Live scoring delivers real-time updates and accurate results for various sports, enhancing your viewing experience by keeping you informed every moment. This technology helps fans follow games closely without missing critical plays or changes in score. Explore the rest of the article to learn how live scoring systems work and why they are essential for modern sports enthusiasts.
Table of Comparison
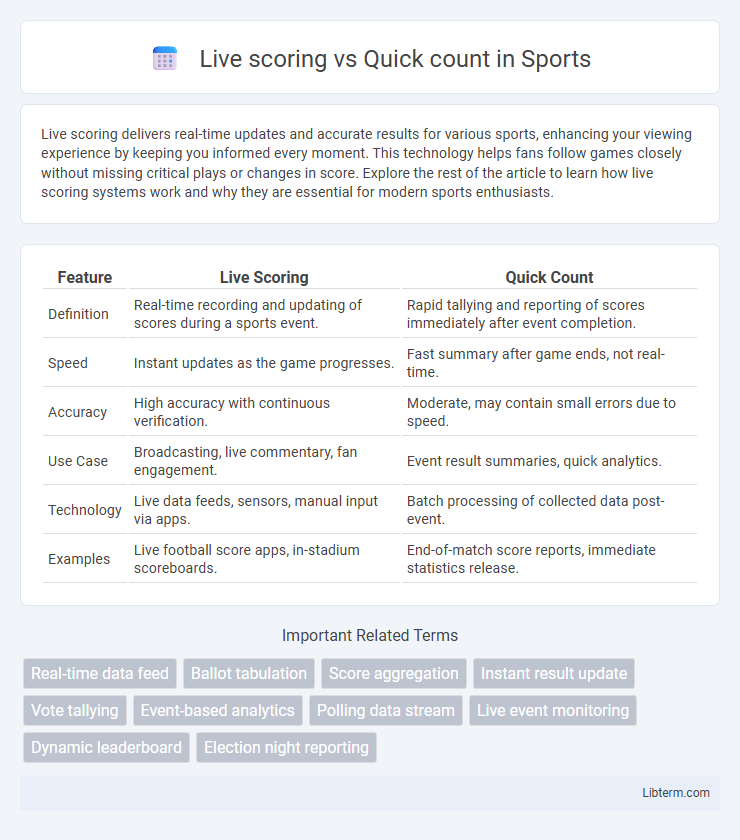
| Feature | Live Scoring | Quick Count |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time recording and updating of scores during a sports event. | Rapid tallying and reporting of scores immediately after event completion. |
| Speed | Instant updates as the game progresses. | Fast summary after game ends, not real-time. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with continuous verification. | Moderate, may contain small errors due to speed. |
| Use Case | Broadcasting, live commentary, fan engagement. | Event result summaries, quick analytics. |
| Technology | Live data feeds, sensors, manual input via apps. | Batch processing of collected data post-event. |
| Examples | Live football score apps, in-stadium scoreboards. | End-of-match score reports, immediate statistics release. |
Introduction to Live Scoring and Quick Count
Live scoring provides real-time vote tallying during elections, using electronic systems to update results as ballots are counted, enhancing transparency and immediacy. Quick count methods rely on statistically sampled polling stations to project election outcomes rapidly, offering an independent verification mechanism separate from official counts. Both techniques improve election monitoring but vary in data sources and operational scope, with live scoring emphasizing continuous data feeds and quick count focusing on representative sample analysis.
Key Differences Between Live Scoring and Quick Count
Live scoring involves real-time data collection and reporting of election results directly from polling stations, ensuring up-to-the-minute accuracy and transparency. Quick count aggregates sample data from select polling stations to provide early predictions of election outcomes, emphasizing statistical reliability and speed rather than complete data coverage. The key differences lie in live scoring's comprehensive immediacy versus quick count's sample-based estimation, impacting result accuracy and reporting timelines.
How Live Scoring Works
Live scoring operates by capturing real-time data from election polling stations through electronic devices or mobile apps, allowing immediate transmission of vote counts to a central system. This method integrates secure data verification processes and continuous updates, providing accurate and timely election results. The efficiency of live scoring depends on robust network connectivity and synchronized communication between local polling staff and the central database.
How Quick Count Functions
Quick Count functions by aggregating and analyzing data from multiple authorized polling stations to provide rapid and accurate election results, using statistical sampling methods to estimate total votes with high reliability. Unlike live scoring, which updates results in real-time from individual reporting units, Quick Count leverages parallel vote tabulation and independent verification to detect discrepancies and ensure transparency. This method enhances election integrity by cross-checking official counts against independently gathered data, minimizing errors and fraud risks.
Accuracy and Reliability Comparison
Live scoring provides real-time tallying of votes with continuous updates, enhancing immediate data accuracy through direct input from polling stations. Quick count aggregates data from multiple sources after voting concludes, offering a reliable cross-verification mechanism that reduces human error and discrepancies. The accuracy and reliability of live scoring depend heavily on stable technology and transparent processes, while quick counts benefit from statistical sampling and independent monitoring to ensure valid results.
Speed and Timeliness of Results
Live scoring delivers real-time updates, enabling immediate access to election or sports results as events unfold. Quick count compiles data from multiple sources at polling stations, offering faster overall result estimates but with a slight delay compared to continuous live scoring. The superior speed of live scoring ensures timely decisions, while quick count balances rapid aggregation with accuracy verification.
Use Cases: When to Use Live Scoring vs Quick Count
Live scoring is ideal for real-time event updates such as sports matches where instant data accuracy and continuous tracking of scores are essential for broadcasters and fans. Quick count is suited for election result tabulation when rapid but approximate vote counts provide timely insights before official tallies are available. Use live scoring in scenarios requiring minute-by-minute accuracy, and quick count when rapid summary data supports decision-making without the need for exhaustive precision.
Challenges and Limitations
Live scoring faces challenges such as real-time data accuracy issues and technological glitches that can disrupt immediate result updates. Quick count methods encounter limitations including reliance on sample data that may not fully represent voter behavior, leading to potential discrepancies. Both approaches are constrained by human error and limited infrastructure in remote or resource-poor regions, impacting overall reliability.
Technological Requirements for Each Method
Live scoring demands robust real-time data transmission infrastructure and advanced software capable of processing and displaying electoral data instantly, ensuring accuracy and minimal latency. Quick count relies on a secure digital platform for aggregating data swiftly from multiple independent sources, emphasizing reliability and cybersecurity to prevent data tampering. Both methods require high-speed internet connectivity, dedicated servers, and trained personnel proficient in handling electoral data analytics and reporting tools.
Future Trends in Real-Time Election Reporting
Live scoring and quick count technologies are rapidly evolving with the integration of AI and blockchain to enhance transparency and accuracy in real-time election reporting. Future trends emphasize the use of machine learning algorithms to predict outcomes faster and secure data transmission methods to prevent tampering. These innovations aim to provide more reliable, real-time election insights for officials and the public, reducing delays and increasing trust in electoral processes.
Live scoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com