Canyoning involves navigating through canyons using techniques such as climbing, swimming, and rappelling, offering an exhilarating way to explore nature's hidden landscapes. This adventurous sport requires both physical fitness and safety awareness to fully enjoy the thrills while minimizing risks. Discover how canyoning can transform your outdoor experiences by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
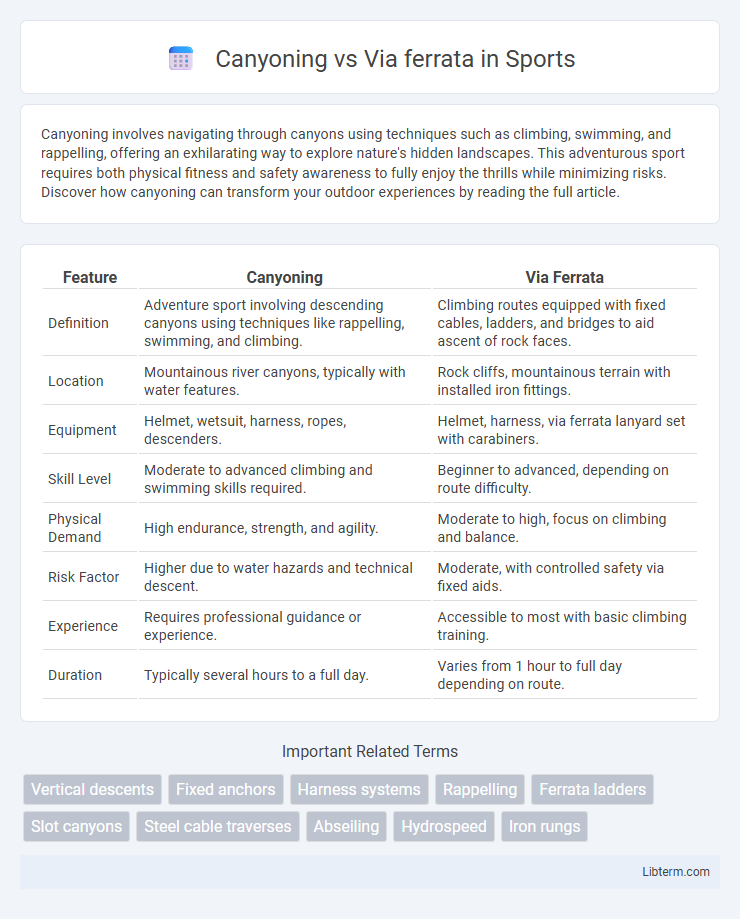
| Feature | Canyoning | Via Ferrata |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adventure sport involving descending canyons using techniques like rappelling, swimming, and climbing. | Climbing routes equipped with fixed cables, ladders, and bridges to aid ascent of rock faces. |
| Location | Mountainous river canyons, typically with water features. | Rock cliffs, mountainous terrain with installed iron fittings. |
| Equipment | Helmet, wetsuit, harness, ropes, descenders. | Helmet, harness, via ferrata lanyard set with carabiners. |
| Skill Level | Moderate to advanced climbing and swimming skills required. | Beginner to advanced, depending on route difficulty. |
| Physical Demand | High endurance, strength, and agility. | Moderate to high, focus on climbing and balance. |
| Risk Factor | Higher due to water hazards and technical descent. | Moderate, with controlled safety via fixed aids. |
| Experience | Requires professional guidance or experience. | Accessible to most with basic climbing training. |
| Duration | Typically several hours to a full day. | Varies from 1 hour to full day depending on route. |
Introduction to Canyoning and Via Ferrata
Canyoning involves navigating natural water-filled gorges through activities such as abseiling, swimming, and climbing, emphasizing adventure in rugged terrains and water features. Via ferrata is a protected climbing route equipped with fixed cables, ladders, and bridges, allowing climbers to traverse cliffs and steep mountain areas safely. Both activities offer unique experiences combining physical challenges with stunning natural landscapes, catering to outdoor enthusiasts seeking adrenaline and scenic exploration.
