A flyball pitcher specializes in throwing pitches designed to induce batters to hit the ball into the air, resulting in fly balls rather than ground balls. Mastering pitch speed, movement, and location is essential to consistently challenge hitters and produce effective fly balls. Discover proven techniques and strategies to enhance your flyball pitching skills in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
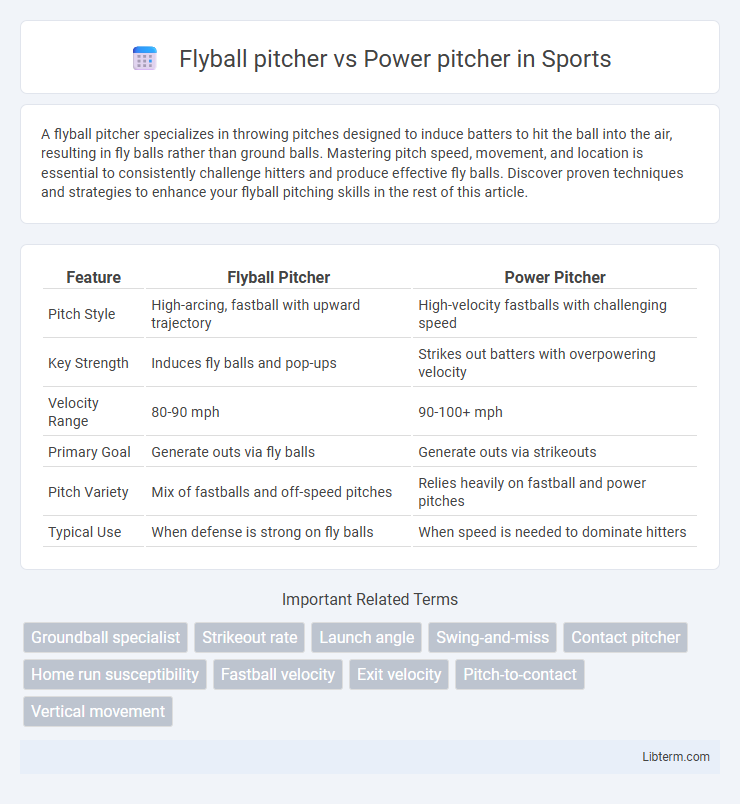
| Feature | Flyball Pitcher | Power Pitcher |
|---|---|---|
| Pitch Style | High-arcing, fastball with upward trajectory | High-velocity fastballs with challenging speed |
| Key Strength | Induces fly balls and pop-ups | Strikes out batters with overpowering velocity |
| Velocity Range | 80-90 mph | 90-100+ mph |
| Primary Goal | Generate outs via fly balls | Generate outs via strikeouts |
| Pitch Variety | Mix of fastballs and off-speed pitches | Relies heavily on fastball and power pitches |
| Typical Use | When defense is strong on fly balls | When speed is needed to dominate hitters |
Introduction to Flyball and Power Pitchers
Flyball pitchers specialize in inducing high, lofted batted balls that increase the likelihood of extra-base hits but also create more home run risks. Power pitchers, on the other hand, rely on high-velocity fastballs and dominant strikeout ability to overpower hitters and limit contact. Understanding the distinct pitching styles helps baseball analysts evaluate pitcher effectiveness and situational usage.
Defining Flyball Pitchers
Flyball pitchers specialize in inducing batted balls that travel high into the air, increasing the likelihood of outs through fly balls and pop-ups. They rely on pitch movement and velocity to generate weak contact, often sacrificing strikeout numbers for groundball avoidance. This approach contrasts with power pitchers, who emphasize high strikeout rates through velocity and overpowering stuff.
Defining Power Pitchers
Power pitchers are defined by their ability to deliver high-velocity fastballs, often exceeding 95 miles per hour, combined with a dominant strikeout rate that overwhelms hitters. Unlike flyball pitchers who induce elevation and rely on outfield defense, power pitchers prioritize strikeouts and minimize ball contact, leveraging their explosive arm strength to overpower batters. This approach typically results in higher pitch counts but fewer balls in play, emphasizing raw pitching force over inducing weak contact.
Key Differences in Pitching Style
Flyball pitchers emphasize a higher release point with an upward trajectory, generating more backspin to lift the ball and induce fly balls, ideal for outfield defense. Power pitchers concentrate on velocity and downward movement, throwing fastballs with lower spin rates to produce hard-to-hit grounders or strikeouts through sheer speed. The primary difference lies in launch angle and spin rate preferences, influencing the hitter's ball contact and defensive strategy.
Impact on Team Defensive Strategy
Flyball pitchers, who induce a high rate of fly balls, often enable teams to implement outfield-heavy defensive alignments, emphasizing range and speed to maximize catch opportunities and limit extra-base hits. Power pitchers, focusing on strikeouts and ground balls, allow infielders to play more aggressively with increased chances for double plays and fewer risks of long fly balls. Teams tailor their defensive strategies based on the predominant pitching style, optimizing player positioning to enhance overall run prevention and field efficiency.
Statistical Performance Comparison
Flyball pitchers typically exhibit higher fly ball rates, often exceeding 45%, which correlates with increased home run and slugging percentages but may result in elevated ERA due to hard contact. Power pitchers generate higher strikeout rates, frequently above 9 K/9, leading to lower BABIP and more effective run prevention metrics like FIP and xFIP. While flyball pitchers benefit from elevated slugging against, power pitchers maintain superior overall statistical performance through dominance in strikeouts and limiting opponent batting average.
Influence on Home Runs and Strikeouts
Flyball pitchers typically generate more home runs due to their tendency to elevate the ball, creating optimal launch angles for power hitters. Power pitchers excel in strikeouts by relying on high velocity and sharp breaking pitches to overpower batters. The trade-off between limiting home runs and maximizing strikeouts depends on a pitcher's ability to balance pitch location and swing-inducing mechanics.
Suitability for Different Ballparks
Flyball pitchers excel in spacious ballparks with deep outfields where their high fly balls are less likely to turn into home runs, making them more suitable for large stadiums like Coors Field or Safeco Field. Power pitchers, known for strikeouts and groundball tendencies, perform well in smaller parks such as Yankee Stadium or Fenway Park, where limiting home runs is critical. The park's dimensions and altitude significantly impact the effectiveness of each pitching style, influencing pitching strategy and pitcher selection.
Career Longevity and Injury Risk
Flyball pitchers typically experience shorter career longevity due to the higher stress placed on their arms from increased backspin and upward ball trajectory, which elevates injury risk, especially in the shoulder and elbow. Power pitchers generate fast, flat pitches with less backspin, potentially reducing arm strain but often subjecting muscles and joints to repetitive explosive force, creating a different injury profile primarily involving tendinitis and muscle strains. Studies reveal that flyball pitchers face higher ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) injury rates, while power pitchers benefit from longer careers but must manage acute muscle fatigue carefully.
Choosing the Right Pitcher for Your Roster
Choosing the right pitcher for your roster depends on the desired pitching style and game strategy. Flyball pitchers are ideal for teams seeking high strikeout rates and weak contact, as they induce more pop-ups and flyballs that can be caught by outfielders. Power pitchers, on the other hand, rely on velocity and strikeouts to dominate hitters, making them suitable for rosters that prioritize rapid outs and aggressive pitching approaches.
Flyball pitcher Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com