Overpronation occurs when your foot rolls inward excessively during walking or running, causing imbalance and strain on muscles and joints. This condition often leads to foot pain, shin splints, and an increased risk of injuries due to improper weight distribution. Discover effective solutions and prevention tips for overpronation in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
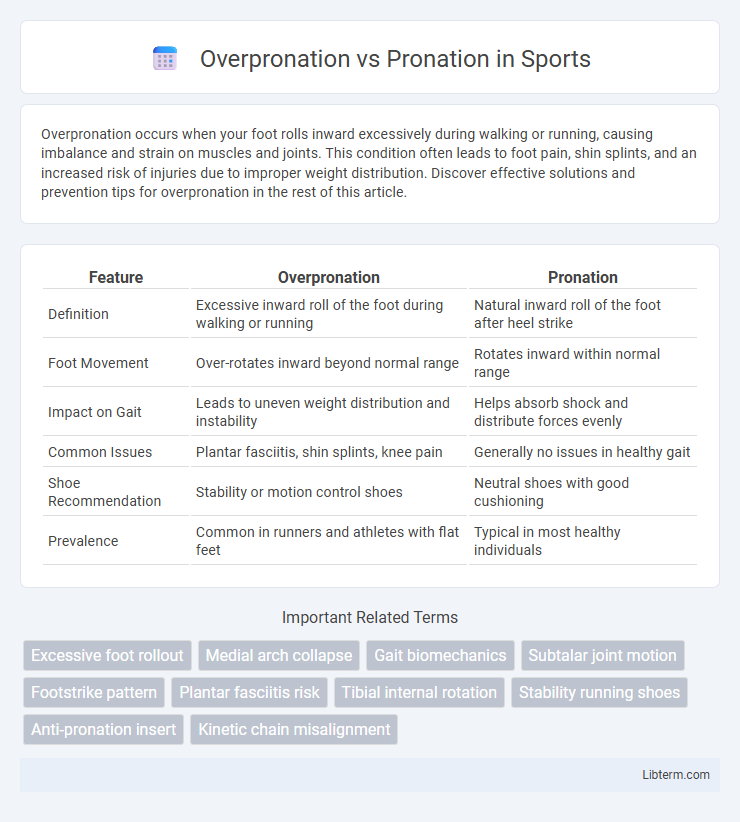
| Feature | Overpronation | Pronation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive inward roll of the foot during walking or running | Natural inward roll of the foot after heel strike |
| Foot Movement | Over-rotates inward beyond normal range | Rotates inward within normal range |
| Impact on Gait | Leads to uneven weight distribution and instability | Helps absorb shock and distribute forces evenly |
| Common Issues | Plantar fasciitis, shin splints, knee pain | Generally no issues in healthy gait |
| Shoe Recommendation | Stability or motion control shoes | Neutral shoes with good cushioning |
| Prevalence | Common in runners and athletes with flat feet | Typical in most healthy individuals |
Understanding Pronation: Definition and Function
Pronation refers to the natural inward roll of the foot during normal walking or running, essential for shock absorption and weight distribution. Overpronation occurs when this inward roll is exaggerated, causing excessive strain on the foot's arch and surrounding tissues. Understanding pronation and its variations helps in selecting appropriate footwear and orthotic supports to maintain proper foot alignment and prevent injuries.
What is Overpronation? Key Differences
Overpronation occurs when the foot excessively rolls inward during walking or running, causing uneven weight distribution and potential strain on the ankles and knees. Pronation is the natural inward roll of the foot that helps absorb shock, whereas overpronation exceeds normal limits, leading to biomechanical imbalances. Key differences include the degree of foot roll, with overpronation often linked to flat feet and increased risk of injuries such as shin splints, plantar fasciitis, and Achilles tendonitis.
The Biomechanics of Foot Motion
Overpronation occurs when the foot excessively rolls inward during the gait cycle, causing increased stress on the medial arch and ankle. Pronation, a natural foot motion, involves the slight inward roll of the foot after heel strike, aiding in shock absorption and weight distribution. Understanding the biomechanics of foot motion highlights how overpronation disrupts normal alignment and can lead to injuries or biomechanical imbalances.
Common Causes of Overpronation
Overpronation occurs when the foot rolls excessively inward during walking or running, often caused by flat feet, weak arches, or imbalanced muscle strength. This condition leads to uneven weight distribution across the foot, contributing to injuries such as plantar fasciitis, shin splints, or knee pain. Pronation itself is a normal foot movement, but overpronation disrupts proper biomechanics, increasing stress on joints and ligaments.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Overpronation is characterized by excessive inward rolling of the foot during walking or running, often leading to symptoms such as flat feet, shin splints, and knee pain. Pronation, a natural movement of the foot, becomes problematic when it is either excessive or insufficient, causing discomfort in the arch, ankle instability, and uneven shoe wear patterns. Signs to watch include persistent foot fatigue, heel pain, and swelling along the inside of the foot or ankle, which can indicate abnormal pronation issues requiring corrective footwear or orthotics.
Health Risks Associated with Overpronation
Overpronation occurs when the foot rolls inward excessively during walking or running, causing uneven weight distribution and increased strain on the foot's ligaments and tendons. This biomechanical issue elevates the risk of developing plantar fasciitis, shin splints, Achilles tendonitis, and knee pain due to improper alignment and shock absorption. Addressing overpronation with orthotic inserts, supportive footwear, and targeted exercises can significantly reduce these health risks and improve overall gait efficiency.
Gait Analysis: Identifying Your Pronation Type
Gait analysis plays a crucial role in identifying pronation types by closely examining foot movement patterns during walking or running. Overpronation involves excessive inward rolling of the foot, leading to uneven weight distribution and potential strain on the ankles and knees, while normal pronation allows the foot to naturally absorb shock and support proper alignment. Accurate assessment through tools like pressure-sensitive mats or motion capture technology helps determine pronation type, guiding personalized footwear and orthotic recommendations to enhance comfort and prevent injury.
Choosing Proper Footwear for Pronation and Overpronation
Choosing proper footwear for pronation and overpronation involves selecting shoes that offer adequate arch support and stability to control foot motion and prevent injuries. Footwear designed for overpronation typically features reinforced medial posts and motion control technology to reduce inward rolling of the foot. For neutral pronation, cushioned shoes with balanced support promote natural foot movement while maintaining comfort and shock absorption.
Effective Treatment and Prevention Strategies
Overpronation involves excessive inward foot rolling during walking or running, leading to issues like plantar fasciitis and shin splints, whereas normal pronation is the natural inward roll that helps absorb shock. Effective treatment includes custom orthotics, supportive footwear with motion control features, and targeted physical therapy focusing on strengthening the tibialis posterior muscle and improving ankle stability. Preventive strategies emphasize maintaining proper foot biomechanics through routine gait analysis, regular stretching of calf muscles, and avoiding overuse by gradually increasing activity intensity.
When to Consult a Specialist
Consult a specialist when experiencing persistent foot pain, discomfort during walking or running, or noticeable changes in gait related to overpronation or pronation. If ankles frequently roll inward or there is uneven shoe wear along the inner edge, a professional assessment can identify structural abnormalities or biomechanical issues. Early consultation helps prevent long-term injuries such as plantar fasciitis, shin splints, or knee problems through tailored orthotics or corrective exercises.
Overpronation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com