Cadence count refers to the number of steps taken per minute while running or walking, a key metric for improving your performance and reducing injury risk. A higher cadence often promotes a more efficient stride and less impact on joints. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to measure and optimize your cadence count effectively.
Table of Comparison
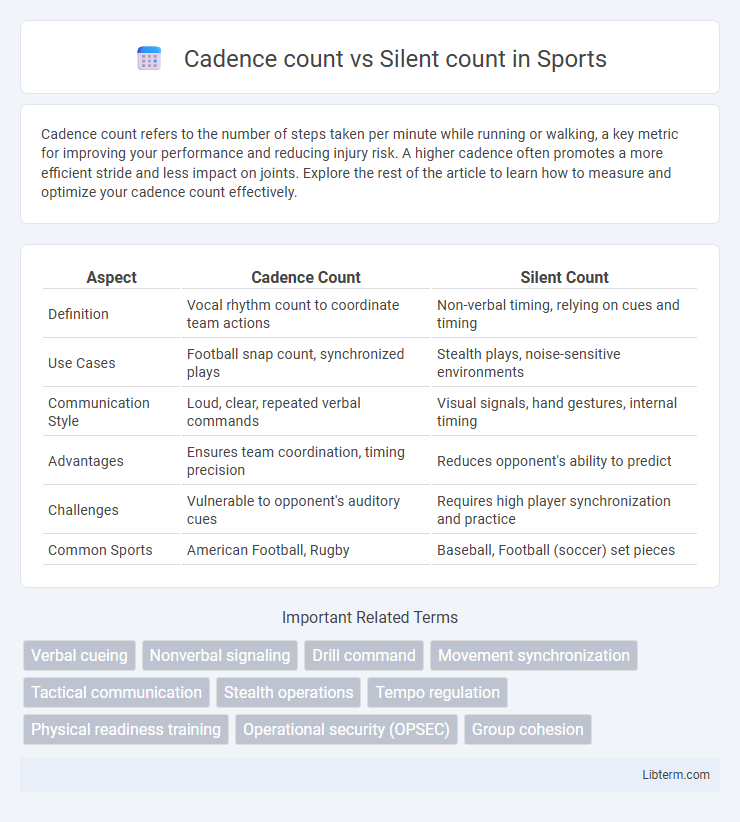
| Aspect | Cadence Count | Silent Count |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vocal rhythm count to coordinate team actions | Non-verbal timing, relying on cues and timing |
| Use Cases | Football snap count, synchronized plays | Stealth plays, noise-sensitive environments |
| Communication Style | Loud, clear, repeated verbal commands | Visual signals, hand gestures, internal timing |
| Advantages | Ensures team coordination, timing precision | Reduces opponent's ability to predict |
| Challenges | Vulnerable to opponent's auditory cues | Requires high player synchronization and practice |
| Common Sports | American Football, Rugby | Baseball, Football (soccer) set pieces |
Understanding Cadence Count: Definition and Purpose
Cadence count refers to the number of steps a cyclist takes per minute, crucial for optimizing pedaling efficiency and performance. It measures the rhythm of pedal rotations, helping athletes maintain a consistent and energy-efficient pace. Understanding cadence count is essential for improving cycling mechanics and reducing fatigue during rides.
What Is Silent Count? An Overview
Silent count refers to the number of errors or defects not detected by traditional quality control or monitoring systems during production or data processing. Unlike cadence count, which measures the total occurrences or cycles of a process, silent count identifies hidden or unreported incidents that escape routine observation. Understanding silent count is crucial for improving accuracy in performance metrics and enhancing overall system reliability.
Key Differences Between Cadence Count and Silent Count
Cadence count refers to the rhythmic number of steps taken per minute during running or walking, often used to enhance performance and reduce injury risk, while silent count measures the duration or interval of silence between these steps, emphasizing timing and foot strike sound control. Cadence count primarily focuses on optimizing movement frequency for efficiency, whereas silent count targets minimizing noise and impact through controlled footfalls. Understanding these differences aids in tailoring training techniques for improved athletic performance and injury prevention strategies.
Applications of Cadence Count in Workouts
Cadence count measures the number of steps taken per minute during workouts, providing critical data to improve running efficiency and reduce injury risk. Applications of cadence count in workouts include optimizing stride rate for endurance, enhancing speed training by maintaining an ideal step frequency, and customizing interval sessions for maximum performance gains. Monitoring cadence helps athletes adjust their technique in real-time, ensuring consistent pace and better overall biomechanics.
Benefits of Using Silent Count in Training
Silent count in training enhances focus by minimizing distractions and allowing athletes to internalize rhythm without external noise interference. This method promotes better muscle memory and improves synchronization in team sports, leading to more precise and consistent performance. Cadence count, while useful for verbal cues, can sometimes disrupt natural movement patterns and reduce overall concentration.
Accuracy and Reliability: Cadence Count vs Silent Count
Cadence count measures the number of steps taken per minute, providing accurate insights into running efficiency and performance metrics, while silent count tracks periods of no movement, ensuring reliable detection of rest or inactivity. The accuracy of cadence count relies on precise sensor calibration to capture true step frequency, whereas silent count's reliability depends on consistent signal interpretation to distinguish genuine pauses from sensor noise. Both metrics complement each other, enhancing overall assessment of movement patterns in training or gait analysis.
Situational Use: When to Choose Each Counting Method
Cadence count is ideal for military drills and synchronized team activities requiring precise, audible timing to maintain uniform movement. Silent count suits noise-sensitive environments like airborne operations or covert missions, where stealth and minimal verbal cues are critical. Choosing between cadence and silent count depends on operational context, communication needs, and the level of auditory control required for successful coordination.
Enhancing Performance With Cadence Counting
Cadence count directly influences running efficiency by synchronizing stride frequency with optimal biomechanics, reducing ground contact time and minimizing energy expenditure. Silent count, or the absence of cadence monitoring, often leads to inconsistent pacing and increased risk of fatigue due to inefficient stride patterns. Enhancing performance with cadence counting enables athletes to maintain a steady rhythm, improve running economy, and prevent injury through better muscular coordination.
Minimizing Distractions: The Advantage of Silent Counting
Silent counting significantly minimizes distractions by allowing individuals to maintain focus during repetitive tasks or physical activities. Unlike cadence count, which uses audible cues, silent counting operates internally, preventing noise interference and fostering concentration. This method enhances performance in environments requiring quiet or high mental engagement, such as libraries or meditation sessions.
Choosing the Right Counting Technique for Your Goals
Selecting the appropriate counting technique depends on your goals: cadence count measures foot strikes per minute, enhancing running rhythm and efficiency, while silent count emphasizes reduced noise and impact for injury prevention. Cadence counting targets improving speed and stride consistency, beneficial for competitive runners seeking performance gains. Silent count suits those aiming to minimize joint stress and enhance barefoot or minimalist running form.
Cadence count Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com