Key Differences Between Canyoning and Via Ferrata
Canyoning involves navigating through water-filled canyons using techniques like rappelling, swimming, and sliding, emphasizing aquatic adventure and technical water skills. Via ferrata requires climbing protected routes with fixed cables, ladders, and bridges, focusing on vertical rock climbing and secure ascent methods. The key difference lies in canyoning's emphasis on water-based terrain versus via ferrata's structured, rock-face climbing paths.
Required Skill Levels for Each Activity
Canyoning demands strong swimming skills, physical endurance, and proficiency in rappelling techniques to navigate waterfalls, pools, and rocky terrain safely. Via ferrata requires climbers to have basic rock climbing skills, comfort with heights, and the ability to use specialized equipment such as harnesses, carabiners, and helmets along fixed steel cables and ladders. Both activities necessitate a good sense of balance and physical fitness, though canyoning generally involves higher technical difficulty and risk management in varied water environments.
Essential Gear and Equipment Comparison
Canyoning requires specialized gear including wetsuits, helmets, harnesses, descenders, and sturdy canyon shoes designed for wet and slippery environments. Via ferrata gear centers around a climbing harness, helmet, via ferrata lanyard with energy absorber, and durable gloves for gripping steel cables along exposed routes. Both activities demand safety equipment tailored to their respective environments, with canyoning emphasizing waterproof and abrasion-resistant materials, while via ferrata focuses on secure clipping systems and grip protection.
Physical and Mental Challenges Involved
Canyoning demands intense physical endurance, agility, and strength to navigate slippery rocks, swift currents, and steep descents, while also requiring mental resilience to manage fear and unexpected environmental obstacles. Via ferrata combines aspects of rock climbing and hiking, challenging climbers with exposed routes secured by steel cables, necessitating mental focus, precise coordination, and sustained upper body strength to safely progress. Both activities push participants to develop problem-solving skills and maintain situational awareness under physically taxing conditions.
Safety Considerations and Risks
Canyoning involves navigating natural waterways and rock formations, exposing participants to risks such as slippery surfaces, strong currents, and sudden weather changes, requiring specialized gear like helmets, wetsuits, and secure harnesses for safety. Via ferrata entails climbing routes equipped with fixed cables, ladders, and bridges, where fall protection systems including lanyards and carabiners are essential to prevent accidents caused by missteps or equipment failure. Both activities demand comprehensive training, proper use of personal protective equipment, and thorough risk assessment to mitigate hazards and ensure participant safety.
Best Locations for Canyoning and Via Ferrata
The best locations for canyoning include the Verdon Gorge in France, known for its crystal-clear waters and challenging descents, and the Blue Mountains in Australia, famous for its rugged cliffs and natural water slides. For via ferrata, the Dolomites in Italy offer iconic routes with steel cables and ladders against dramatic alpine backdrops, while the Julian Alps in Slovenia provide varied difficulty levels and breathtaking views. Both activities require specific gear and local expertise to safely explore these prime adventure destinations.
Ideal Weather and Seasonal Conditions
Canyoning is best enjoyed in warm, dry weather with stable water levels, typically during late spring to early autumn when rivers and waterfalls are accessible but not dangerously swollen. Via ferrata suits a wider range of conditions, favoring clear, dry days in spring through autumn for safe climbing and secure footing on metal rungs and cables. Both activities require avoiding heavy rain or snow seasons to minimize risks such as flash floods in canyons and slippery rock surfaces on via ferrata routes.
Environmental Impact and Wildlife Considerations
Canyoning involves navigating through river gorges, which can disrupt aquatic ecosystems and disturb wildlife habitats sensitive to water quality and flow changes. Via ferrata, constructed on rock faces with fixed cables and ladders, primarily impacts cliff vegetation and nesting bird sites but generally causes less direct disturbance to aquatic environments. Both activities require careful route management and adherence to environmental guidelines to minimize erosion, habitat destruction, and stress on local flora and fauna.
Choosing the Right Adventure for You
Choosing between canyoning and via ferrata depends on your preferred terrain and physical challenge. Canyoning offers an adrenaline-filled experience through waterfalls, pools, and narrow gorges, ideal for those who enjoy water-based adventures. Via ferrata provides a thrilling climb on protected routes with fixed cables and ladders, perfect for thrill-seekers who favor heights and panoramic mountain views.
Canyoning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com