The away side refers to the opposing team's location in sports events, typically indicating the team playing on the road. Understanding the dynamics of the away side can offer insights into team performance and strategies during away games. Explore the rest of the article to discover how the away side influences game outcomes and what it means for your favorite teams.
Table of Comparison
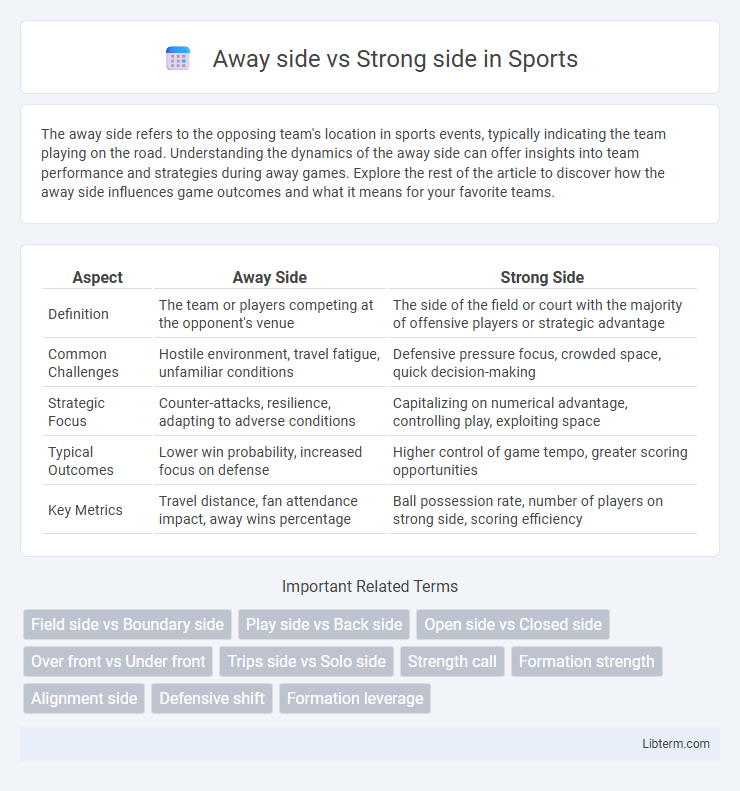
| Aspect | Away Side | Strong Side |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The team or players competing at the opponent's venue | The side of the field or court with the majority of offensive players or strategic advantage |
| Common Challenges | Hostile environment, travel fatigue, unfamiliar conditions | Defensive pressure focus, crowded space, quick decision-making |
| Strategic Focus | Counter-attacks, resilience, adapting to adverse conditions | Capitalizing on numerical advantage, controlling play, exploiting space |
| Typical Outcomes | Lower win probability, increased focus on defense | Higher control of game tempo, greater scoring opportunities |
| Key Metrics | Travel distance, fan attendance impact, away wins percentage | Ball possession rate, number of players on strong side, scoring efficiency |
Introduction to Away Side vs Strong Side
The concepts of Away Side and Strong Side are fundamental in basketball strategy, where the Strong Side refers to the side of the court with the ball and offensive action, often featuring more players and plays designed to create scoring opportunities. In contrast, the Away Side, or Weak Side, is the opposite side of the court with fewer offensive players, used strategically for spacing, cutting, and potential passing options to exploit defensive weaknesses. Understanding the dynamics between the Away Side and Strong Side allows teams to optimize ball movement, player positioning, and overall offensive efficiency.
Defining Away Side and Strong Side
The away side refers to the defensive alignment opposite the strong side of the offensive formation, typically where fewer offensive players are positioned. The strong side is identified by the presence of the tight end or the side with more offensive personnel, creating a heavier concentration of blockers or receivers. Understanding the distinction between the away side and strong side is crucial for defensive schemes and matchups in football strategy.
Tactical Importance in Sports Strategy
Away side and strong side distinctions are critical for spatial awareness and player positioning in sports strategy, particularly in basketball and football. The strong side, where the ball is located, demands concentrated defensive pressure and offensive support to capitalize on scoring opportunities, while the away side requires strategic covering to prevent fast breaks and weak-side attacks. Effective management of these zones enhances team dynamics, optimizes ball movement, and disrupts opponent formations.
Key Differences Between Away Side and Strong Side
The key difference between the away side and strong side in sports like football lies in their positioning relative to the ball and the offensive formation; the strong side usually includes the side with the tight end or more offensive players, creating a numerical advantage. The away side, often called the weak side, is opposite the strong side and typically has fewer blockers or receivers, influencing defensive matchups and coverage strategies. Understanding these distinctions helps teams optimize blocking schemes, defensive alignments, and passing attacks by exploiting or protecting vulnerabilities on each side of the field.
Advantages of Utilizing the Strong Side
Utilizing the strong side in offensive basketball improves scoring opportunities by aligning teammates on the side with the ball, creating better spacing and driving lanes. This positioning maximizes defensive pressure, forcing opponents to collapse and opening up perimeter shots. Strong side play amplifies ball movement efficiency, leading to higher percentage shots and increased offensive rhythm.
Benefits of Attacking the Away Side
Attacking the away side exploits defensive imbalances by targeting the weaker or less prepared side of the field, creating opportunities for quick, high-percentage plays. It forces defenders to rotate and adjust, often opening up passing lanes and space for shooters or driving lanes for attackers. Teams that efficiently attack the away side increase their scoring chances through improved ball movement and reduced defensive pressure.
Defensive Adjustments: Away Side vs Strong Side
Defensive adjustments between the away side and strong side involve shifting coverage to counter the offensive formation's strengths and ball location. On the strong side, defenses typically allocate more personnel, such as linebackers and safeties, to cover tight ends and receivers aligned with the offense's formation, enhancing run support and pass coverage. Conversely, away side adjustments focus on maintaining zone integrity and pass rush lanes, often requiring defensive backs to anticipate crossing routes and maintain deeper coverage responsibilities.
Common Mistakes in Side Selection
Common mistakes in side selection between the away side and strong side include misjudging player positioning and failing to account for the opponent's defensive setup, leading to ineffective ball distribution and missed scoring opportunities. Ignoring the spatial dynamics often results in overloading one side while leaving the other vulnerable, disrupting team balance and reducing offensive efficiency. Correctly identifying and adapting to the opponent's formation and in-game adjustments is crucial to avoid these pitfalls in side selection.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
In basketball, the strong side refers to the half of the court with the ball, while the away side is the opposite, without the ball. Real-world examples from NBA games illustrate how teams exploit the strong side for high-percentage plays, such as the Golden State Warriors utilizing their strong side spacing for Stephen Curry's three-point shots. Case studies from college basketball highlight defensive strategies focused on the away side, like the University of Virginia's pack-line defense that limits penetration and forces opponents to make low-quality shots away from the ball.
Conclusion: Maximizing Performance through Side Awareness
Maximizing performance in basketball requires a keen understanding of the differences between the away side and strong side of the court, as each influences offensive and defensive strategies uniquely. Players who develop side awareness can exploit the strong side's advantage for scoring opportunities while effectively using the away side to create spacing and passing lanes. Strategic side awareness enhances decision-making, improves team spacing, and ultimately leads to higher efficiency and success during gameplay.
Away side Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com