Push-to-pass technology temporarily boosts engine performance, providing extra power during overtaking maneuvers or critical racing moments. This system enhances acceleration by increasing fuel flow or activating electric boost, giving drivers a competitive edge on the track. Explore the full article to understand how push-to-pass can improve your driving strategy.
Table of Comparison
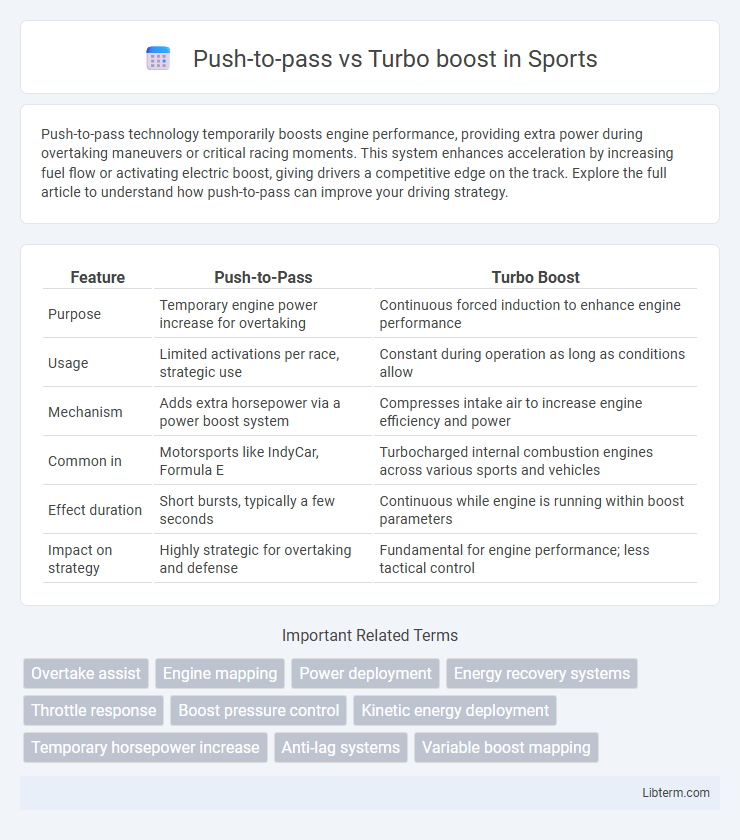
| Feature | Push-to-Pass | Turbo Boost |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Temporary engine power increase for overtaking | Continuous forced induction to enhance engine performance |
| Usage | Limited activations per race, strategic use | Constant during operation as long as conditions allow |
| Mechanism | Adds extra horsepower via a power boost system | Compresses intake air to increase engine efficiency and power |
| Common in | Motorsports like IndyCar, Formula E | Turbocharged internal combustion engines across various sports and vehicles |
| Effect duration | Short bursts, typically a few seconds | Continuous while engine is running within boost parameters |
| Impact on strategy | Highly strategic for overtaking and defense | Fundamental for engine performance; less tactical control |
Introduction to Push-to-Pass and Turbo Boost
Push-to-Pass and Turbo Boost are performance-enhancing features used primarily in motorsports and computing, respectively. Push-to-Pass provides drivers with a temporary increase in engine power to facilitate overtaking during races, often by injecting extra fuel or adjusting boost pressure in turbocharged engines. Turbo Boost, commonly associated with CPUs, dynamically increases processor clock speed above the base frequency to enhance performance under demanding workloads without overheating.
Historical Evolution of Racing Power Enhancements
Push-to-pass systems emerged in the early 2000s as a strategic racing power enhancement, offering temporary horsepower boosts through electronic fuel and ignition control adjustments, primarily in IndyCar and Formula E. Turbo boost technology dates back to the 1960s, revolutionizing racing by increasing engine air intake pressure to significantly elevate power output, exemplified by Formula 1's turbo era in the 1980s. The evolution from mechanical turbochargers to sophisticated electronic push-to-pass controls illustrates the shift towards precision power management, optimizing overtaking opportunities and race strategy in modern motorsports.
