Abstract art transforms traditional forms into expressive visuals that emphasize color, shape, and emotion over realistic representation. This art style encourages viewers to interpret meanings personally, making each experience unique to your perspective. Continue exploring the article to discover the history, techniques, and significance of abstract art.
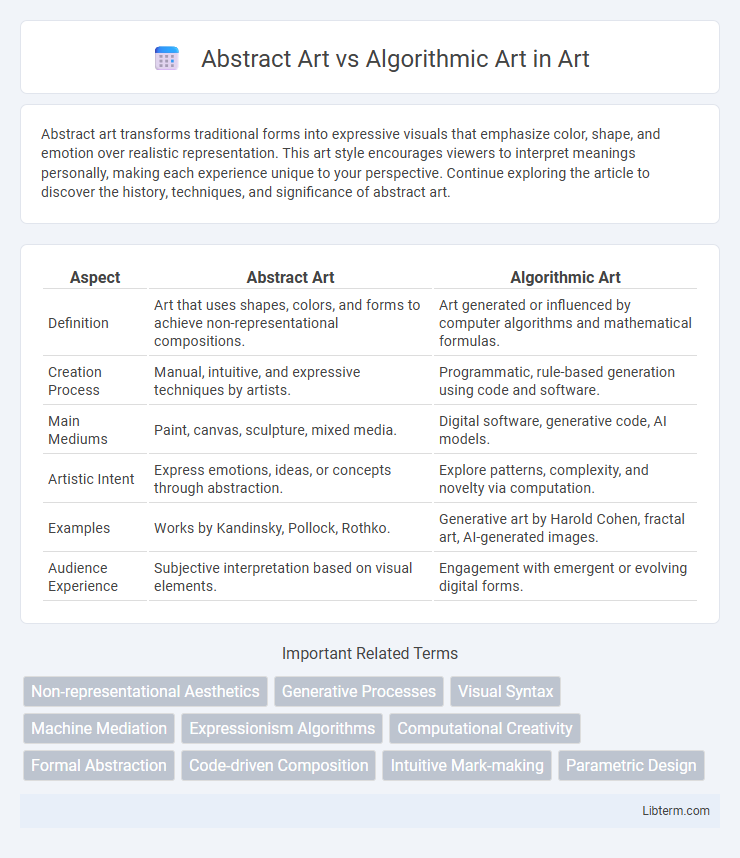
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Abstract Art | Algorithmic Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art that uses shapes, colors, and forms to achieve non-representational compositions. | Art generated or influenced by computer algorithms and mathematical formulas. |
| Creation Process | Manual, intuitive, and expressive techniques by artists. | Programmatic, rule-based generation using code and software. |
| Main Mediums | Paint, canvas, sculpture, mixed media. | Digital software, generative code, AI models. |
| Artistic Intent | Express emotions, ideas, or concepts through abstraction. | Explore patterns, complexity, and novelty via computation. |
| Examples | Works by Kandinsky, Pollock, Rothko. | Generative art by Harold Cohen, fractal art, AI-generated images. |
| Audience Experience | Subjective interpretation based on visual elements. | Engagement with emergent or evolving digital forms. |
Introduction to Abstract Art and Algorithmic Art
Abstract art emphasizes visual language through shapes, colors, and forms detached from realistic representation, originating in the early 20th century with pioneers like Wassily Kandinsky and Piet Mondrian. Algorithmic art, emerging from computational creativity, uses mathematical algorithms and code to generate artworks, blending technology with artistic expression. Both styles challenge traditional aesthetics, with abstract art rooted in human emotion and intuition and algorithmic art characterized by systematic, rule-based creation.
Historical Evolution of Abstract Art
Abstract art originated in the early 20th century with pioneers like Wassily Kandinsky and Kazimir Malevich, emphasizing non-representational forms and vibrant color schemes. This movement evolved through various phases including Cubism, Futurism, and Abstract Expressionism, profoundly impacting the trajectory of modern art. Algorithmic art, emerging in the digital age, contrasts with abstract art by using computer algorithms to generate visuals, creating a bridge between human creativity and computational logic.
