Press coverage significantly enhances brand visibility by reaching a broad audience through trusted media outlets. It builds credibility and shapes public perception, making your message more persuasive and impactful. Explore the rest of the article to discover how to maximize your press coverage effectively.
Table of Comparison
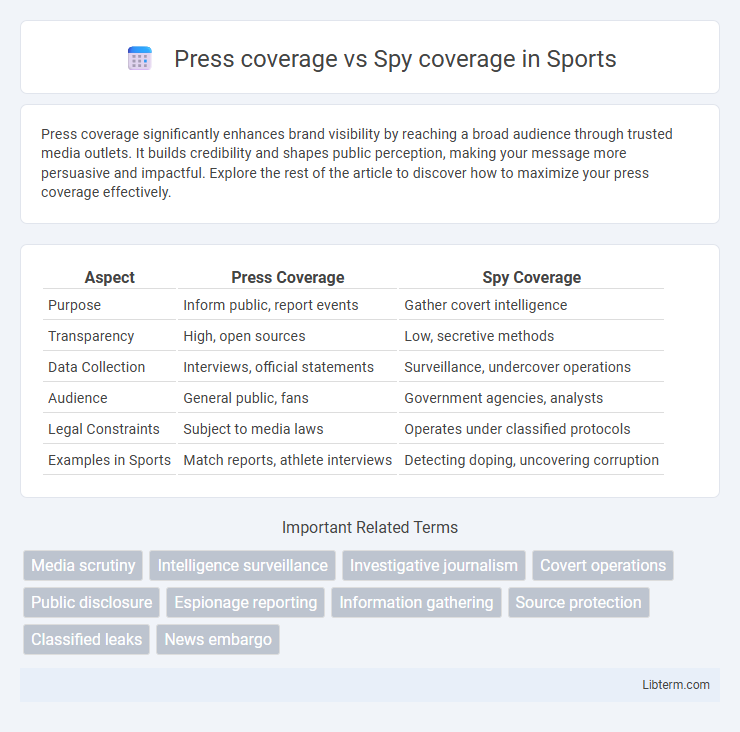
| Aspect | Press Coverage | Spy Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Inform public, report events | Gather covert intelligence |
| Transparency | High, open sources | Low, secretive methods |
| Data Collection | Interviews, official statements | Surveillance, undercover operations |
| Audience | General public, fans | Government agencies, analysts |
| Legal Constraints | Subject to media laws | Operates under classified protocols |
| Examples in Sports | Match reports, athlete interviews | Detecting doping, uncovering corruption |
Introduction: Understanding Press Coverage and Spy Coverage
Press coverage involves the public dissemination of information through news outlets, focusing on transparency and factual reporting to inform the general audience. Spy coverage, in contrast, entails covert intelligence gathering aimed at uncovering confidential or sensitive information often hidden from public view. Both forms of coverage serve distinct roles in information acquisition and dissemination, reflecting differing objectives and methodologies.
Defining Press Coverage: Purpose and Methods
Press coverage involves journalists reporting news stories through interviews, on-site observations, and document analysis to inform the public and maintain transparency. Its purpose is to provide accurate, timely information and hold authorities accountable by presenting diverse perspectives. Methods include fact-checking, ethical sourcing, and adherence to journalistic standards to ensure credibility and impartiality.
What Constitutes Spy Coverage? Key Characteristics
Spy coverage refers to covert surveillance conducted to gather confidential or sensitive information without the subject's knowledge, often involving techniques such as wiretapping, spyware, or physical observation. Key characteristics include stealth, unauthorized access, and a focus on extracting hidden insights or secrets rather than public-facing information. This contrasts with press coverage, which is transparent, legally compliant, and aims to inform the public through openly obtained data.
Historical Evolution of Press and Spy Coverage
Press coverage has evolved from 17th-century handwritten newsletters to today's real-time digital journalism, shaping public perception through transparent reporting. Spy coverage, rooted in ancient espionage, developed sophisticated intelligence gathering during the World Wars, influencing geopolitical strategies invisibly. Both evolved under technological advancements, with press emphasizing public dissemination and spies prioritizing covert information acquisition.
Ethical Considerations: Journalism vs. Espionage
Press coverage emphasizes transparency, accountability, and public interest, adhering to strict ethical standards such as truthfulness, fairness, and respect for privacy. Spy coverage operates under secrecy, often involving deception, surveillance, and covert operations that prioritize national security over individual rights or public disclosure. The ethical divide hinges on journalism's commitment to informed consent and open information versus espionage's need for confidentiality and strategic advantage.
Legal Boundaries: Press Freedom vs. National Security
Press coverage operates within the legal framework that upholds freedom of expression and the public's right to know, protected by constitutional rights such as the First Amendment in the United States. Spy coverage, however, involves clandestine activities governed by national security laws that restrict information disclosure to protect state secrets and prevent threats to security. Balancing press freedom with national security demands clear legal boundaries, where courts often mediate the tension between transparency and the confidentiality required for intelligence operations.
Major Differences: Information Gathering Techniques
Press coverage relies on open-source information such as interviews, press releases, and public records to report news while spy coverage employs covert methods including surveillance, infiltration, and signal interception to collect intelligence. Journalists prioritize transparency and verification, gathering data through accessible channels, whereas spies utilize clandestine operations and encrypted communications to obtain sensitive information. The fundamental difference lies in the ethical framework and access level, with press coverage emphasizing public accountability and spy coverage focusing on secrecy and strategic advantage.
Impact on Public Perception and Policy
Press coverage shapes public perception by highlighting events through investigative journalism, thereby influencing voter opinion and driving policy debates. Spy coverage, often classified and released selectively, impacts public perception indirectly by informing policymakers and shaping national security decisions. The transparency of press coverage fosters democratic accountability, whereas spy coverage prioritizes strategic advantage, occasionally limiting public awareness and engagement in policy-making.
Famous Cases: When Press and Spy Worlds Collided
Famous cases like the Watergate scandal and the Rosenberg espionage highlighted intense clashes between press coverage and spy operations, revealing how investigative journalism exposed covert intelligence activities. The press often navigated ethical challenges while unmasking spy networks, influencing public perception and government accountability. These collisions underscore the complex dynamic where media scrutiny can both protect democracy and jeopardize national security.
Conclusion: Balancing Transparency and Confidentiality
Press coverage ensures public transparency by disseminating verified information to maintain accountability and trust in institutions. Spy coverage operates under strict confidentiality, gathering intelligence critical for national security while minimizing the risk of sensitive data exposure. Balancing these two requires careful management to protect democratic openness without compromising strategic secrecy.
Press coverage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com