Engagement drives meaningful interactions between brands and their audience, fostering loyalty and long-term relationships. High engagement rates indicate that your content resonates, encouraging customers to take action and share their experiences. Discover effective strategies to boost engagement and connect deeply with your target market in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
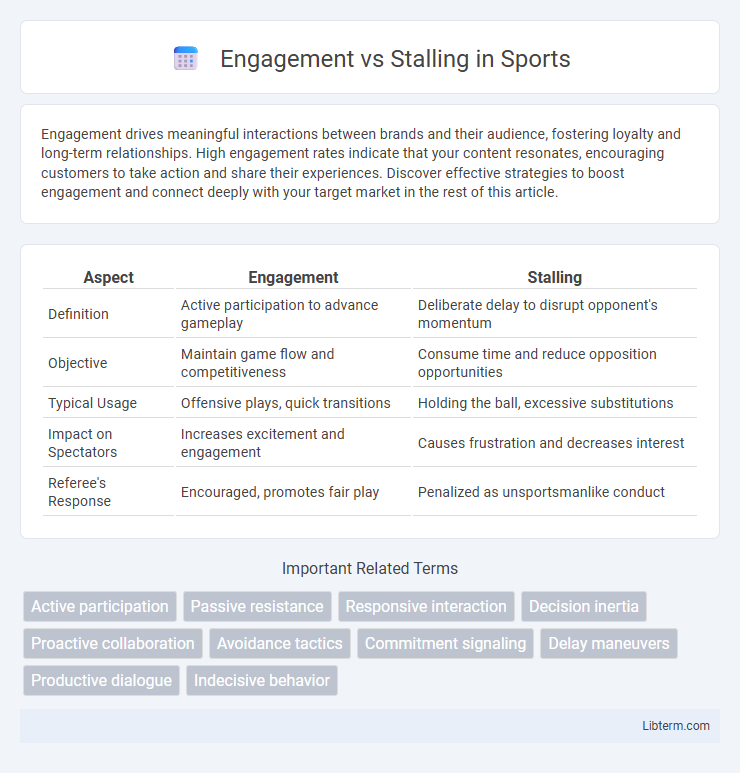
| Aspect | Engagement | Stalling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active participation to advance gameplay | Deliberate delay to disrupt opponent's momentum |
| Objective | Maintain game flow and competitiveness | Consume time and reduce opposition opportunities |
| Typical Usage | Offensive plays, quick transitions | Holding the ball, excessive substitutions |
| Impact on Spectators | Increases excitement and engagement | Causes frustration and decreases interest |
| Referee's Response | Encouraged, promotes fair play | Penalized as unsportsmanlike conduct |
Defining Engagement and Stalling
Engagement refers to active participation, emotional investment, and focused attention in a task or interaction, leading to productive outcomes and meaningful connections. Stalling involves delaying tactics, avoidance behaviors, or procrastination that hinder progress and reduce effectiveness. Understanding the distinction helps optimize motivation and time management in personal and professional settings.
Key Differences Between Engagement and Stalling
Engagement involves active participation and meaningful interaction, while stalling is characterized by delaying tactics without productive contribution. In conversations or meetings, engagement fosters progress through responsiveness and genuine input, whereas stalling relies on avoidance and deflection to impede decision-making. Key differences include intent, outcome, and level of involvement, with engagement driving forward momentum and stalling causing stagnation.
Psychological Drivers Behind Engagement and Stalling
Engagement is driven by intrinsic motivation, curiosity, and a sense of competence, which activate reward centers in the brain and enhance cognitive focus. Stalling often results from psychological barriers such as fear of failure, anxiety, and low self-efficacy that trigger avoidance behaviors and activation of the amygdala. Understanding these neuropsychological mechanisms helps tailor interventions that promote productive engagement and reduce procrastination.
Impacts of Engagement on Relationships
Engagement fosters trust, deepens emotional connection, and promotes effective communication in relationships, creating a foundation for mutual understanding and support. Active participation and genuine interest reduce conflicts and enhance satisfaction by addressing concerns promptly and collaboratively. In contrast, stalling leads to frustration, emotional distance, and unresolved issues, undermining relationship stability and growth.
Consequences of Stalling in Communication
Stalling in communication often leads to misunderstandings and decreased trust between parties, undermining the effectiveness of interactions. It can cause frustration, reduced collaboration, and lost opportunities for timely decision-making and problem-solving. Persistent stalling may damage relationships and hinder the achievement of common goals by creating barriers to open and honest dialogue.
Signals of Genuine Engagement
Signals of genuine engagement include consistent eye contact, active listening through nodding or verbal affirmations, and responsive body language that mirrors the speaker's emotions. Genuine engagement is marked by thoughtful questions and relevant contributions that indicate attention and understanding. In contrast, stalling behaviors such as distracted glances, fidgeting, or delayed responses suggest a lack of authentic interest.
Warning Signs of Stalling Behavior
Stalling behavior often manifests through repeated delays, avoidance of decision-making, and consistent postponement of commitments, serving as key warning signs. Individuals exhibiting engagement typically demonstrate proactive communication, responsiveness, and willingness to address challenges timely. Recognizing stalled interactions early can prevent project setbacks, improve collaboration, and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
Strategies to Promote Engagement
Effective strategies to promote engagement include interactive content, personalized communication, and timely feedback. Utilizing data-driven insights to tailor experiences enhances user involvement and motivation. Implementing gamification and collaborative activities fosters active participation and reduces stalling behaviors.
Overcoming Stalling: Practical Approaches
Overcoming stalling involves identifying underlying causes such as fear, lack of clarity, or resource constraints and addressing them with targeted strategies like time management techniques, goal setting, and accountability partnerships. Implementing iterative progress tracking and breaking tasks into manageable steps can reduce overwhelm and increase momentum. Leveraging cognitive-behavioral approaches and maintaining motivation through rewards or social support enhances sustained engagement and reduces procrastination.
Long-Term Outcomes: Engagement vs Stalling
Engagement fosters long-term outcomes by promoting sustained commitment, skill development, and meaningful progress toward goals, which enhances overall success and satisfaction. Stalling often leads to missed opportunities, decreased motivation, and the accumulation of unresolved challenges, hindering growth and productivity over time. Prioritizing active engagement ensures continuous improvement and positive trajectory in both personal and professional contexts.
Engagement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com