A trap is a device or strategy designed to catch or deceive an individual or animal, often used for hunting or security purposes. Effective traps rely on careful placement and understanding of the target's behavior to maximize capture success. Discover more about different trap types, uses, and techniques by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
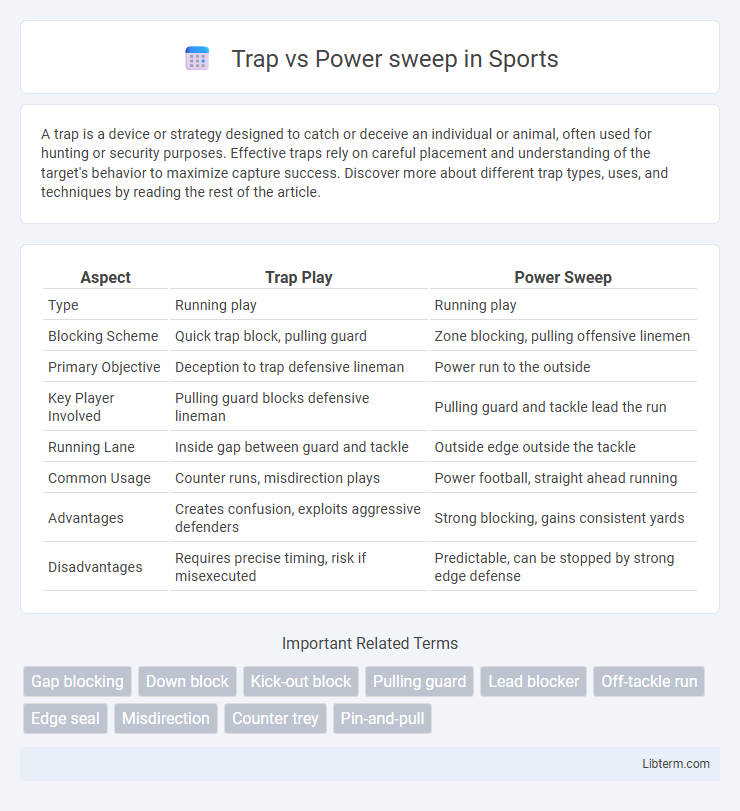
| Aspect | Trap Play | Power Sweep |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Running play | Running play |
| Blocking Scheme | Quick trap block, pulling guard | Zone blocking, pulling offensive linemen |
| Primary Objective | Deception to trap defensive lineman | Power run to the outside |
| Key Player Involved | Pulling guard blocks defensive lineman | Pulling guard and tackle lead the run |
| Running Lane | Inside gap between guard and tackle | Outside edge outside the tackle |
| Common Usage | Counter runs, misdirection plays | Power football, straight ahead running |
| Advantages | Creates confusion, exploits aggressive defenders | Strong blocking, gains consistent yards |
| Disadvantages | Requires precise timing, risk if misexecuted | Predictable, can be stopped by strong edge defense |
Introduction to Trap and Power Sweep
The Trap and Power Sweep are fundamental football running plays designed to exploit defensive weaknesses through coordinated blocking schemes. The Trap play features a delayed block by a lineman who "traps" an unblocked defender, creating a running lane, while the Power Sweep uses pulling guards or tackles to lead the ball carrier around the edge with multiple blockers. Both plays emphasize deception and leverage to generate significant yardage through precise timing and execution.
Historical Origins of Trap and Power Sweep
The trap play originated in the early 20th century as a deception-based run designed to mislead defensive linemen by allowing them to penetrate before blocking them from the side, popularized by coach Pop Warner in the 1920s. The power sweep emerged in the 1930s, largely credited to coach Vince Lombardi's Green Bay Packers, emphasizing pulling guards and a strong lead block to outflank defenders at the edge. Both plays revolutionized football tactics by exploiting defensive aggression and creating opportunities for versatile running backs.
