Reserve serves as a crucial financial buffer safeguarding your assets during unforeseen expenses or economic downturns. Building a robust reserve enhances stability and trustworthiness, whether for personal savings or business liquidity management. Explore the rest of this article to discover effective strategies for establishing and growing your reserves.
Table of Comparison
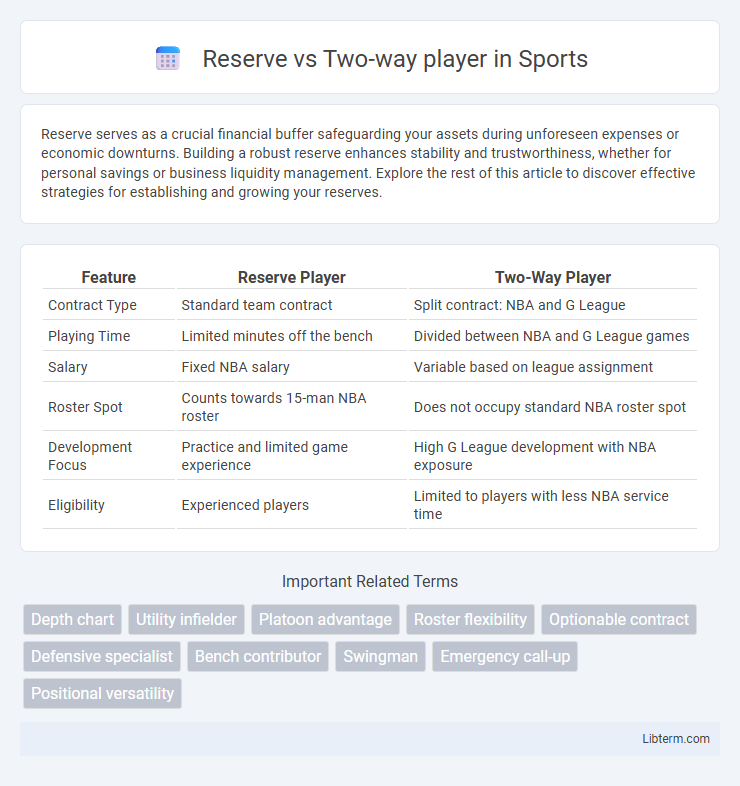
| Feature | Reserve Player | Two-Way Player |
|---|---|---|
| Contract Type | Standard team contract | Split contract: NBA and G League |
| Playing Time | Limited minutes off the bench | Divided between NBA and G League games |
| Salary | Fixed NBA salary | Variable based on league assignment |
| Roster Spot | Counts towards 15-man NBA roster | Does not occupy standard NBA roster spot |
| Development Focus | Practice and limited game experience | High G League development with NBA exposure |
| Eligibility | Experienced players | Limited to players with less NBA service time |
Introduction to Reserve and Two-Way Players
Reserve players serve as essential team assets, providing depth and flexibility by filling in during injuries or tactical adjustments. Two-way players uniquely contribute on both offense and defense, enhancing team dynamics through versatile skill sets that adapt to multiple positions. Understanding the distinct roles of reserves and two-way players helps optimize roster management and strategic game planning.
Definitions: Reserve Player vs Two-Way Player
A Reserve Player is a team member primarily designated to substitute for starters and provide depth, often limited to a single team's roster without additional assignment opportunities. A Two-Way Player holds a unique contract allowing them to play concurrently for both a Major League Baseball (MLB) team and its Minor League affiliate, facilitating development through flexible game time. This distinction emphasizes the Two-Way Player's role in maximizing playing opportunities across multiple competitive levels compared to the Reserve Player's singular team focus.
Historical Evolution of Player Roles
The historical evolution of player roles in sports highlights the transition from strictly defined reserve players to versatile two-way players who contribute both offensively and defensively. Early teams relied heavily on specialized reserves, but strategic shifts and rule changes encouraged the development of two-way players for greater flexibility and endurance. This evolution reflects broader trends in athletic training, game pace, and tactical complexity that continue to shape modern team dynamics.
Key Differences Between Reserve and Two-Way Designations
Reserve players are typically rostered on the main team but see limited playing time and can be activated or deactivated based on team needs, while two-way players split their time between the NBA and its G League affiliate with a contract allowing up to 50 NBA games. The primary distinction lies in the contract structure: reserve players hold standard NBA contracts, whereas two-way players have specialized agreements designed for development and flexibility. Two-way designations also impact salary and cap space differently, with two-way players earning a prorated salary based on their time in each league, contrasting with the fixed salary of reserves.
Contract Structures and Eligibility Rules
Reserve players typically have fixed, lower-salary contracts that guarantee roster spots but limit movement between major and minor leagues, while two-way players hold contracts allowing varying salaries depending on whether they play in the NHL or AHL, enhancing flexibility for team assignments. Eligibility rules for reserve players generally restrict them to a specific team roster status, whereas two-way contracts enable quicker transitions between leagues without waivers, optimizing salary cap management. These contract structures impact player development paths, team roster strategies, and salary cap considerations within professional hockey organizations.
Impact on Team Roster Management
Reserve players provide essential depth and flexibility, allowing coaches to manage fatigue, injuries, and mismatches across the season. Two-way players, capable of contributing significantly in multiple positions, enhance roster versatility by filling dual roles without occupying additional roster spots. This efficiency enables teams to maximize strategic deployment and maintain competitive balance under roster constraints.
Pros and Cons for Players and Teams
Reserve players provide teams with reliable depth and flexibility, allowing strategic rest for starters and reducing injury risks, but these players often face limited playing time that can hinder skill development and career growth. Two-way players offer versatility by contributing both offensively and defensively or across multiple positions, enhancing team adaptability and in-game adjustments, yet they may experience higher physical demands and inconsistent roles that affect performance consistency. For teams, reserves optimize roster management and injury contingencies, while two-way players enable tactical fluidity, but both require balancing player workload and potential impact on player specialization and long-term value.
Notable Examples in Professional Sports
Notable examples of reserve players excelling as two-way players include Shohei Ohtani in Major League Baseball, who dominates both as a pitcher and hitter, redefining roster versatility. In the NBA, LeBron James often serves as a reserve in his early years but evolved into a two-way player excelling on offense and defense, influencing team dynamics. Soccer's James Milner consistently functions as a utility player, showing reserve depth while contributing effectively in multiple positions.
Effects on Player Development and Career Progression
Reserve players often receive limited playing time, which can slow skill development and reduce exposure to high-pressure game situations essential for growth. Two-way players, alternating between major and minor leagues, benefit from consistent game experience at various competition levels, accelerating adaptability and skill refinement. This dual exposure enhances career progression by providing more opportunities to demonstrate value to teams, increasing chances for permanent roster spots and long-term contracts.
Future Trends in Reserve and Two-Way Roles
Reserve and two-way player roles are evolving to meet increasing demands for versatility and efficiency in professional sports. Advancements in analytics and player tracking technologies enable teams to optimize these roles by strategically deploying athletes who can perform in multiple positions or both offense and defense, enhancing roster flexibility. Future trends indicate a rise in hybrid players capable of adapting dynamically to game situations, driven by data-driven coaching and performance management systems.
Reserve Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com