Interval training alternates short bursts of intense exercise with periods of rest or low-intensity activity, boosting cardiovascular fitness and calorie burn efficiently. This method enhances endurance, speed, and overall performance while reducing workout time compared to steady-state cardio. Discover how incorporating interval training into your routine can transform your fitness--read the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
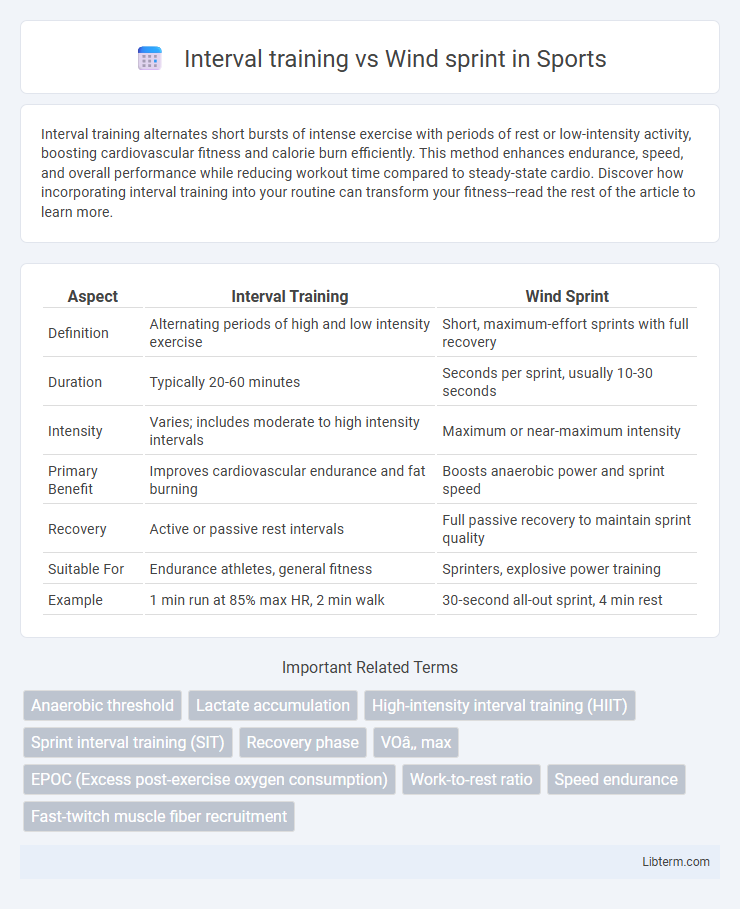
| Aspect | Interval Training | Wind Sprint |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alternating periods of high and low intensity exercise | Short, maximum-effort sprints with full recovery |
| Duration | Typically 20-60 minutes | Seconds per sprint, usually 10-30 seconds |
| Intensity | Varies; includes moderate to high intensity intervals | Maximum or near-maximum intensity |
| Primary Benefit | Improves cardiovascular endurance and fat burning | Boosts anaerobic power and sprint speed |
| Recovery | Active or passive rest intervals | Full passive recovery to maintain sprint quality |
| Suitable For | Endurance athletes, general fitness | Sprinters, explosive power training |
| Example | 1 min run at 85% max HR, 2 min walk | 30-second all-out sprint, 4 min rest |
Introduction to Interval Training and Wind Sprints
Interval training consists of alternating periods of high-intensity exercise and recovery, enhancing cardiovascular endurance and metabolic rate. Wind sprints, short bursts of maximum effort running followed by rest, specifically target speed and anaerobic capacity. Both methods improve overall fitness but differ in structure and focus, with interval training offering broader conditioning and wind sprints emphasizing explosive power.
Key Differences Between Interval Training and Wind Sprints
Interval training involves alternating periods of high-intensity exercise with recovery phases, optimizing cardiovascular endurance and fat burning through varied pacing. Wind sprints consist of short bursts of maximum effort running followed by longer rest, primarily targeting explosive speed and anaerobic power. The key differences lie in duration, intensity, and recovery timing, with interval training offering structured endurance benefits while wind sprints emphasize speed and muscle explosiveness.
Benefits of Interval Training
Interval training improves cardiovascular efficiency by alternating high-intensity bursts with recovery periods, enhancing aerobic and anaerobic capacity more effectively than wind sprints alone. It promotes greater fat oxidation, muscle endurance, and metabolic rate, contributing to sustained weight loss and improved athletic performance. This method reduces injury risk by balancing exertion with recovery, making it suitable for diverse fitness levels.
Advantages of Wind Sprints
Wind sprints offer superior explosive power development and enhance anaerobic capacity more effectively than traditional interval training. They improve fast-twitch muscle fiber recruitment, leading to increased speed and agility essential for athletic performance. Wind sprints also require less time commitment while delivering high-intensity cardiovascular and muscular benefits.
Impact on Cardiovascular Health
Interval training and wind sprints both significantly enhance cardiovascular health by improving heart rate variability and boosting VO2 max, which increases overall endurance and heart efficiency. Interval training alternates between moderate and high-intensity exercise, promoting improved blood pressure regulation and reduced resting heart rate. Wind sprints, characterized by short bursts of maximum effort followed by rest, intensify heart muscle function and improve oxygen utilization, leading to better cardiovascular resilience.
Muscle Development and Fat Loss
Interval training enhances muscle development by alternating between high-intensity effort and rest periods, promoting muscle endurance and growth through varied resistance and duration. Wind sprints primarily target fast-twitch muscle fibers, accelerating muscle power and explosive strength, which also boosts fat loss via high-intensity calorie burn. Both methods effectively increase metabolic rate and improve body composition, but interval training offers a more balanced approach for sustained muscle growth and fat reduction.
Training Structure and Intensity Levels
Interval training involves alternating periods of high-intensity exercise with recovery phases, allowing structured variation in intensity to optimize cardiovascular endurance and fat burning. Wind sprints consist of short, maximal effort bursts followed by longer rest intervals, emphasizing peak power output and anaerobic capacity. Both methods increase overall training intensity but differ in work-to-rest ratios and targeted energy systems for athletic performance.
Suitability for Different Fitness Goals
Interval training suits those aiming to improve overall cardiovascular endurance and burn fat efficiently through alternating periods of high and low intensity. Wind sprints target athletes seeking to increase explosive speed, anaerobic capacity, and muscle power by performing short bursts of maximum effort running. Choosing between interval training and wind sprints depends on whether the primary goal is sustained endurance improvements or rapid speed and power development.
Common Mistakes and Safety Tips
Interval training and wind sprints both demand high-intensity effort, but common mistakes include neglecting proper warm-up, overtraining, and poor running form, which increase injury risk. Safety tips emphasize gradual intensity progression, maintaining correct posture, and ensuring adequate hydration and rest between sessions. Monitoring heart rate and listening to the body help prevent overexertion and improve workout effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Workout
Interval training offers structured periods of high-intensity effort followed by recovery, enhancing cardiovascular endurance and fat burn efficiently. Wind sprints emphasize maximal sprinting speed over short distances, improving explosive power and fast-twitch muscle activation. Selecting the right method depends on your fitness goals: use interval training for overall stamina and metabolic boost, and wind sprints to build speed and anaerobic capacity.
Interval training Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com