Qualifying sessions are crucial in motorsports as they determine the starting grid positions for the race, impacting overall performance and strategy. Drivers push their limits to secure the best lap times, balancing speed and precision under intense pressure. Discover how qualifying shapes your favorite racing events and what factors influence those critical moments in our full article.
Table of Comparison
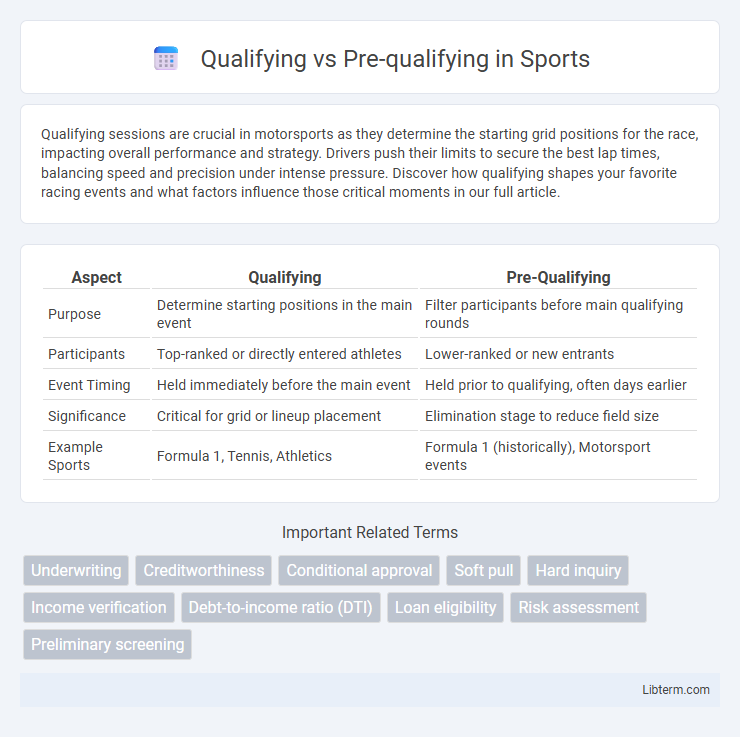
| Aspect | Qualifying | Pre-Qualifying |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Determine starting positions in the main event | Filter participants before main qualifying rounds |
| Participants | Top-ranked or directly entered athletes | Lower-ranked or new entrants |
| Event Timing | Held immediately before the main event | Held prior to qualifying, often days earlier |
| Significance | Critical for grid or lineup placement | Elimination stage to reduce field size |
| Example Sports | Formula 1, Tennis, Athletics | Formula 1 (historically), Motorsport events |
Understanding Qualifying vs Pre-qualifying
Understanding qualifying vs pre-qualifying involves recognizing their roles in the lending process; pre-qualifying provides an initial estimate of loan eligibility based on self-reported financial information, while qualifying requires thorough verification of income, credit, and assets by a lender. Pre-qualifying helps borrowers gauge potential loan amounts quickly, whereas qualifying is a formal step toward loan approval with detailed documentation. Distinguishing these phases enables borrowers to navigate mortgage or credit applications effectively and set realistic expectations.
Key Definitions: Qualifying and Pre-qualifying
Qualifying is the process where lenders assess a borrower's financial information, such as income, credit score, and debt-to-income ratio, to determine loan eligibility and the maximum loan amount. Pre-qualifying is an initial estimate based on self-reported financial data that provides a preliminary idea of how much a borrower might be approved for, without a hard credit check. Understanding both processes helps buyers navigate mortgage options and set realistic expectations for loan approval.
Purpose of Qualifying and Pre-qualifying
Qualifying assesses a borrower's ability to secure a loan by evaluating factors like income, credit score, and debt-to-income ratio to determine loan eligibility and amount. Pre-qualifying is an initial estimate based on self-reported information, providing a rough idea of borrowing capacity without in-depth verification. The primary purpose of qualifying is to confirm financial readiness and loan approval potential, while pre-qualifying serves to guide borrowers on preliminary loan options before formal application.
The Process: Step-by-Step Overview
Qualifying involves a thorough evaluation of a borrower's financial status, credit history, and ability to repay a loan, typically requiring documentation such as income statements, credit reports, and employment verification. Pre-qualifying is a preliminary assessment based on self-reported information, providing an estimate of loan eligibility without in-depth verification. The process of qualifying follows a step-by-step approach: application submission, detailed financial review, credit analysis, verification of documents, and final approval, while pre-qualifying usually consists of submitting basic information, receiving an estimate, and moving forward with formal qualifying upon interest.
Benefits of Pre-qualifying
Pre-qualifying for a loan streamlines the home buying process by providing buyers with a clear estimate of their borrowing capacity, saving time and reducing uncertainty. It helps identify potential credit issues early, allowing borrowers to address them before formally applying for a mortgage. Real estate agents and sellers often view pre-qualified buyers as more serious, increasing negotiation power and expediting the approval timeline.
Advantages of Full Qualification
Full qualification offers lenders a comprehensive view of a borrower's financial status, enhancing accuracy in loan approval decisions. It enables borrowers to understand exact loan terms, interest rates, and potential approval amounts, ensuring realistic expectations. This thorough process reduces the risk of unexpected issues during underwriting, speeding up closing times and improving overall transaction confidence.
Common Misconceptions
Qualifying and pre-qualifying are often confused in mortgage lending, but they differ significantly in terms of depth and purpose. Pre-qualifying is a preliminary assessment based on self-reported financial information, offering an estimate of borrowing potential without credit checks or documentation. Qualifying involves a thorough evaluation using verified income, credit scores, and debt-to-income ratios to finalize loan eligibility, which many mistakenly believe can be determined solely through pre-qualification.
Factors Influencing Each Stage
Qualifying involves a thorough evaluation of a prospect's financial stability, creditworthiness, and specific needs to determine eligibility for a product or service, making factors like income verification, credit scores, and debt-to-income ratios crucial. Pre-qualifying serves as an initial assessment based mainly on self-reported information like estimated income and credit range, emphasizing speed and simplicity over detailed validation. Both stages hinge on accurate data collection, but qualifying requires deeper financial analysis, while pre-qualifying relies more on preliminary estimations to filter candidates early in the process.
Impact on Decision Making
Qualifying involves a thorough evaluation of a prospect's needs, budget, and decision-making authority, enabling sales teams to tailor solutions precisely and allocate resources efficiently. Pre-qualifying filters leads early by assessing basic eligibility criteria, which streamlines the sales funnel but may miss nuanced buyer intent. The impact on decision making lies in qualifying's ability to produce high-confidence opportunities, while pre-qualifying accelerates screening yet risks lower conversion rates due to less detailed insights.
When to Choose Qualifying or Pre-qualifying
Choose qualifying when you need a comprehensive assessment of creditworthiness, income verification, and financial stability to secure a mortgage or loan with full confidence. Pre-qualifying is best suited for an initial estimate of borrowing capacity based on self-reported information, ideal for early-stage homebuyers exploring loan options. Opt for qualifying when submitting a formal application to lenders, and pre-qualifying when seeking a quick, informal evaluation.
Qualifying Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com