Drawing enhances creativity and sharpens observational skills, making it a valuable hobby for people of all ages. Mastering basic techniques like shading, perspective, and proportion can significantly improve your artwork's realism and expression. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips and expert advice for elevating your drawing skills.
Table of Comparison
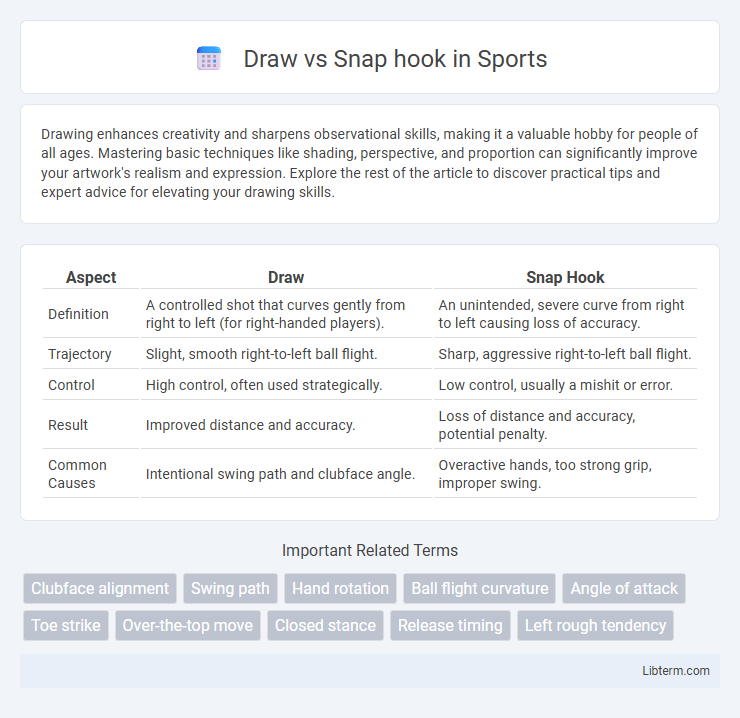
| Aspect | Draw | Snap Hook |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A controlled shot that curves gently from right to left (for right-handed players). | An unintended, severe curve from right to left causing loss of accuracy. |
| Trajectory | Slight, smooth right-to-left ball flight. | Sharp, aggressive right-to-left ball flight. |
| Control | High control, often used strategically. | Low control, usually a mishit or error. |
| Result | Improved distance and accuracy. | Loss of distance and accuracy, potential penalty. |
| Common Causes | Intentional swing path and clubface angle. | Overactive hands, too strong grip, improper swing. |
Understanding the Basics: Draw vs Snap Hook
Draw hooks feature a smooth, secure gate mechanism ideal for controlled attachment and quick release, making them favored in climbing and rigging applications. Snap hooks utilize a spring-loaded gate that automatically closes upon release, offering rapid, one-handed connection suited for light-duty uses like keychains or pet leashes. Understanding the mechanical differences and load capacities between draw hooks and snap hooks is essential for selecting the right hardware for safety and performance.
Key Differences Between a Draw and a Snap Hook
A draw hook features a simple, open gate that allows for quick attachment and detachment, primarily designed for ease of use in climbing gear loops, whereas a snap hook includes a spring-loaded gate providing more secure closure for holding loads under tension. Draw hooks are typically lighter and suited for non-load-bearing purposes, while snap hooks are engineered to resist accidental opening and greater mechanical stress. The key difference lies in their gate mechanism and load capacity, making snap hooks preferable for safety-critical applications and draw hooks for convenient, fast connections.
Causes of a Draw in Golf
In golf, a draw occurs when the ball curves gently from right to left for a right-handed player, primarily caused by an inside-to-outside swing path combined with a clubface that is slightly closed relative to the swing path at impact. This shot shape results from factors such as strong grip pressure, improper alignment, or an over-the-top swing motion. Correcting these issues involves adjusting grip, stance, and swing mechanics to promote a more neutral clubface and swing path.
Causes of a Snap Hook in Golf
A snap hook in golf is primarily caused by an overly strong grip combined with an inside-to-out swing path, leading to excessive clubface closure at impact. This results in the ball curving sharply from right to left for right-handed golfers. Other factors include improper weight shift and excessive wrist rotation during the downswing, which exacerbate the hook tendency.
Ball Flight Path: Draw vs Snap Hook
The ball flight path of a draw curves gently from right to left for right-handed golfers, producing a controlled and powerful shot with reduced slicing risk. In contrast, a snap hook exhibits a sharp, sudden leftward break due to an overly closed clubface and excessive swing path, often resulting in loss of distance and accuracy. Understanding these flight characteristics helps golfers adjust grip, swing plane, and clubface angle to optimize performance.
Clubface and Swing Path: Technical Factors
Draw shots require a clubface that is slightly closed relative to the swing path, promoting a right-to-left ball curvature for right-handed golfers. Snap hooks involve an excessively closed clubface combined with an overly inside-out swing path, causing the ball to sharply curve left. Precise control of the clubface angle and swing path is crucial to differentiate a controlled draw from an undesirable snap hook.
Common Mistakes Leading to Snap Hooks
Common mistakes leading to snap hooks include improper grip pressure, inconsistent swing path, and incorrect clubface alignment at impact. Overactive hands or excessive wrist rotation cause the clubface to close too quickly, resulting in the ball veering sharply to the left for right-handed golfers. Lack of proper sequencing in the downswing and poor body rotation also contribute to unintended snap hooks, reducing shot accuracy and distance.
How to Control and Produce a Draw Shot
To control and produce a draw shot, focus on a slightly closed clubface at impact combined with an inside-to-outside swing path that encourages right-to-left ball flight for right-handed golfers. Proper grip pressure, maintaining a strong grip, and rotating the forearms through impact helps square the clubface and promotes the desired draw curvature. Consistent weight transfer and keeping the clubhead low through impact are critical to generating the draw's controlled trajectory and increased distance.
Fixing and Preventing Snap Hooks
Snap hooks often fail due to improper fixing or inadequate material strength, making secure attachment methods critical in preventing accidental release. Using locking mechanisms or threaded closures significantly enhances the reliability of snap hooks by preventing unintended openings under load or movement. Regular inspection and replacing worn or damaged components further ensure snap hooks maintain optimal performance and safety in dynamic environments.
Best Drills for Mastering Draws and Avoiding Snap Hooks
Mastering draws and avoiding snap hooks require drills that emphasize proper clubface alignment and swing path control, such as the gate drill for consistent inside-to-outside swing paths and the towel drill to prevent early release causing snap hooks. Using alignment sticks to guide swing planes helps golfers feel the correct trajectory needed for a draw while minimizing over-rotation that leads to hooks. Incorporating impact bag drills reinforces solid contact with slightly closed clubface angles, promoting controlled draws while reducing the risk of snap hooks.
Draw Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com