The weak side in various contexts often refers to the less dominant or vulnerable position that requires strategic attention to improve performance or security. Understanding your weak side allows you to address potential risks and enhance overall effectiveness. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips for strengthening your weak side and turning it into an advantage.
Table of Comparison
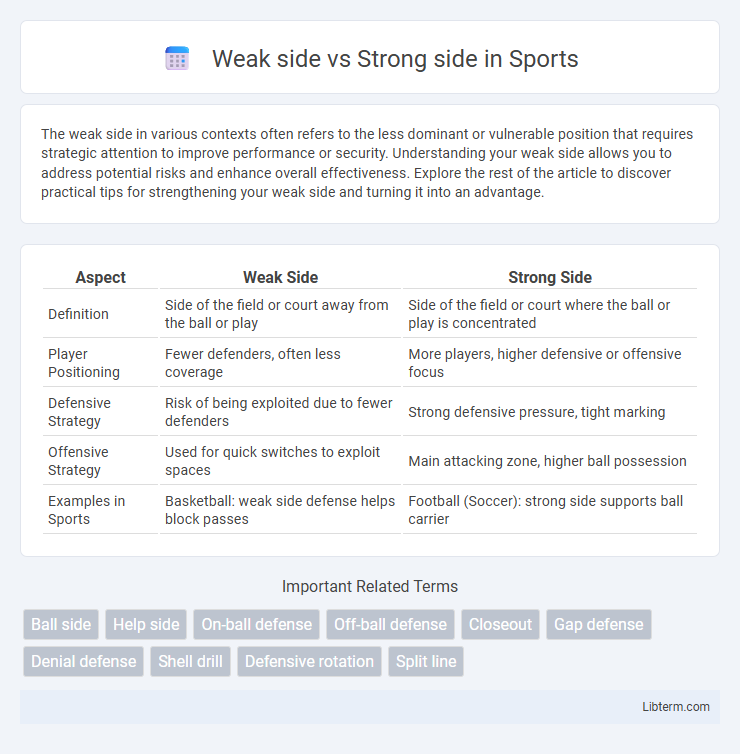
| Aspect | Weak Side | Strong Side |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Side of the field or court away from the ball or play | Side of the field or court where the ball or play is concentrated |
| Player Positioning | Fewer defenders, often less coverage | More players, higher defensive or offensive focus |
| Defensive Strategy | Risk of being exploited due to fewer defenders | Strong defensive pressure, tight marking |
| Offensive Strategy | Used for quick switches to exploit spaces | Main attacking zone, higher ball possession |
| Examples in Sports | Basketball: weak side defense helps block passes | Football (Soccer): strong side supports ball carrier |
Understanding Weak Side vs Strong Side
Understanding weak side vs strong side in sports like basketball and football is crucial for strategic gameplay, where the strong side refers to the side with the ball or most offensive activity, and the weak side is the opposite, often less defended. Defensive players position themselves to anticipate passes and movements, exploiting the weak side to create turnovers or block scoring opportunities. Recognizing these dynamics optimizes team formations and enhances both offensive drives and defensive coverage.
Key Differences Between Weak Side and Strong Side
The strong side in basketball refers to the side of the court where the ball is located, typically featuring more offensive players and creating greater scoring opportunities, while the weak side is the opposite side, often less crowded and used strategically for spacing and defensive rotations. Key differences include player positioning, with the strong side emphasizing ball handling and post play, and the weak side prioritizing cuts, screens, and perimeter shooting to balance the offense. Defensively, the strong side demands more immediate pressure on the ball handler, whereas the weak side defenders focus on help defense and anticipating passes.
Importance of Identifying Strong and Weak Sides
Identifying strong and weak sides in basketball is crucial for optimizing offensive and defensive strategies, allowing players to exploit mismatches and enhance team coordination. Recognizing the strong side, where the ball is and most players align, helps in creating effective scoring opportunities, while awareness of the weak side aids in defensive positioning and preventing easy passes or cuts. Coaches leverage this understanding to design plays that maximize team strengths and minimize vulnerabilities, ultimately improving overall performance and game control.
Advantages of Utilizing the Strong Side
Utilizing the strong side in basketball leverages the natural alignment of the offensive players, creating optimal spacing and passing lanes that enhance scoring opportunities. Defenders are forced to adjust and often overcommit, allowing for easier ball movement and driving lanes. This strategic advantage increases offensive efficiency by maximizing team strengths and minimizing defensive pressure.
When to Rely on the Weak Side
Rely on the weak side in defense when opponents heavily commit to the strong side, creating gaps and opportunities for quick rotations and interceptions. In basketball, weak side defenders must anticipate cuts and passes, exploiting unguarded lanes to disrupt offensive plays. Leveraging weak side positioning enhances overall team flexibility and counters strong side pressure effectively.
Common Mistakes with Side Dominance
Common mistakes with side dominance in basketball often include over-reliance on the strong side, leading to predictability and limited offensive versatility. Players frequently neglect the weak side, reducing opportunities for effective spacing, off-ball movement, and defensive balance. Developing ambidexterity and awareness on both sides enhances overall performance and prevents exploitability by opponents.
Training Techniques to Strengthen the Weak Side
Targeted unilateral exercises such as single-arm dumbbell presses and single-leg squats enhance muscle activation on the weak side, promoting balanced strength development. Incorporating resistance bands and slow eccentric movements helps correct neuromuscular imbalances by increasing time under tension for the weaker muscles. Consistent training with progressive overload and focused attention on form improves coordination and reduces injury risk on the underperforming side.
Strategic Applications in Sports and Fitness
Weak side and strong side concepts are critical in strategic applications within sports and fitness, influencing player positioning and movement efficiency. Coaches leverage weak side recognition to exploit defensive gaps and create scoring opportunities by directing plays toward less guarded zones, while strong side alignment maximizes power and stability for offensive or defensive maneuvers. Understanding these dynamics enhances performance by optimizing spatial awareness, improving tactical decisions, and preventing injury through balanced muscular development.
Adapting Tactics: Balancing Weak and Strong Sides
Adapting tactics involves leveraging the strong side's advantages while mitigating vulnerabilities on the weak side to maintain overall strategic balance. Effective balance requires flexible resource allocation, continuous assessment of strengths and weaknesses, and real-time adjustments to exploit opportunities on the strong side without exposing the weak side. This dynamic approach improves resilience, optimizes performance, and ensures that neither side becomes a critical liability during execution.
Enhancing Performance Through Side Awareness
Recognizing the weak side and strong side in athletic performance allows targeted training interventions that improve muscle balance, coordination, and stability. Emphasizing side-specific exercises enhances neuromuscular control and prevents injury by correcting asymmetries in strength and movement patterns. Optimizing side awareness contributes to overall athletic efficiency, leading to better functional outcomes and peak performance.
Weak side Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com