Photomontage is a creative technique that combines multiple photographs into a single, cohesive image to convey a unique story or artistic vision. This method allows artists and designers to manipulate elements, playing with perspective, scale, and context to create visually compelling compositions. Discover how photomontage can transform your projects and elevate your visual storytelling by exploring the detailed techniques and examples ahead.
Table of Comparison
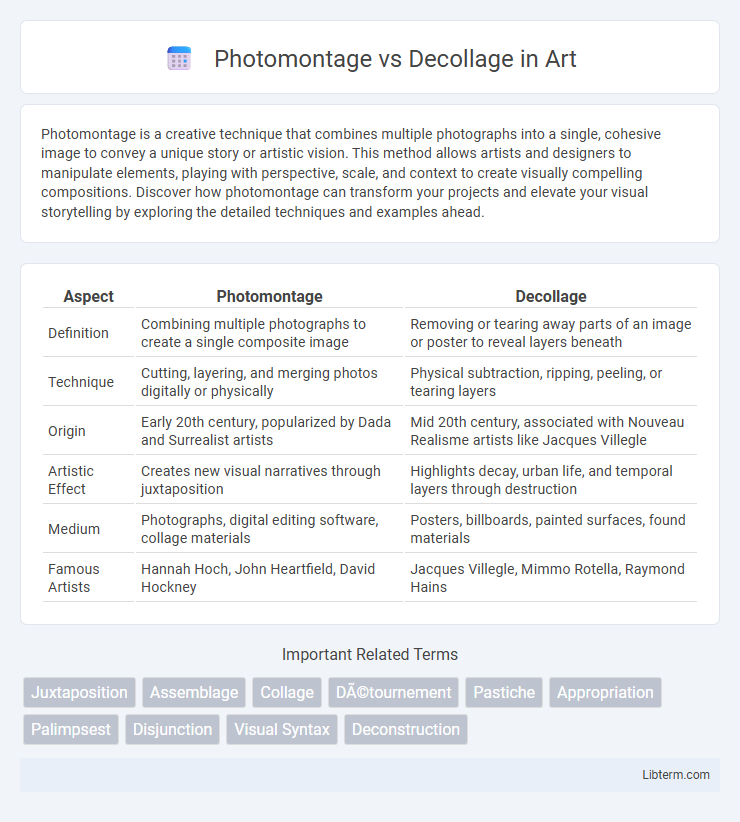
| Aspect | Photomontage | Decollage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining multiple photographs to create a single composite image | Removing or tearing away parts of an image or poster to reveal layers beneath |
| Technique | Cutting, layering, and merging photos digitally or physically | Physical subtraction, ripping, peeling, or tearing layers |
| Origin | Early 20th century, popularized by Dada and Surrealist artists | Mid 20th century, associated with Nouveau Realisme artists like Jacques Villegle |
| Artistic Effect | Creates new visual narratives through juxtaposition | Highlights decay, urban life, and temporal layers through destruction |
| Medium | Photographs, digital editing software, collage materials | Posters, billboards, painted surfaces, found materials |
| Famous Artists | Hannah Hoch, John Heartfield, David Hockney | Jacques Villegle, Mimmo Rotella, Raymond Hains |
Introduction to Photomontage and Decollage
Photomontage is an artistic technique that combines multiple photographs or images into a single composition to create surreal or narrative effects, often used in advertising and contemporary art for its ability to convey complex messages. Decollage, contrastingly, involves the process of tearing away or removing layers of posters or images from surfaces to reveal fragments beneath, emphasizing texture and deconstruction in visual storytelling. Both techniques challenge traditional imagery by manipulating photographic elements, but photomontage constructs new visuals while decollage uncovers hidden layers.
Origins and Historical Development
Photomontage emerged in the early 20th century, notably used by Dada artists like Hannah Hoch to challenge traditional aesthetics through the collage of photographic images, emphasizing political and social critique. Decollage, originating in post-war France with artists such as Jacques Villegle, involves the tearing and layering of posters to reveal fragmented urban dialogues, reflecting the disruption and reconstruction of public space. Both techniques developed as responses to modernity, utilizing media imagery to explore cultural and political upheavals during their respective eras.
