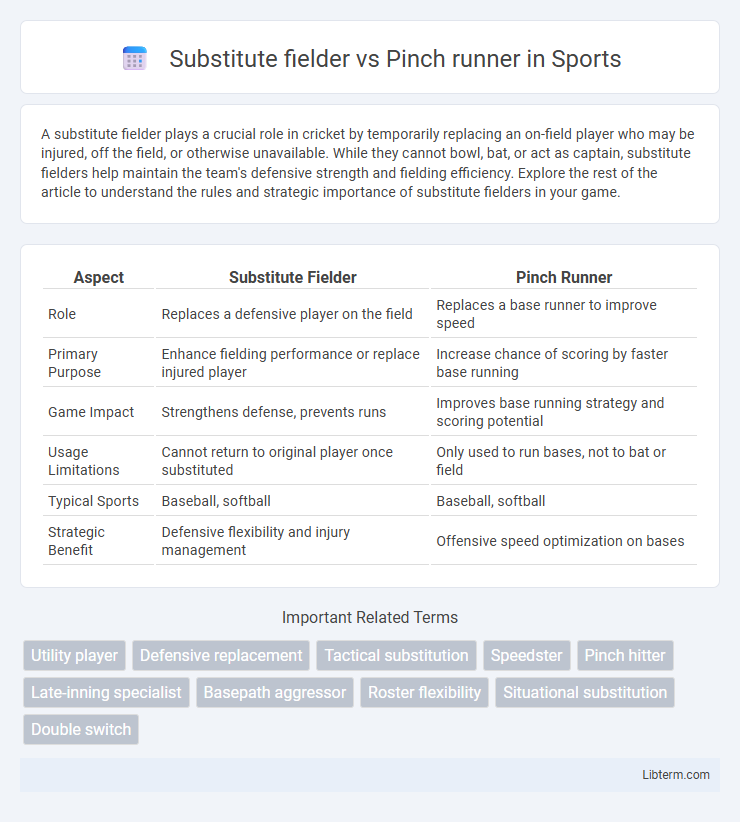
| Aspect | Substitute Fielder | Pinch Runner |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Replaces a defensive player on the field | Replaces a base runner to improve speed |
| Primary Purpose | Enhance fielding performance or replace injured player | Increase chance of scoring by faster base running |
| Game Impact | Strengthens defense, prevents runs | Improves base running strategy and scoring potential |
| Usage Limitations | Cannot return to original player once substituted | Only used to run bases, not to bat or field |
| Typical Sports | Baseball, softball | Baseball, softball |
| Strategic Benefit | Defensive flexibility and injury management | Offensive speed optimization on bases |
Understanding the Roles: Substitute Fielder vs Pinch Runner
A substitute fielder enters the game to replace a defensive player, often to bring improved fielding skills or to rest a starter, and must assume the defensive responsibilities of the replaced player. A pinch runner replaces a baserunner to increase team speed or base-running efficiency, without immediately participating in fielding or hitting. Understanding these roles highlights strategic player management in baseball, emphasizing defense enhancement through substitute fielders and offensive base-running tactics via pinch runners.
Key Differences Between Substitute Fielders and Pinch Runners
Substitute fielders enter the game primarily to replace an injured or fatigued player on defense without altering the batting order, while pinch runners are used solely to replace a base runner, aiming to improve base running speed or strategy. Unlike pinch runners, substitute fielders participate fully on defense and may take additional roles, but once replaced, they cannot re-enter the game. The tactical use of substitute fielders focuses on maintaining defensive strength, whereas pinch runners are a strategic offensive move to enhance scoring opportunities.
When to Use a Substitute Fielder in Baseball
A substitute fielder in baseball is typically used when a defensive player is injured, fatigued, or strategically replaced to enhance fielding performance. Managers often deploy substitute fielders late in the game to strengthen defense during critical innings or when facing strong hitters. Using a substitute fielder preserves the original player's batting spot for future use while improving overall defensive alignment.
Strategic Advantages of Deploying a Pinch Runner
Deploying a pinch runner enhances team strategy by introducing a faster baserunner, increasing the likelihood of scoring during critical game moments. This substitution minimizes the risk of double plays and maximizes base-stealing potential, creating pressure on the opposing defense. Unlike a substitute fielder, a pinch runner specifically optimizes offensive opportunities by leveraging speed and base-running skills.
Rules Governing Substitutions: Fielders vs Runners
Substitute fielders must enter the game only when the umpire is informed, and once removed, cannot re-enter the same inning, whereas pinch runners replace a player on base and must assume that player's identity for the remainder of the game. Rules stipulate that a substitute fielder can only be used for defensive purposes and must adhere to positional regulations, while pinch runners are only used to advance base running without changing defensive lineup immediately. Both substitutions require official notification before taking effect, ensuring compliance with league-specific substitution policies and maintaining game integrity.
Impact on Team Dynamics and Game Strategy
Substitute fielders enhance defensive flexibility by allowing managers to replace tired or less skilled players, directly impacting team dynamics with improved fielding efficiency and strategic positioning. Pinch runners primarily boost offensive dynamics and base-running speed, creating scoring opportunities by replacing slower runners during high-stakes moments. Both roles influence game strategy by enabling timely player adjustments that optimize performance and respond to evolving game situations.
Notable Historical Moments Featuring Substitute Fielders
Substitute fielders have made significant impacts in baseball history, such as Kirk Gibson's pivotal role as a pinch runner and defensive substitution during the 1988 World Series, helping the Dodgers clinch the title. Another notable moment includes Herb Washington, a world-class sprinter, who served exclusively as a pinch runner for the Oakland Athletics in 1974, highlighting strategic use of substitute players. These instances emphasize the tactical importance of substitute fielders in critical game situations, influencing outcomes beyond standard playing roles.
Famous Pinch Runner Appearances in Baseball History
Famous pinch runner appearances in baseball history include Herb Washington, known as the "world's fastest pinch runner" for the Oakland Athletics during the 1970s, who specialized exclusively in running duties without batting or fielding. Another notable example is Vince Coleman, whose base-stealing prowess made him a critical pinch runner in postseason games for the St. Louis Cardinals in the 1980s and 1990s. These appearances highlight the strategic use of pinch runners to maximize scoring opportunities by leveraging speed and base-running skills, differentiating their role from substitute fielders who primarily replace defensive positions.
Managerial Decisions: Choosing Between Fielding and Running Substitutes
Managers weigh the advantages of a substitute fielder versus a pinch runner by evaluating game context, player speed, and defensive skills. A substitute fielder enhances defensive positioning and can prevent runs in critical innings, while a pinch runner maximizes scoring opportunities through speed and base-stealing ability. Strategic decisions hinge on factors like inning number, score margin, and the upcoming opponent's batting strength to optimize team performance.
Summary Table: Substitute Fielder vs Pinch Runner Comparison
A substitute fielder replaces a defensive player on the field, primarily enhancing fielding capabilities without altering batting order, while a pinch runner is introduced specifically to replace a base runner to increase scoring potential by utilizing faster speed. The summary table highlights roles, strategic purposes, and key regulations: substitute fielders can enter only during defensive innings and must adhere to roster limitations, whereas pinch runners are used exclusively during base running situations and can be replaced by the original player later. Understanding these distinctions aids managerial decisions by optimizing player deployment based on game situations and player strengths.
Substitute fielder Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com