A split stance enhances stability and balance during dynamic movements by positioning one foot forward and the other back, mimicking a natural athletic posture. This technique engages core muscles and improves power transfer in exercises such as lunges, kettlebell swings, and various combat sports stances. Discover how incorporating a split stance can transform Your training and performance by exploring the detailed benefits and techniques in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
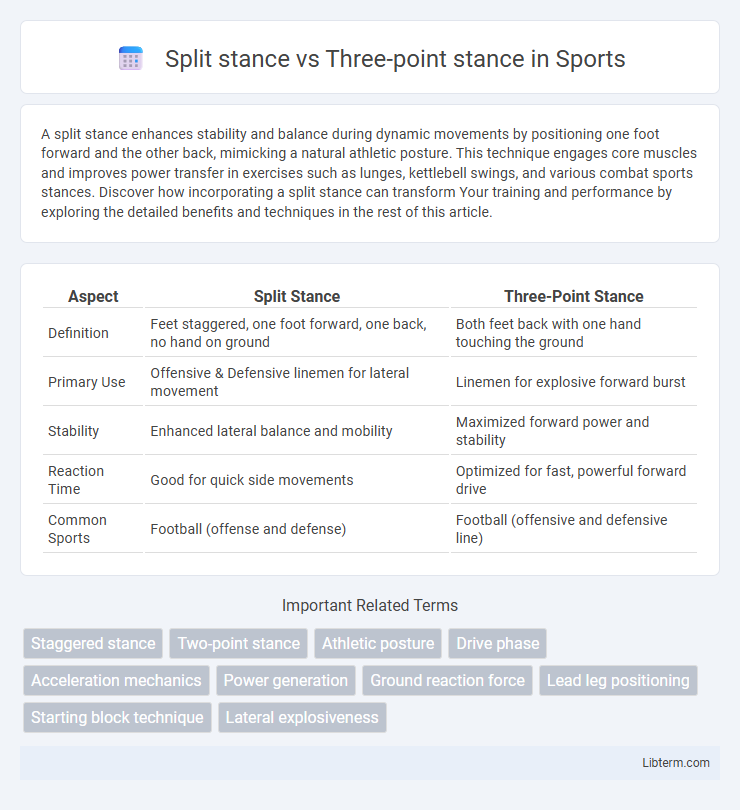
| Aspect | Split Stance | Three-Point Stance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Feet staggered, one foot forward, one back, no hand on ground | Both feet back with one hand touching the ground |
| Primary Use | Offensive & Defensive linemen for lateral movement | Linemen for explosive forward burst |
| Stability | Enhanced lateral balance and mobility | Maximized forward power and stability |
| Reaction Time | Good for quick side movements | Optimized for fast, powerful forward drive |
| Common Sports | Football (offense and defense) | Football (offensive and defensive line) |
Understanding Split Stance and Three-Point Stance
The split stance involves placing one foot forward and the other back, providing balance and mobility for quick lateral movements, commonly used in basketball and volleyball. The three-point stance requires one hand on the ground with both feet positioned for explosive forward power, often employed in American football by linemen. Understanding these stances is crucial for optimizing performance in sports that demand different types of agility and force generation.
Key Differences Between Split and Three-Point Stances
The split stance positions the feet shoulder-width apart with weight evenly distributed, emphasizing balance and readiness for lateral movement, while the three-point stance places one hand on the ground, creating a lower center of gravity for explosive forward starts. Split stance allows quicker transitions between movements due to its upright posture, whereas the three-point stance provides enhanced power and leverage during initial bursts off the line. Athletes often select the split stance for agility and responsiveness, contrasting with the three-point stance's focus on strength and forward momentum in football and similar sports.
Biomechanical Advantages of Split Stance
The split stance optimizes lower body power by allowing greater hip and knee flexion, which enhances force generation and balance during explosive movements. This stance promotes a more stable center of gravity compared to the three-point stance, reducing reaction time and improving initial burst speed. Athletes employing the split stance benefit from improved weight distribution, enabling quicker directional changes and better overall agility.
Power Generation in Three-Point Stance
The three-point stance maximizes power generation by allowing players to engage more muscles in the legs, hips, and core, creating explosive forward momentum at the snap. Its lower center of gravity and tighter body alignment enable a quicker, more forceful drive off the line of scrimmage compared to the split stance. This stance is preferred in positions requiring rapid bursts of strength, such as offensive and defensive linemen in football.
Sports Applications: When to Use Each Stance
Athletes utilize the split stance in sports requiring quick lateral movements and agility, such as basketball and soccer, for enhanced balance and rapid directional changes. The three-point stance is favored in football, particularly among linemen, for powerful forward bursts and stability during contact. Choosing between these stances depends on game demands: split stance for agility and reactive positioning, three-point stance for explosive power and leverage on the line.
Impact on Speed and Acceleration
The split stance enhances initial acceleration by allowing quicker weight transfer and explosive forward movement, making it ideal for athletes requiring rapid bursts of speed. The three-point stance provides a lower center of gravity and greater stability, which can improve power generation but may slightly delay initial acceleration compared to the split stance. Speed in short sprints benefits more from the split stance's quick engagement, while sustained power output is often better supported by the three-point stance.
Injury Risk and Safety Considerations
Split stance offers greater stability and balance, reducing the likelihood of ankle and knee injuries by distributing weight evenly across both legs. In contrast, the three-point stance places more stress on the lead arm and shoulder, increasing the risk of upper limb strain and impact-related injuries, especially in contact sports. Proper technique and conditioning are essential in both stances to minimize injury risk and enhance athlete safety during dynamic movements.
Coaching Tips for Mastering Each Stance
Coaches emphasize balance and foot positioning when teaching the split stance, ensuring players maintain a wide base for quick lateral movement and immediate power off the line. In the three-point stance, focus on hand placement and hip alignment to maximize leverage and explosiveness at the snap. Drills targeting reaction time and lower body strength are essential for mastering both stances and enhancing overall performance on the field.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common mistakes in split stance include improper foot alignment and uneven weight distribution that reduce balance and power output; correcting these involves maintaining feet shoulder-width apart and centering weight evenly. In three-point stance, errors often involve incorrect hand placement and poor body positioning, which limit explosiveness; avoiding these requires placing the hand firmly on the ground with hips aligned slightly higher than shoulders. Proper coaching cues and consistent practice are essential for mastering stance mechanics and maximizing performance in both techniques.
Choosing the Right Stance for Optimal Performance
Choosing the right stance between split stance and three-point stance directly impacts agility and power in football players. The split stance offers enhanced lateral movement and quick directional changes, ideal for receivers and defensive backs, while the three-point stance maximizes explosive forward momentum, benefiting linemen and linebackers. Matching the stance to position-specific demands optimizes performance by improving balance, reaction time, and force generation during play.
Split stance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com