Core Mechanisms: How Push-to-Pass Works
Push-to-pass enhances engine power by temporarily increasing fuel flow and adjusting turbocharger settings to boost acceleration in racing cars. This system bypasses standard engine mapping, providing an extra surge of horsepower for limited periods, crucial in overtaking scenarios. Turbo boost, by comparison, continuously controls air pressure in the intake manifold via the turbocharger to improve overall engine efficiency and power output.
Turbo Boost: Technology and Functionality
Turbo Boost technology dynamically increases the clock speed of a processor's cores to enhance performance during demanding tasks by automatically adjusting based on workload and thermal conditions. It improves computing efficiency by providing extra performance power without user intervention, optimizing power consumption while maintaining system stability. Unlike push-to-pass systems in engines or racing, Turbo Boost is a semiconductor-based performance enhancement designed specifically for CPU cores in modern processors.
Key Differences: Strategy and Usage
Push-to-pass systems provide temporary power boosts mainly in race cars to enhance overtaking by increasing engine output for short durations, often activated by the driver through a button. Turbo boost adjusts the engine's air pressure via a turbocharger, improving overall engine efficiency and sustained power output rather than short bursts, and is typically managed automatically by the vehicle's control system. The key difference lies in push-to-pass being a strategic, driver-controlled feature for critical moments, whereas turbo boost offers continuous performance enhancement through mechanical and electronic controls.
Impact on Race Performance
Push-to-pass systems temporarily increase engine power, providing drivers with short bursts of acceleration that can be strategically used for overtaking or defending position during a race, significantly impacting race dynamics and lap times. Turbo boost enhances engine performance by increasing air intake pressure, delivering sustained power improvements that improve overall speed and efficiency throughout a race. Both technologies influence race performance by optimizing power delivery, but push-to-pass offers tactical advantages while turbo boost contributes to consistent race pace.
Driver Experience and Tactical Considerations
Push-to-pass systems provide drivers with a temporary power increase, enhancing overtaking opportunities by delivering instant throttle response without turbo lag. Turbo boost relies on manipulating turbocharger pressure to increase engine power, offering sustained performance improvements but requiring careful management to avoid overheating or engine stress. Drivers must strategically balance push-to-pass usage for short bursts in critical moments, while turbo boost demands tactical decisions over race duration to maintain optimal performance and reliability.
Regulations and Limitations in Motorsport
Push-to-pass systems in motorsport provide temporary power boosts regulated by strict usage limits and duration defined by race officials to ensure fairness. Turbo boost involves increasing the turbocharger's pressure, but regulations cap maximum boost levels to prevent engine damage and maintain competitive balance. Both technologies face constraints in FIA Formula 1 and World Endurance Championship, with push-to-pass more common in IndyCar and turbo limitations strictly enforced across all turbocharged series.
Fan Engagement and Entertainment Factor
Push-to-pass systems enhance fan engagement by providing drivers with temporary bursts of extra power, creating dynamic overtaking opportunities that increase race excitement and unpredictability. Turbo boost, while primarily focused on engine performance, indirectly supports entertainment by enabling faster acceleration and higher speeds, but lacks the tactical element that push-to-pass introduces to driving strategy. The interactive nature of push-to-pass encourages fan involvement by highlighting strategic use during critical race moments, making it a more engaging feature for audiences compared to the constant, passive benefits of turbo boost.
Future Trends in Racing Power Technologies
Push-to-pass and turbo boost technologies are evolving toward greater integration of energy recovery systems and electrification to enhance power delivery and efficiency in racing. Future trends emphasize hybrid powertrains combining internal combustion engines with electric motors to optimize push-to-pass systems, delivering instantaneous torque boosts without turbo lag. Advanced control algorithms and predictive analytics are also being developed to maximize strategic use of these power enhancements, improving lap times and fuel management in competitive motorsports.
Push-to-pass Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com