Verbal count is a crucial metric in writing that measures the number of words spoken or written within a specific text or dialogue. Understanding your verbal count helps improve clarity, manage wordiness, and tailor communication to meet audience expectations effectively. Explore the rest of this article to learn how verbal count impacts communication and ways to optimize it for your writing.
Table of Comparison
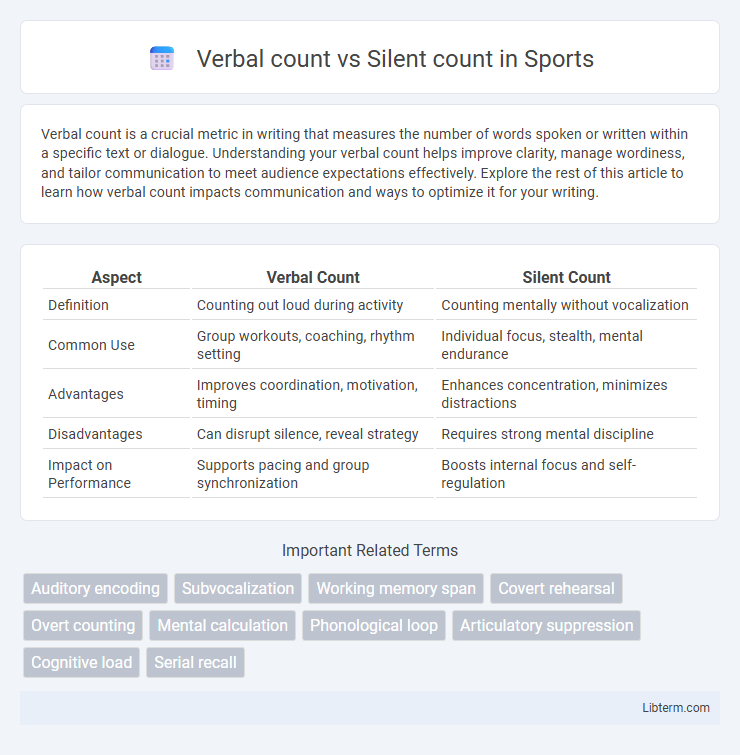
| Aspect | Verbal Count | Silent Count |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Counting out loud during activity | Counting mentally without vocalization |
| Common Use | Group workouts, coaching, rhythm setting | Individual focus, stealth, mental endurance |
| Advantages | Improves coordination, motivation, timing | Enhances concentration, minimizes distractions |
| Disadvantages | Can disrupt silence, reveal strategy | Requires strong mental discipline |
| Impact on Performance | Supports pacing and group synchronization | Boosts internal focus and self-regulation |
Introduction to Verbal Count and Silent Count
Verbal count involves articulating numbers aloud during exercises, enhancing rhythm and coordination in activities like running or weightlifting. Silent count, in contrast, relies on internal numerical pacing without vocalization, promoting mental focus and reducing auditory distractions in environments such as yoga or meditation. Both counting methods serve distinct purposes, improving performance and concentration based on activity-specific demands.
Defining Verbal Count
Verbal count refers to the process of counting numbers aloud, which engages both cognitive and speech production regions of the brain, enhancing memory retention and numerical understanding. It contrasts with silent count, where numbers are counted mentally without vocalization, relying more heavily on internal cognitive processes. Verbal counting is commonly used in early childhood education to develop phonological awareness and strengthen the connection between numerical concepts and language skills.
Understanding Silent Count
Silent count, also known as internal counting, involves mentally tracking repetitions or actions without vocalizing numbers, enhancing focus and efficiency in various activities. This technique is essential in disciplines like fitness, music, and meditation, where verbal count can be distracting or impractical. Understanding silent count improves concentration and timing accuracy by fostering a deeper internal awareness of rhythm and movement.
Key Differences Between Verbal and Silent Counting
Verbal counting involves aloud articulation of numbers, which aids memory retention and cognitive processing through auditory feedback, while silent counting occurs internally without speech, relying on mental visualization and concentration. Verbal counting enhances engagement in group activities and early math learning by reinforcing number sequences, whereas silent counting is often used for personal tasks requiring quiet focus or when verbalizing is impractical. The key differences lie in their sensory involvement--auditory for verbal and purely mental for silent--and their application contexts, influencing efficiency and situational appropriateness.
Cognitive Effects of Verbal Counting
Verbal counting engages auditory and articulatory neural circuits, enhancing working memory and promoting better numerical comprehension compared to silent counting. This cognitive stimulation increases phonological loop activity, which supports information retention and processing speed in mathematical tasks. Studies reveal that verbal counting can improve problem-solving abilities and facilitate more accurate numerical reasoning by reinforcing language-based cognitive pathways.
Benefits of Silent Counting
Silent counting enhances focus and mental clarity by minimizing distractions often caused by vocalization. This cognitive technique supports improved working memory and concentration, crucial for complex problem-solving and meditation practices. Research indicates silent counting promotes efficient brain activity in areas related to attention control and information processing.
Applications in Education and Learning
Verbal count techniques enhance language development and reading fluency by encouraging students to articulate numbers aloud, fostering auditory processing and memory retention. Silent count methods improve concentration and internal cognitive processing, beneficial for tasks requiring mental calculation and focus without external distractions. Integrating both verbal and silent counting in educational settings promotes balanced cognitive skills, supporting diverse learning styles and improving numerical comprehension.
Impact on Memory Retention
Verbal counting activates the phonological loop in working memory, enhancing the encoding and retention of numerical information through auditory rehearsal. Silent counting, while less engaging for the phonological loop, relies more on visual-spatial sketchpad resources, potentially reducing immediate recall accuracy. Studies show verbal counting leads to stronger memory retention in tasks requiring sequential digit recall compared to silent counting methods.
Choosing the Right Counting Method
Choosing the right counting method between verbal count and silent count depends on context and purpose. Verbal count enhances focus and coordination in activities like exercise or group settings by vocalizing numbers out loud, while silent count suits situations requiring discretion or individual mental tracking, such as meditation or inventory tasks. Understanding the benefits of each approach ensures accurate, efficient, and context-appropriate counting outcomes.
Conclusion: Enhancing Skills Through Counting Methods
Verbal count enhances auditory processing and memory retention by engaging speech mechanisms, while silent count promotes internal focus and mental clarity by reducing external distractions. Combining both methods fosters comprehensive cognitive development, improving numerical fluency and concentration skills. Integrating verbal and silent counting strategies in practice can significantly boost overall learning efficiency and skill acquisition.
Verbal count Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com