OPS, or Operations Per Second, is a critical metric measuring the efficiency and speed of computing systems, especially in data processing and transaction handling. Understanding OPS helps optimize your system's performance and ensures smooth workflow management in various applications. Explore this article to learn how OPS can impact your technology setup and productivity.
Table of Comparison
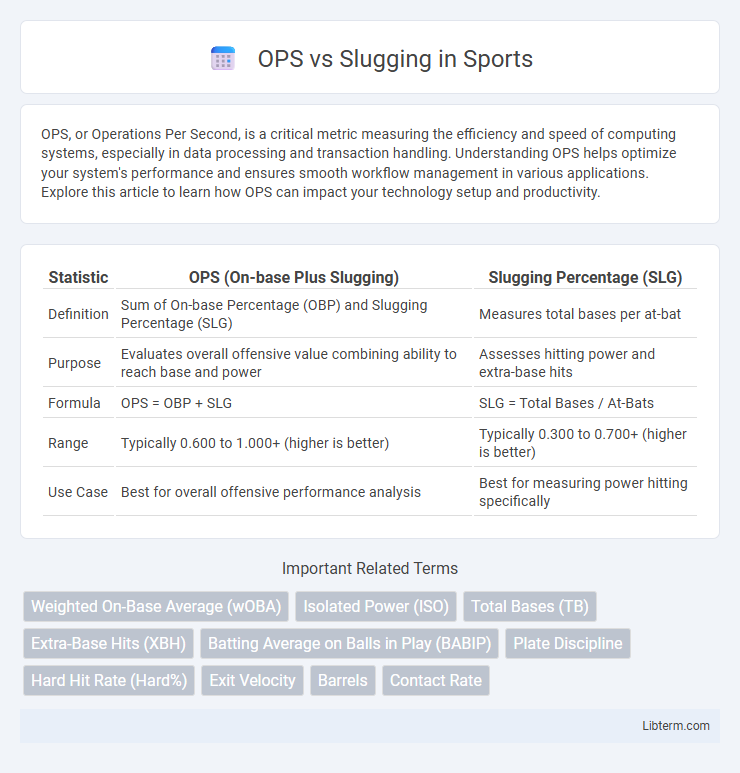
| Statistic | OPS (On-base Plus Slugging) | Slugging Percentage (SLG) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sum of On-base Percentage (OBP) and Slugging Percentage (SLG) | Measures total bases per at-bat |
| Purpose | Evaluates overall offensive value combining ability to reach base and power | Assesses hitting power and extra-base hits |
| Formula | OPS = OBP + SLG | SLG = Total Bases / At-Bats |
| Range | Typically 0.600 to 1.000+ (higher is better) | Typically 0.300 to 0.700+ (higher is better) |
| Use Case | Best for overall offensive performance analysis | Best for measuring power hitting specifically |
Understanding OPS and Slugging: Key Differences
OPS (On-base Plus Slugging) combines a player's on-base percentage (OBP) and slugging percentage (SLG) to provide a comprehensive measure of offensive performance, capturing both the ability to get on base and hit for power. Slugging percentage strictly measures the total number of bases a player records per at-bat, reflecting power hitting without accounting for walks or on-base events. Understanding OPS versus slugging highlights how OPS offers a more complete evaluation of a batter's overall offensive value by integrating on-base skills with slugging ability.
The Origins of On-base Plus Slugging (OPS)
The origins of On-base Plus Slugging (OPS) trace back to combining two fundamental baseball statistics: On-base Percentage (OBP) and Slugging Percentage (SLG). Bill James, a pioneering sabermetrician, popularized OPS in the late 20th century as a more comprehensive measure of a player's offensive value by capturing both the ability to reach base and power hitting. This statistic reflects a player's overall offensive contribution by merging on-base skills and slugging power into a single, easy-to-understand metric.
What is Slugging Percentage (SLG)?
Slugging Percentage (SLG) measures a baseball player's power-hitting ability by calculating total bases achieved per at-bat, valuing singles, doubles, triples, and home runs differently. It is computed by dividing total bases by at-bats, reflecting the player's capacity to hit for extra bases beyond just getting on base. SLG offers a more nuanced view of offensive performance compared to simple batting average, emphasizing the quality of hits rather than just frequency.
How OPS Is Calculated in Baseball
OPS in baseball is calculated by adding a player's On-Base Percentage (OBP) and Slugging Percentage (SLG). On-Base Percentage measures how frequently a batter reaches base via hits, walks, and hit-by-pitches, while Slugging Percentage quantifies the total bases a player records per at-bat. Combining OBP and SLG provides a comprehensive metric that evaluates a player's overall offensive performance.
The Role of Slugging in Measuring Power Hitters
Slugging percentage (SLG) directly measures a hitter's power by calculating total bases per at-bat, emphasizing extra-base hits like doubles, triples, and home runs. On-base plus slugging (OPS) combines SLG with on-base percentage, providing a holistic view of a player's ability to reach base and hit for power. Slugging remains the key metric to evaluate pure power hitting, highlighting a batter's effectiveness in producing runs through powerful contact.
OPS: A Comprehensive Batting Metric
OPS (On-base Plus Slugging) integrates a player's ability to reach base with their power hitting, combining on-base percentage (OBP) and slugging percentage (SLG) into a single, comprehensive metric. By measuring both how often a batter gets on base and the quality of their hits, OPS provides a more complete evaluation of offensive performance than slugging percentage alone. This statistic is widely used in advanced baseball analytics for player comparison, lineup construction, and predicting run production.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Slugging Percentage
Slugging percentage (SLG) measures a hitter's power by calculating total bases per at-bat, highlighting their ability to hit for extra bases like doubles, triples, and home runs. Its strength lies in capturing power hitting more precisely than On-Base Plus Slugging (OPS), which blends on-base skills and slugging but may dilute pure power metrics. A key weakness of slugging percentage is its failure to account for a player's ability to get on base, making it less comprehensive for evaluating overall offensive value compared to OPS.
Why OPS Is Favored by Modern Analysts
OPS combines on-base percentage (OBP) and slugging percentage (SLG) to provide a comprehensive metric that measures a player's ability to both reach base and hit for power, capturing offensive value more effectively than slugging alone. Modern analysts favor OPS because it balances hitting proficiency and power output, offering a more complete evaluation of a hitter's overall offensive contribution. The metric's simplicity and strong correlation with run production make OPS a preferred tool in advanced baseball analysis and player comparison.
Comparing Historical OPS and Slugging Leaders
Historical OPS leaders often showcase a more comprehensive offensive skill set by combining on-base percentage and slugging percentage, surpassing players who excel solely in slugging. While slugging percentage highlights raw power through extra-base hits, OPS provides a balanced view by incorporating the player's ability to reach base. Comparing figures like Barry Bonds' .921 OPS and .606 slugging against players with high slugging but lower on-base percentages demonstrates why OPS is a preferred metric for evaluating overall offensive contribution.
Which Metric Matters Most: OPS or Slugging?
OPS (On-base Plus Slugging) combines on-base percentage and slugging percentage to provide a comprehensive measure of a player's offensive ability, capturing both getting on base and power hitting. Slugging percentage isolated power by focusing solely on extra-base hits, offering deep insight into a player's power but ignoring plate discipline and on-base skills. OPS is often considered the more valuable metric by analysts and teams because it reflects overall offensive production, making it crucial for evaluating a player's impact on run scoring.
OPS Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com