Wall sits strengthen your quadriceps, glutes, and calves by engaging these muscles in a static hold against a wall. This low-impact exercise improves muscular endurance and stability, making it ideal for building lower body strength without heavy equipment. Discover how incorporating wall sits into your routine can enhance your fitness journey by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
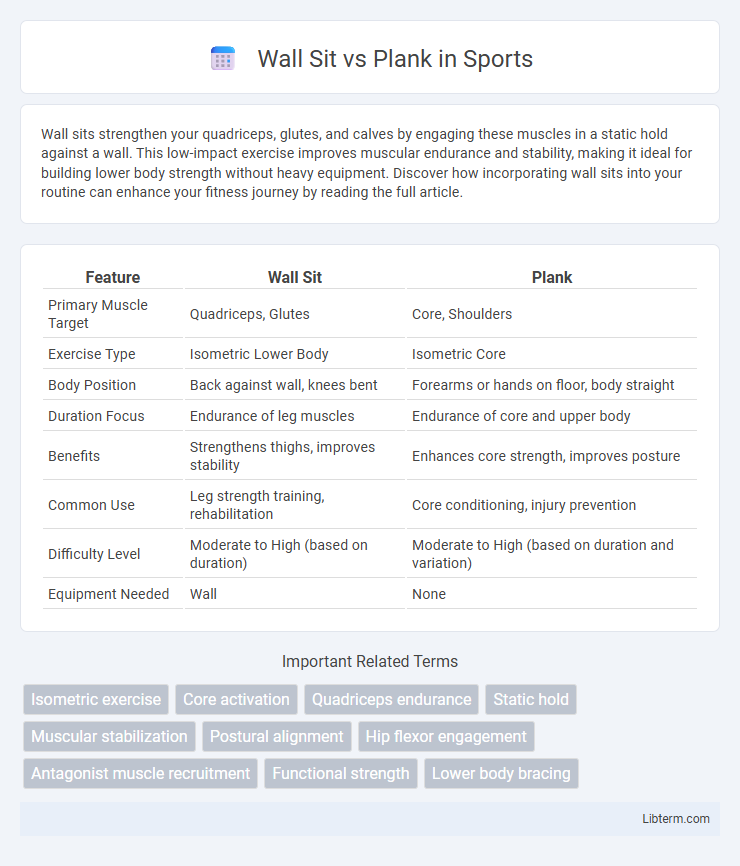
| Feature | Wall Sit | Plank |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Muscle Target | Quadriceps, Glutes | Core, Shoulders |
| Exercise Type | Isometric Lower Body | Isometric Core |
| Body Position | Back against wall, knees bent | Forearms or hands on floor, body straight |
| Duration Focus | Endurance of leg muscles | Endurance of core and upper body |
| Benefits | Strengthens thighs, improves stability | Enhances core strength, improves posture |
| Common Use | Leg strength training, rehabilitation | Core conditioning, injury prevention |
| Difficulty Level | Moderate to High (based on duration) | Moderate to High (based on duration and variation) |
| Equipment Needed | Wall | None |
Introduction: Wall Sit vs Plank
Wall sit and plank are effective isometric exercises targeting different muscle groups; wall sits primarily engage the quadriceps, glutes, and calves, while planks focus on the core, including the abdominals, lower back, and shoulders. These bodyweight exercises enhance muscular endurance and stability without requiring equipment, making them accessible for various fitness levels. Understanding the distinct benefits of wall sit versus plank helps tailor workouts to specific strength and conditioning goals.
What Is a Wall Sit?
A wall sit is an isometric exercise that targets the quadriceps, glutes, and hamstrings by having you hold a seated position against a wall with your knees bent at a 90-degree angle. This static movement builds muscular endurance and stability in the lower body without requiring any equipment. Unlike a plank, which primarily engages the core muscles, a wall sit emphasizes lower-body strength and endurance.
What Is a Plank?
A plank is an isometric core exercise that targets the abdominal muscles, lower back, and shoulders by maintaining a position similar to a push-up with a straight body line. This exercise improves core stability, enhances posture, and builds endurance without dynamic movement. Planks engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making them effective for overall core strength and injury prevention.
Muscles Worked: Wall Sit vs Plank
The Wall Sit primarily targets the quadriceps, glutes, and calves by engaging lower body muscles isometrically to maintain the seated position against a wall. The Plank predominantly activates the core muscles, including the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques, while also engaging the shoulders, chest, and lower back for full-body stabilization. Both exercises improve muscular endurance but focus on different muscle groups, with the Wall Sit emphasizing lower body strength and the Plank enhancing core stability.
Core Strength Benefits
Wall sits primarily engage the lower body muscles, particularly the quadriceps, while also activating the core to maintain stability. Planks deliver superior core strength benefits by targeting the entire abdominal region, including the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques, which enhances overall core stability and endurance. Integrating planks into workouts effectively improves posture, balance, and reduces the risk of back injuries through increased core muscle activation.
Lower Body Engagement Comparison
Wall sits primarily target the quadriceps, glutes, and hamstrings by holding a static squat position, creating intense isometric tension in the lower body muscles. Planks engage the lower body to a lesser extent, mainly activating the gluteal muscles and stabilizers to maintain a straight alignment, with more emphasis on the core and upper body. For maximal lower body engagement and endurance, wall sits provide a more concentrated and sustained muscle activation compared to planks.
Calorie Burn Differences
Wall sits primarily engage the quadriceps, glutes, and calves, resulting in a moderate calorie burn of approximately 4-6 calories per minute depending on body weight and intensity. Planks activate a broader range of muscles, including the core, shoulders, and back, which can increase calorie expenditure slightly higher, averaging around 5-7 calories per minute. The sustained isometric contraction in planks typically leads to a greater overall metabolic demand compared to wall sits, making planks marginally more effective for calorie burn during similar durations.
Injury Risks and Safety Tips
Wall sits and planks both engage core and lower body muscles but pose different injury risks due to their mechanics. Wall sits may strain the knees if performed with improper alignment or existing knee conditions, while planks can cause wrist or lower back pain when form is compromised. To ensure safety, maintain proper posture: keep knees aligned above ankles during wall sits and engage the core fully during planks to avoid sagging or arching the back.
When to Choose Wall Sit or Plank
Choose a Wall Sit when targeting lower body strength, especially the quadriceps, glutes, and calves, as it effectively simulates a sitting position against a wall to build endurance and muscle tone. Opt for a Plank to enhance core stability, shoulder strength, and overall body balance by engaging the abdominal muscles, back, and shoulders in a static hold. Select Wall Sits for lower body rehabilitation or strengthening, while Planks are ideal for improving core endurance and posture correction.
Conclusion: Which Exercise Is Best for You?
Wall sits primarily target the quadriceps, glutes, and calves, making them ideal for lower body strength and endurance, while planks engage the core, shoulders, and lower back, enhancing overall stability and posture. Choosing the best exercise depends on your fitness goals: select wall sits for improving leg muscle endurance and planks for core strengthening and spinal support. Incorporate both exercises into your routine for a balanced approach to full-body strength and muscular endurance.
Wall Sit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com