Key Artists and Movements
Photomontage, pioneered by artists such as Hannah Hoch and John Heartfield in the Dada movement, combines photographic images to create new, often politically charged compositions. Decollage, associated with the Nouveau Realisme movement and artists like Jacques Villegle and Mimmo Rotella, involves tearing away or removing sections of posters to reveal layered visual textures and meanings. Both techniques challenge traditional art forms but diverge in approach, with photomontage constructing imagery and decollage deconstructing it.
Defining Features of Photomontage
Photomontage is a technique involving the precise assembly of multiple photographs into a single composite image, emphasizing deliberate layering and juxtaposition to create new visual narratives. It utilizes cut-and-paste methods or digital software to blend disparate elements seamlessly, often conveying complex themes or social commentary. In contrast, decollage involves the removal or tearing away of parts of an image or poster to reveal underlying layers, highlighting fragmentation and destruction as artistic expressions.
Unique Characteristics of Decollage
Decollage is characterized by the technique of cutting, tearing away, or removing layers from posters or printed materials, revealing fragmented images beneath, which contrasts with photomontage's method of assembling various photographic elements into a single composition. This destructive yet creative process emphasizes texture, depth, and unpredictability, allowing for spontaneous visual narratives. Artists like Jacques Villegle and Raymond Hains pioneered decollage as a form of urban expression, highlighting its raw, layered aesthetics distinct from the structured assembly of photomontage.
Techniques and Materials Used
Photomontage involves digitally or manually combining multiple photographs to create a seamless composite image, utilizing materials such as printed photographs, adhesive, scissors, and digital editing software like Adobe Photoshop. Decollage is an artistic technique that entails physically tearing, cutting, or removing layers from posters or printed images to reveal underlying layers, often relying on mixed media materials including glue, paint, and paper. These contrasting techniques highlight photomontage's emphasis on synthesis and precise assembly versus decollage's focus on deconstruction and textural depth.
Artistic Intent: Construction vs. Destruction
Photomontage emphasizes artistic intent through the construction of new visual narratives by combining multiple images to create cohesive, transformative compositions. In contrast, decollage involves the deliberate destruction or removal of layers from existing images, exposing underlying elements to reveal hidden meanings or provoke reinterpretation. This dichotomy highlights photomontage as a process of synthesis and creation, whereas decollage functions through fragmentation and deconstruction.
Cultural Impact and Influence
Photomontage revolutionized visual culture by merging disparate photographic elements to create new, politically charged narratives that challenged traditional artistic boundaries and influenced movements like Dada and Surrealism. Decollage, by physically tearing or removing layers from posters and advertisements, exposed urban cultural dialogues and the transient nature of public imagery, significantly impacting Pop Art and street art aesthetics. Both techniques reshaped cultural expression by questioning media consumption and reflecting societal fragmentation in the 20th century.
Contemporary Applications and Trends
Contemporary photomontage integrates digital technology to blend multiple images into cohesive, surreal compositions, widely used in advertising, social media, and visual arts for storytelling and brand identity. Decollage, contrastingly, emphasizes the artistic impact of tearing and deconstructing existing images, reflecting themes of urban decay and cultural critique, with prominence in street art and gallery exhibitions. Current trends show photomontage evolving through AI-generated content and augmented reality, while decollage embraces sustainability by repurposing physical materials and advocating for artistic recycling.
Choosing Between Photomontage and Decollage
Choosing between photomontage and decollage depends on the desired artistic effect and technique. Photomontage involves creating new compositions by assembling and layering photographic images, ideal for controlled, detailed visual storytelling. Decollage emphasizes the removal or tearing away of parts from posters or images to reveal underlying layers, producing raw, textured, and organic aesthetics.
Photomontage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com