Core Mechanics of Trap Play
Trap plays rely on precise timing and blocking schemes to create running lanes by leveraging offensive linemen's initial pass-blocking positioning, causing defenders to be caught out of place. The core mechanic involves pulling guards or tackles to block defenders outside the original line of scrimmage, allowing the running back to exploit the delayed gap. This contrasts with power sweeps, where the focus is on tempo and strength at the point of attack rather than deceiving defenders through misdirection.
Core Mechanics of Power Sweep
Power Sweep generates significant offensive pressure by targeting a wide area with a powerful horizontal attack, leveraging its broad hitbox and frame advantage to disrupt enemies. Its core mechanics rely on its safety on block and the ability to control space effectively, making it a reliable move for maintaining momentum during pressure sequences. Compared to Trap, Power Sweep excels in creating whiff punish opportunities and setting up frame traps due to its extended hit range and quick recovery.
Key Differences Between Trap and Power Sweep
Trap plays focus on deception by initially allowing defensive linemen to penetrate the offensive line before quickly blocking them from unexpected angles, creating running lanes with misdirection. Power sweep emphasizes strength and speed, involving pulling guards and tackles who aggressively lead block outside the offensive tackle to clear a path for the ball carrier. The key difference lies in trap's reliance on timing and surprise versus power sweep's emphasis on physical dominance and coordinated outside blocking.
Offensive Line Responsibilities Comparison
The trap block emphasizes pulling offensive linemen, typically guards, who move laterally to block defenders away from the play's point of attack, relying on timing and deception. In contrast, the power sweep requires synchronized down blocks and double teams by linemen, focusing on driving defenders off the line to create a running lane on the outside. Both techniques demand precise coordination and leverage, but trap blocking prioritizes misdirection, while power sweep centers on overpowering defenders at the point of attack.
Ideal Personnel for Trap vs Power Sweep
The Trap play is ideal for personnel groups with agile offensive linemen and versatile running backs who excel in quick cuts and exploiting defensive over-pursuits, such as a 2 RB or 1 RB with a mobile fullback. Power Sweep favors heavier, more physical linemen and a lead blocker fullback or H-back, making it optimal for 22 or 23 personnel featuring strong, gap-clearing blockers to establish outside running lanes. Choosing between Trap and Power Sweep depends largely on the team's strength in either nimble, quick-hitting blockers or stout, power-driven frontbacks and backs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Play
Trap plays effectively exploit aggressive defensive linemen by allowing them to penetrate the line before being blocked unexpectedly, creating running lanes; they are advantageous in confusing defenses but risk negative yardage if defenders read the play quickly. Power sweeps emphasize strong blocking and outside runs, leveraging pulling guards to overpower defenders and gain consistent yardage; however, they can be slower to develop, making them vulnerable to fast defensive reactions. Both plays offer strategic value depending on defensive tendencies, with trap runs excelling in misdirection and power sweeps in physical dominance.
Notable Teams and Coaches Using Trap or Power Sweep
The Trap play is famously associated with the Minnesota Vikings under Bud Grant, leveraging their powerful offensive line and strategic misdirection to control the game pace. The Power Sweep gained prominence with the Green Bay Packers during Vince Lombardi's coaching era, emphasizing strong blocking and outside running to dominate defenses. Both plays have become staples in NFL strategy, with modern teams adapting these concepts to fit their evolving offensive schemes.
Strategic Application in Modern Football
Trap and power sweep plays in modern football offer distinct strategic applications; the trap focuses on misdirection to exploit aggressive defensive linemen by allowing them to penetrate before sealing off their path, creating running lanes for the ball carrier. The power sweep relies on coordinated pulling guards and fullbacks to overpower defenders at the edge, emphasizing speed and physicality to outflank the defense. Teams utilize the trap to capitalize on defensive tendencies and disrupt gap assignments, while the power sweep targets weaknesses in edge containment and leverages blocking superiority for consistent yardage gains.
Trap Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com