Butterfly Save is a revolutionary goalkeeping technique that enhances agility and reaction time, allowing goalkeepers to cover more ground and make crucial saves during high-pressure moments. This method focuses on quick lateral movements and low body positioning to maximize reach and control. Discover how Butterfly Save can transform your goalkeeping skills by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
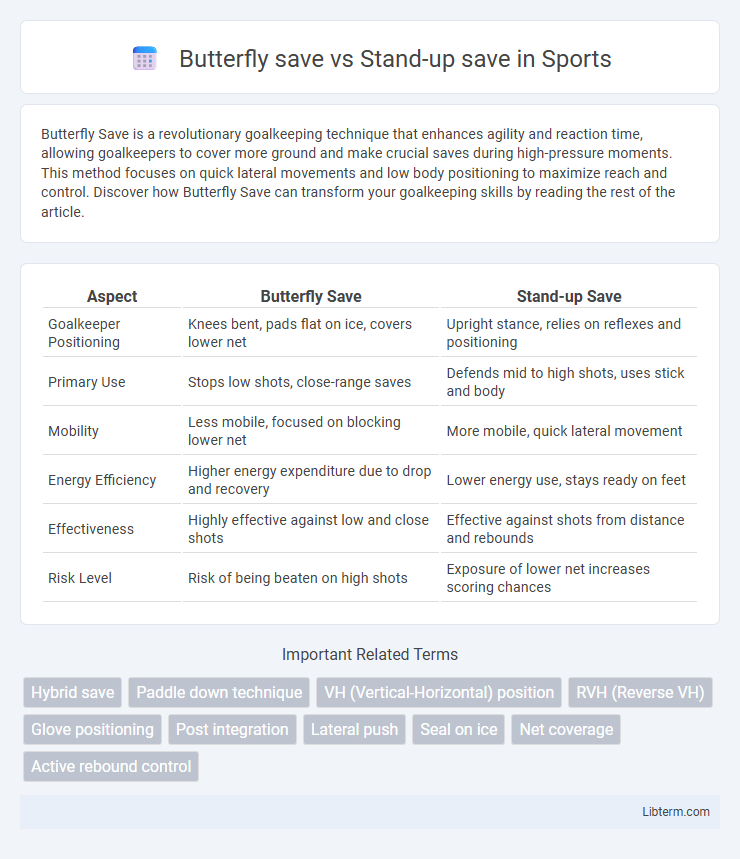
| Aspect | Butterfly Save | Stand-up Save |
|---|---|---|
| Goalkeeper Positioning | Knees bent, pads flat on ice, covers lower net | Upright stance, relies on reflexes and positioning |
| Primary Use | Stops low shots, close-range saves | Defends mid to high shots, uses stick and body |
| Mobility | Less mobile, focused on blocking lower net | More mobile, quick lateral movement |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher energy expenditure due to drop and recovery | Lower energy use, stays ready on feet |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective against low and close shots | Effective against shots from distance and rebounds |
| Risk Level | Risk of being beaten on high shots | Exposure of lower net increases scoring chances |
Introduction to Butterfly Save vs Stand-Up Save
Butterfly save and stand-up save are two fundamental goaltending techniques used in ice hockey to block shots effectively. The butterfly save involves dropping to the knees with pads spread out to cover the lower part of the net, optimizing coverage of low shots. The stand-up save relies on maintaining an upright posture to react quickly to high shots, providing greater mobility and vision of the play.
Historical Evolution of Goaltending Techniques
The historical evolution of goaltending techniques reflects a shift from stand-up saves, dominant in the early 20th century, to the butterfly save emerging in the 1960s and gaining widespread adoption by the 1990s. Stand-up goaltenders relied on positioning and quick reflexes to block shots while remaining upright, whereas the butterfly technique emphasizes dropping to the knees with pads spread to cover the lower net, improving save percentage on low shots. Innovations by goalies like Glenn Hall popularized the butterfly style, revolutionizing goaltending strategies and influencing modern training and equipment design.
Key Differences Between Butterfly and Stand-Up Saves
The Butterfly save technique involves a goaltender dropping to their knees with pads flared out to cover the lower part of the net, effectively blocking low shots and forcing opponents to aim higher. In contrast, the Stand-up save maintains an upright position, relying on quick reflexes and stick work to deflect shots while preserving mobility to react to rebounds and high shots. Key differences include the Butterfly save's emphasis on blocking the lower net area versus the Stand-up save's focus on vertical agility and positioning for mid-to-high shot coverage.
Mechanics of the Butterfly Save
The mechanics of the butterfly save involve the goalie dropping to their knees while flaring their leg pads outward to cover the lower portion of the net, creating a wide barrier against low shots. This position maximizes surface area contact and allows for quick lateral movements to block rebounds or follow-up attempts. In contrast, the stand-up save relies on remaining upright to react to shots at various heights but offers less coverage of the lower net compared to the butterfly technique.
Mechanics of the Stand-Up Save
The mechanics of the Stand-up save emphasize a goaltender staying on their feet to maximize mobility and vision, allowing quick lateral movements and efficient puck tracking. This technique relies on the goalie maintaining a strong, balanced stance with knees slightly bent, weight distributed evenly, and hands positioned to react swiftly to shots. Unlike the Butterfly save, which requires dropping to the knees and sealing the lower net, the Stand-up save prioritizes upright positioning to cover high shots and rebounds effectively.
Situational Effectiveness: When to Use Each Save
Butterfly save excels in situations demanding low shots to the bottom corners, effectively blocking fast, low-angle attempts during breakaways and close-range attacks. Stand-up saves perform best against high shots and when maintaining mobility is crucial, allowing goalies to react quickly to rebounds or lateral passes. Choosing between butterfly and stand-up saves depends on the shot's height, angle, and the need for quick positional adjustments in dynamic game scenarios.
Pros and Cons of Butterfly Save
The Butterfly save technique in hockey offers superior coverage of the lower net area by dropping to the knees, making it highly effective against low shots and fast, close-range attempts. Pros include quick lateral movement and reduced rebound control, enhancing shot-blocking precision in the goal crease. However, its cons are limited upper-body coverage and increased vulnerability to high or wrist shots, requiring exceptional agility and positional awareness from the goaltender.
Pros and Cons of Stand-Up Save
The Stand-Up save technique offers better visibility and mobility for goaltenders, allowing quicker reactions to high shots and improved puck control during rebounds. However, it can be less effective against low shots and offers less net coverage compared to the Butterfly save, increasing the risk of goals along the ice. While Stand-Up saves favor agility and positioning, they may leave goaltenders more vulnerable to modern offensive strategies that exploit low shot opportunities.
Impact on Modern Goaltending Styles
The Butterfly save revolutionized modern goaltending by emphasizing low positioning and pad coverage, leading to enhanced net protection against low shots. In contrast, the Stand-up save centers on maintaining an upright posture, allowing quicker lateral mobility and better visibility but often leaving lower net areas vulnerable. Contemporary goaltenders increasingly integrate Butterfly techniques with selective Stand-up maneuvers to optimize reaction time and coverage, shaping hybrid styles in elite hockey leagues.
Training Tips for Mastering Both Saves
Mastering butterfly save techniques requires consistent leg strength training and flexibility exercises to enhance lateral movement and quick drop timing. Stand-up saves demand sharp hand-eye coordination and rapid reaction drills to improve upright positioning and glove control. Combining plyometric workouts with focused rebound control practice ensures goalkeepers excel in both butterfly and stand-up save styles, optimizing overall net coverage.
Butterfly save Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com