Ace is a term used in various contexts, including sports, games, and aviation, symbolizing excellence and top performance. In tennis, an ace refers to a serve that the opponent fails to touch, showcasing skill and precision. Discover how mastering the concept of an ace can elevate your game by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
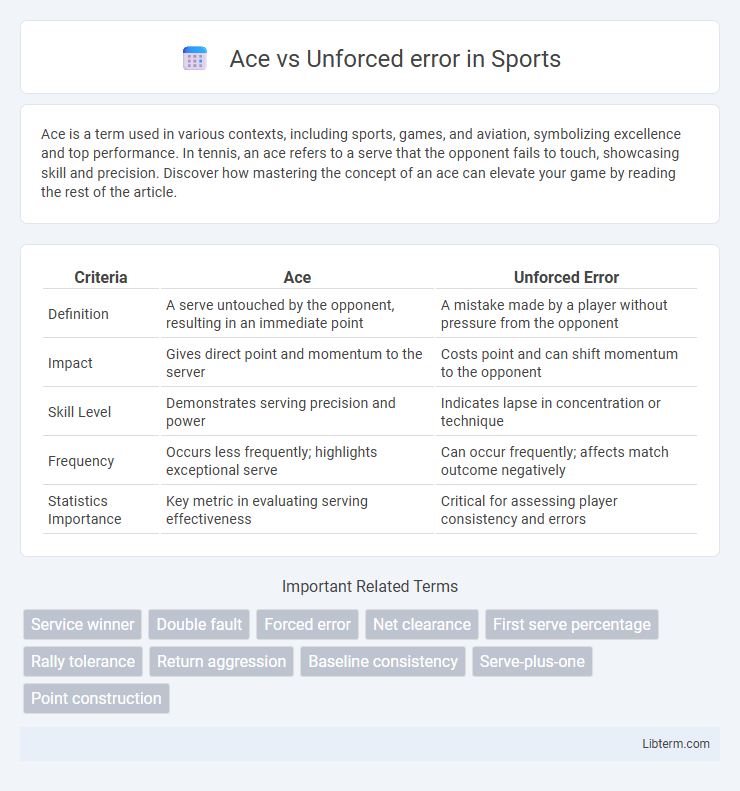
| Criteria | Ace | Unforced Error |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A serve untouched by the opponent, resulting in an immediate point | A mistake made by a player without pressure from the opponent |
| Impact | Gives direct point and momentum to the server | Costs point and can shift momentum to the opponent |
| Skill Level | Demonstrates serving precision and power | Indicates lapse in concentration or technique |
| Frequency | Occurs less frequently; highlights exceptional serve | Can occur frequently; affects match outcome negatively |
| Statistics Importance | Key metric in evaluating serving effectiveness | Critical for assessing player consistency and errors |
Ace vs Unforced Error: Key Differences Explained
An ace occurs when a player serves the ball and the opponent fails to touch it, demonstrating precision and power. An unforced error happens when a player makes a mistake during a rally without pressure from the opponent, reflecting lapses in focus or technique. Understanding these key differences helps analyze player performance by distinguishing between aggressive scoring and avoidable mistakes.
Definition of Ace in Tennis
An ace in tennis is a serve that lands in the opponent's service box and is untouched, meaning the opponent fails to make any contact with the ball. This is a clear point-winning shot, showcasing a player's serving precision and speed. Unlike an unforced error, which is a mistake made by a player without pressure from the opponent, an ace demonstrates offensive dominance rather than a fault.
What Constitutes an Unforced Error?
An unforced error in tennis occurs when a player makes a mistake on a shot without significant pressure from their opponent, such as hitting the ball into the net or out of bounds during a routine rally. This contrasts with an ace, which is a serve that the opponent cannot touch or return, resulting in an immediate point. Unforced errors reflect lapses in a player's precision or consistency, impacting match outcomes by providing easy points to the opposition.
Psychological Impact of Aces and Unforced Errors
Aces deliver a significant psychological boost to players, instilling confidence and applying pressure on opponents by demonstrating dominance during serve. Unforced errors, however, often trigger frustration and self-doubt, disrupting focus and momentum for the player who commits them. The contrasting mental effects of aces and unforced errors can swing match dynamics, influencing strategic adjustments and overall performance.
Tactical Importance of Aces in Matches
Aces serve as powerful tactical weapons in tennis, directly winning points while applying pressure on opponents to avoid aggressive returns, which can shift momentum in crucial stages of a match. By delivering accurate and high-speed serves that limit the opponent's reaction time, players exploit weaknesses in the opponent's service return, often forcing errors or passive shots. The strategic deployment of aces not only boosts a player's confidence but disrupts the opponent's rhythm, making it a critical factor in match outcomes compared to the negative impact of unforced errors.
How Unforced Errors Influence Match Outcomes
Unforced errors significantly impact match outcomes by directly contributing to lost points, tipping the balance in favor of the opponent. Players with lower unforced error counts demonstrate higher consistency and mental fortitude, often leading to more wins in high-stakes matches. Statistical analysis shows that reducing unforced errors correlates strongly with improved serve percentages and overall match success rates.
Techniques to Increase Aces
Improving serve speed and precision through targeted strength training and biomechanical analysis significantly increase the number of aces in tennis matches. Mastery of various serve techniques such as the flat, slice, and kick serve creates unpredictability, forcing opponents into receiving errors rather than successful returns. Players who consistently practice serve placement drills to target opponent weaknesses typically see a marked decrease in unforced errors while boosting ace statistics.
Strategies to Reduce Unforced Errors
Reducing unforced errors in tennis requires focused strategies such as improving footwork to maintain balance and positioning, enhancing shot selection by prioritizing high-percentage plays, and developing consistent stroke mechanics through regular practice. Incorporating mental training techniques like concentration exercises and stress management can further minimize mistakes caused by pressure. Practicing rally drills that simulate match conditions also helps players anticipate shots better, reducing the frequency of unforced errors while increasing opportunities to serve more aces.
Ace and Unforced Error Statistics in Professional Tennis
Aces and unforced errors serve as critical statistical indicators in professional tennis, reflecting a player's offensive precision and defensive reliability. High ace counts often correspond to powerful, well-placed serves that contribute directly to winning points with minimal response from opponents. Conversely, unforced error rates measure the frequency of mistakes made without external pressure, influencing match outcomes by signaling lapses in focus or technique.
Ace vs Unforced Error: Impact on Player Performance
Aces and unforced errors significantly influence player performance by affecting momentum and scoring efficiency in tennis matches. A high number of aces correlates with strong serve effectiveness, increasing pressure on opponents and shortening points, while unforced errors lead to lost points and signal lapses in concentration or technique. Balancing aggressive play to maximize aces while minimizing unforced errors is crucial for optimal match outcomes and sustained player confidence.
Ace Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com