A switch is a fundamental networking device that connects multiple devices within a local area network (LAN), enabling efficient data transfer by forwarding data only to the intended recipient device. By operating at the data link layer, switches reduce network congestion and improve overall performance compared to hubs. Explore the rest of the article to understand how switches enhance your network's speed and security.
Table of Comparison
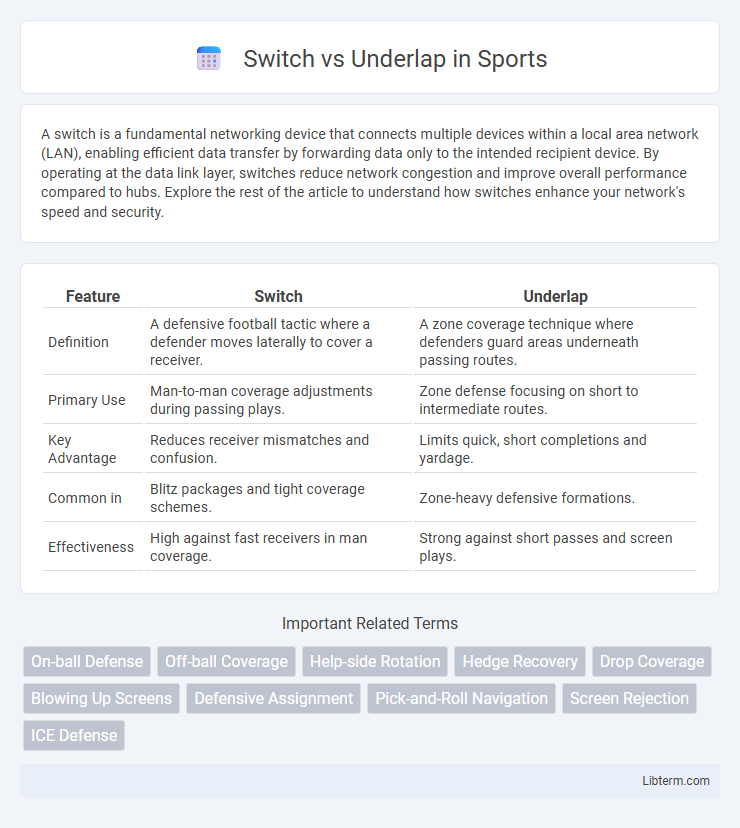
| Feature | Switch | Underlap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A defensive football tactic where a defender moves laterally to cover a receiver. | A zone coverage technique where defenders guard areas underneath passing routes. |
| Primary Use | Man-to-man coverage adjustments during passing plays. | Zone defense focusing on short to intermediate routes. |
| Key Advantage | Reduces receiver mismatches and confusion. | Limits quick, short completions and yardage. |
| Common in | Blitz packages and tight coverage schemes. | Zone-heavy defensive formations. |
| Effectiveness | High against fast receivers in man coverage. | Strong against short passes and screen plays. |
Introduction to Switch and Underlap Techniques
Switch and underlap techniques are essential strategies in design and manufacturing to assemble components efficiently and accurately. Switch refers to the intentional overlap and engagement of parts to ensure secure fitting and alignment, commonly used in electronic connectors and mechanical assemblies. Underlap involves designing components with slight gaps or reduced overlap to accommodate thermal expansion, tolerances, or ease of assembly without compromising structural integrity.
Fundamental Differences Between Switch and Underlap
Switch and underlap are critical concepts in semiconductor transistor design, primarily differentiated by their biasing conditions and current conduction properties. A switch operates by toggling between on and off states with significant current flow when on, controlled by a gate voltage that above threshold allows strong inversion in the channel. Underlap, in contrast, refers to the region where the gate does not fully cover the source or drain extensions, leading to reduced gate control and affecting short-channel effects, resulting in higher resistance and lower current drive in that partial overlap area.
Technical Definitions: Switch Explained
Switch refers to a networking device that connects multiple devices within a local area network (LAN) by using packet switching to forward data to the destination device based on MAC addresses. It operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model, efficiently managing traffic and reducing collisions by creating separate collision domains for each connected device. Switches improve network performance and security through features such as VLANs, port mirroring, and link aggregation.
Technical Definitions: Underlap Explained
Underlap refers to the intentional design choice where adjacent elements do not fully cover each other, leaving a visible gap or margin for spacing and structural purposes. In semiconductor design, underlap regions between the gate and source/drain reduce short-channel effects and improve device performance by controlling electric fields. Unlike switching functions that manage signal flow, underlap is crucial for optimizing transistor scalability and reliability through precise physical layout adjustments.
Applications of Switch in Modern Offense
Switch techniques in modern offensive basketball are employed to counter defensive pressure and create mismatches by exchanging defensive assignments during screens. This strategy enhances team flexibility, allowing faster ball movement and better spacing to exploit opponent weaknesses effectively. Coaches utilize switches to minimize defensive disruptions, maintaining offensive flow and increasing scoring opportunities in both half-court sets and transition play.
Applications of Underlap in Tactical Play
Underlap in tactical play, characterized by midfielders or wingers cutting inside behind the opposition's full-backs, enhances offensive unpredictability and passing options. This movement creates numerical superiority in central areas, facilitating quick combinations and penetrating passes critical in formations like 4-3-3 and 3-5-2. Unlike switch plays that exploit wide spaces, underlap strategies emphasize compactness and direct attacking lanes, proving effective in breaking organized defenses and maintaining ball retention under pressure.
Key Advantages of Using Switch
Switch technology enhances network efficiency by reducing data collision through dedicated communication paths, ensuring faster data transfer rates compared to underlap configurations. It offers improved bandwidth management by segmenting traffic and minimizing congestion in high-demand environments. Switches also provide enhanced security features, enabling better control over data flow and access within the network.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Underlap
Underlap offers the benefit of reducing interference and enhancing battery life in semiconductor devices by selectively increasing the gate-to-drain spacing, which lowers parasitic capacitance and leakage currents. However, drawbacks include potential performance degradation due to reduced gate control, leading to slower switching speeds and increased short-channel effects compared to conventional switches. Careful design optimization is required to balance underlap advantages with its impact on drive current and overall device efficiency.
Choosing Between Switch and Underlap: Tactical Considerations
Choosing between switch and underlap strategies in football hinges on the defensive alignment and offensive objectives. Switch aims to exploit man-to-man mismatches by swapping coverage responsibilities, ideal against zone defenses or when creating separation for receivers. Underlap focuses on short, quick routes inside the coverage, leveraging underused spaces and timing to neutralize aggressive cornerbacks and linebackers.
Conclusion: Which Method is Better for Your Team?
Choosing between switch and underlap methods depends on your team's communication style and project complexity; switch suits teams needing rapid feedback and dynamic collaboration, while underlap benefits those requiring deep focus and detailed work intervals. Analyzing your team's workflow, deadlines, and interaction preferences helps determine the optimal method. Prioritizing balance between collaboration and independent tasks will maximize productivity and team cohesion.
Switch Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com