Aggression manifests as behaviors intended to cause harm or assert dominance, often rooted in underlying psychological or environmental triggers. Understanding the signs, causes, and effective coping mechanisms can help manage aggressive tendencies constructively. Discover more insights on how to recognize and address aggression in your daily life in the full article.
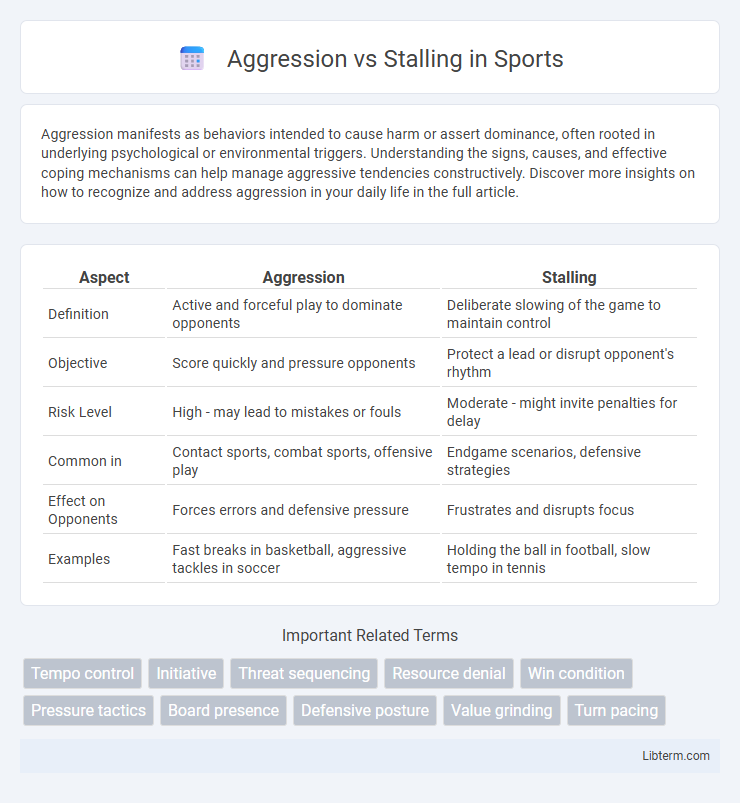
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Aggression | Stalling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active and forceful play to dominate opponents | Deliberate slowing of the game to maintain control |
| Objective | Score quickly and pressure opponents | Protect a lead or disrupt opponent's rhythm |
| Risk Level | High - may lead to mistakes or fouls | Moderate - might invite penalties for delay |
| Common in | Contact sports, combat sports, offensive play | Endgame scenarios, defensive strategies |
| Effect on Opponents | Forces errors and defensive pressure | Frustrates and disrupts focus |
| Examples | Fast breaks in basketball, aggressive tackles in soccer | Holding the ball in football, slow tempo in tennis |
Understanding Aggression and Stalling: Definitions and Key Differences
Aggression in gameplay refers to proactive, assertive actions aimed at gaining immediate advantage, such as initiating attacks or forcing opponents into defensive positions. Stalling involves deliberate delays and cautious play to avoid risks while waiting for favorable conditions or opponents' mistakes. The key difference lies in aggression's emphasis on control and momentum versus stalling's focus on preservation and timing.
The Psychology Behind Aggressive Tactics
Aggressive tactics in poker leverage psychological pressure to exploit opponents' fear and uncertainty, forcing them into suboptimal decisions. This approach capitalizes on dominance and control, often causing opponents to fold stronger hands due to intimidation. Understanding cognitive biases such as loss aversion and risk aversion explains why players frequently capitulate under sustained aggression.
Why Do Individuals or Teams Resort to Stalling?
Individuals or teams resort to stalling to gain additional time for strategic planning or to disrupt an opponent's momentum, often when they feel unprepared or disadvantaged. Psychological factors such as fear of failure, uncertainty about outcomes, or the desire to avoid immediate confrontation drive stalling behaviors. Stalling can also be a tactical move aimed at frustrating adversaries, inducing errors, or waiting for external conditions to change in their favor.
Impacts of Aggression vs Stalling on Outcomes
Aggression in decision-making often leads to faster results but comes with increased risk, potentially resulting in higher rewards or significant losses depending on the context. Stalling, characterized by delaying actions, can provide more time to gather information and reassess strategies, which may improve decision accuracy but risks missed opportunities and decreased momentum. The impact of aggression versus stalling on outcomes heavily depends on the balance between risk tolerance, timing, and the dynamic environment in which decisions are made.
Recognizing Aggressive Behavior in Competitive Environments
Recognizing aggressive behavior in competitive environments involves identifying intense verbal or physical actions aimed at dominating opponents, such as hostile gestures, confrontational language, and rapid decision-making that pressures others. This behavior often escalates conflict and disrupts cooperative dynamics, signaling a strategic push for advantage rather than collaboration. Understanding these signs enables timely intervention to mitigate potential escalation and maintain a balanced competitive atmosphere.
Spotting Signs of Stalling: Common Strategies
Spotting signs of stalling involves recognizing strategies such as evasive responses, prolonged decision-making, and repeated requests for clarification that delay progress. Common tactics include deflecting questions, providing incomplete information, and excessive referencing of rules or procedures to buy time. Identifying these patterns helps in differentiating between legitimate caution and deliberate stalling in negotiations or discussions.
When to Choose Aggression Over Stalling
Choosing aggression over stalling is optimal when opponents display passive tendencies or weak hands, allowing pressure to exploit their mistakes. In high-stakes poker or competitive scenarios, leverage aggression to seize initiative, forcing opponents into difficult decisions and capitalizing on their hesitations. However, aggressive strategies should align with accurate reads and situational awareness to maximize profits and minimize risks.
Risks and Rewards: Evaluating Both Approaches
Aggression in decision-making offers high rewards through swift gains and dominance but carries significant risks like hasty errors and increased exposure to counterattacks. Stalling prioritizes caution and information gathering, reducing immediate risks but potentially missing critical opportunities and allowing opponents to strengthen. Balancing aggression and stalling requires evaluating situational factors, risk tolerance, and long-term strategy objectives.
Balancing Assertiveness and Patience for Success
Balancing assertiveness and patience is crucial for success when navigating aggression versus stalling in competitive environments. Aggression drives proactive decision-making and seizes opportunities, while stalling strategically delays actions to gather information and wait for optimal conditions. Effective leadership harnesses the power of both approaches by recognizing when to act decisively and when to exercise restraint, ensuring adaptive and tactical responses to evolving challenges.
Expert Tips to Manage Aggression and Prevent Stalling
Expert tips to manage aggression and prevent stalling include maintaining a balanced pace with consistent effort and clear goals to avoid overwhelming stress. Monitoring emotional triggers and practicing mindfulness techniques can help control impulsive reactions while fostering productive communication. Implementing structured routines and allowing for strategic pauses ensures progress without unnecessary delays or conflict escalation.
Aggression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com