Understanding your strong side helps leverage your natural talents and enhances performance in various aspects of life. Focusing on your strengths enables you to build confidence and achieve goals more efficiently. Explore the rest of this article to discover how to identify and maximize your strong side for success.
Table of Comparison
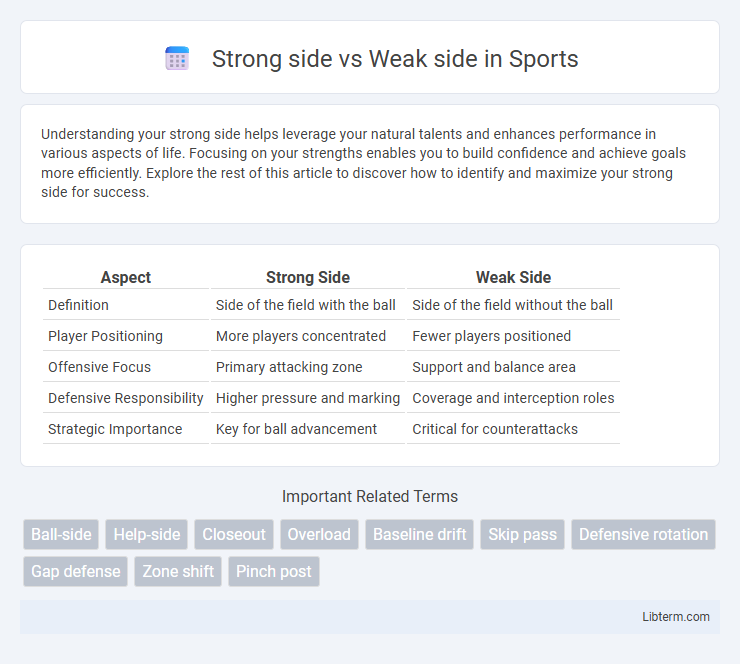
| Aspect | Strong Side | Weak Side |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Side of the field with the ball | Side of the field without the ball |
| Player Positioning | More players concentrated | Fewer players positioned |
| Offensive Focus | Primary attacking zone | Support and balance area |
| Defensive Responsibility | Higher pressure and marking | Coverage and interception roles |
| Strategic Importance | Key for ball advancement | Critical for counterattacks |
Understanding the Concept: Strong Side vs Weak Side
Strong side and weak side refer to spatial concepts in team sports, particularly in basketball and football, defining the side of the court or field with more players versus fewer players. The strong side typically hosts the ball and offensive players, creating opportunities for scoring, while the weak side provides defensive balance and potential for quick ball reversal. Understanding these dynamics helps teams optimize positioning, exploit defensive weaknesses, and improve overall strategy.
Historical Perspectives on Strong and Weak Sides
Historical perspectives on strong and weak sides in military tactics highlight their strategic importance in battlefield formations and maneuvers. The strong side typically refers to the flank with reinforced troops or advantageous terrain, often leveraged to achieve breakthroughs or defend critical positions. Conversely, the weak side was historically vulnerable to enemy exploitation, necessitating adaptable strategies in campaigns from ancient Greece to modern warfare.
Anatomical Differences: What Defines Strong and Weak Sides
The strong side typically exhibits greater muscle mass, bone density, and neural activation, reflecting its dominance and frequent use in daily activities. In contrast, the weak side shows reduced muscular strength, diminished proprioception, and often altered joint mechanics due to less frequent engagement. Anatomical differences between the two sides influence overall motor control, balance, and rehabilitation outcomes after injury or neurological impairment.
The Impact of Dominance on Athletic Performance
Athletic performance often hinges on the dominance of the strong side versus the weak side, where the strong side typically generates more power, coordination, and stability during movements. Imbalances between sides can lead to inefficient biomechanics, increased injury risk, and limited overall performance potential. Training protocols that address and reduce these disparities enhance muscle symmetry, neuromuscular control, and functional strength, optimizing athletic output and resilience.
Training Techniques to Balance Strong and Weak Sides
Training techniques to balance strong and weak sides include unilateral exercises like single-leg squats and single-arm presses, which specifically target weaker muscles to promote symmetry. Incorporating bilateral exercises with focus on controlled, equal effort from both sides helps prevent compensation by the dominant side. Utilizing resistance bands and proprioceptive training enhances neuromuscular coordination, ensuring balanced development and reducing injury risk caused by muscular imbalances.
Common Mistakes When Addressing Side Imbalances
Common mistakes when addressing strong side versus weak side imbalances include neglecting proper form and overcompensating with the dominant side, which can exacerbate muscle imbalances and lead to injury. Failing to implement targeted unilateral exercises that focus on strengthening the weak side limits balanced muscle development and functional symmetry. Ignoring consistent assessment and progressive overload for the weaker side results in plateaued progress and persistent strength discrepancies.
Sports Strategies: Exploiting Opponent’s Weak Side
Exploiting an opponent's weak side in sports strategies involves targeting areas where their defense is less organized or slower to react, often opposite their strong side. Teams capitalize on this by directing plays, passes, or attacks toward the weak side to create scoring opportunities or force turnovers. Effective analysis of player positioning and tendencies enhances the ability to exploit these weaknesses, leading to improved offensive efficiency and strategic advantage.
Injury Risks Associated with Muscle Imbalances
Muscle imbalances between the strong side and weak side increase injury risks by causing uneven joint stress and compensatory movement patterns. The weak side is more prone to strains, sprains, and overuse injuries due to insufficient muscle strength and stability. Correcting these imbalances through targeted strength training reduces asymmetrical loading and enhances overall musculoskeletal health.
Rehabilitation Approaches for Strengthening the Weak Side
Rehabilitation approaches for strengthening the weak side emphasize targeted resistance training and neuromuscular re-education to restore muscle balance and improve functional symmetry. Techniques such as unilateral exercises, proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF), and task-specific training enhance motor control and strength in the affected limb. Consistent monitoring with electromyography (EMG) biofeedback supports optimal muscle activation and progress assessment during rehabilitation.
Long-Term Benefits of Achieving Symmetry and Balance
Achieving symmetry and balance between the strong side and weak side enhances overall muscle development, reducing the risk of injury caused by muscular imbalances and compensatory movements. Long-term benefits include improved athletic performance, increased functional strength, and better joint stability, promoting longevity in physical activities. Consistent training that targets the weak side ensures proportional growth and neuromuscular coordination, leading to sustained strength gains and optimal biomechanical efficiency.
Strong side Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com