The Rise of Algorithmic Art
Algorithmic art has surged with advancements in computer science, utilizing mathematical algorithms and code to create complex, dynamic visuals that transcend traditional abstract art. Unlike abstract art, which relies on human intuition and spontaneous expression, algorithmic art leverages automation, procedural generation, and artificial intelligence to produce intricate patterns and evolving designs. This rise reflects a shift towards computational creativity, blending technology with artistic innovation to expand the boundaries of visual art.
Defining Key Characteristics: Abstract vs Algorithmic
Abstract art emphasizes non-representational forms, focusing on colors, shapes, and textures to evoke emotions and ideas without depicting real-world objects. Algorithmic art relies on mathematical algorithms and computer code to generate visual patterns and structures, often producing complex and iterative designs beyond manual creation. The key distinction lies in abstract art's expressive, human-driven creativity versus algorithmic art's systematic, programmable generation process.
Creative Process: Human Intuition vs Computational Logic
Abstract art thrives on human intuition, allowing artists to express emotions, subconscious thoughts, and spontaneity through organic forms and unpredictable brushstrokes. Algorithmic art relies on computational logic, utilizing mathematical algorithms, code, and systematic procedures to generate precise, often complex patterns and structures. The creative process in abstract art emphasizes subjective interpretation and emotional depth, while algorithmic art prioritizes logical design and reproducibility through programming languages like Python, Processing, or JavaScript.
Tools and Techniques: Brushes versus Code
Abstract art relies on traditional tools like brushes, palettes, and physical media to create expressive, non-representational forms with emphasis on texture, color, and gestural strokes. Algorithmic art uses programming languages, algorithms, and computational processes to generate visual compositions, often employing code to define shapes, patterns, and spatial relationships. The contrast between tactile brushwork and digital computation highlights differences in creative methodology, where manual brush techniques offer intuitive spontaneity while algorithmic coding enables precise control and reproducible complexity.
Emotional Impact and Viewer Interpretation
Abstract Art evokes emotional responses through its use of color, form, and texture, allowing viewers to project personal interpretations and feelings. Algorithmic Art generates visuals via computational processes, often incorporating complexity and patterns that can provoke intellectual curiosity alongside emotional engagement. Both forms challenge traditional aesthetics but differ in that Abstract Art emphasizes spontaneous expression while Algorithmic Art invites contemplation of the underlying systems influencing the artwork.
Notable Artists and Iconic Works
Wassily Kandinsky and Jackson Pollock are seminal figures in Abstract Art, known for pioneering non-representational forms with works like Kandinsky's "Composition VII" and Pollock's "No. 5, 1948". In Algorithmic Art, creators such as Harold Cohen, who developed the AARON program, and Casey Reas, co-founder of Processing, have pushed the boundaries with digital and generative pieces like Cohen's computer-generated drawings and Reas's "Software Structures". These artists illustrate the divergence between manual abstraction and computer-aided creation, marking key evolutions in contemporary art history.
Challenges and Controversies in Both Art Forms
Abstract art faces challenges related to subjective interpretation and skepticism about its artistic value, often sparking debates over the definition of creativity. Algorithmic art encounters controversies around authorship and originality, as artworks are generated through code rather than traditional human craftsmanship. Both art forms provoke ongoing discussions about the role of human intention and technology in shaping artistic expression and cultural significance.
The Future of Abstract and Algorithmic Art
The future of abstract and algorithmic art lies in the convergence of human creativity and artificial intelligence, where algorithms generate complex, evolving patterns that challenge traditional artistic boundaries. Advances in machine learning and neural networks enable artists to create dynamic, interactive pieces that adapt to viewer input or environmental factors, expanding the potential for immersive art experiences. As digital platforms grow, algorithmic art will increasingly influence abstract art forms, reshaping aesthetics and redefining the art market.
Abstract Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com