Sinopia is a rich, dark red pigment historically prized for its vibrant hue and durability in artworks and frescoes. Known for its natural earth origins, it provides warmth and depth that artists have cherished for centuries. Discover how Sinopia can enhance your understanding of art and its timeless appeal throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
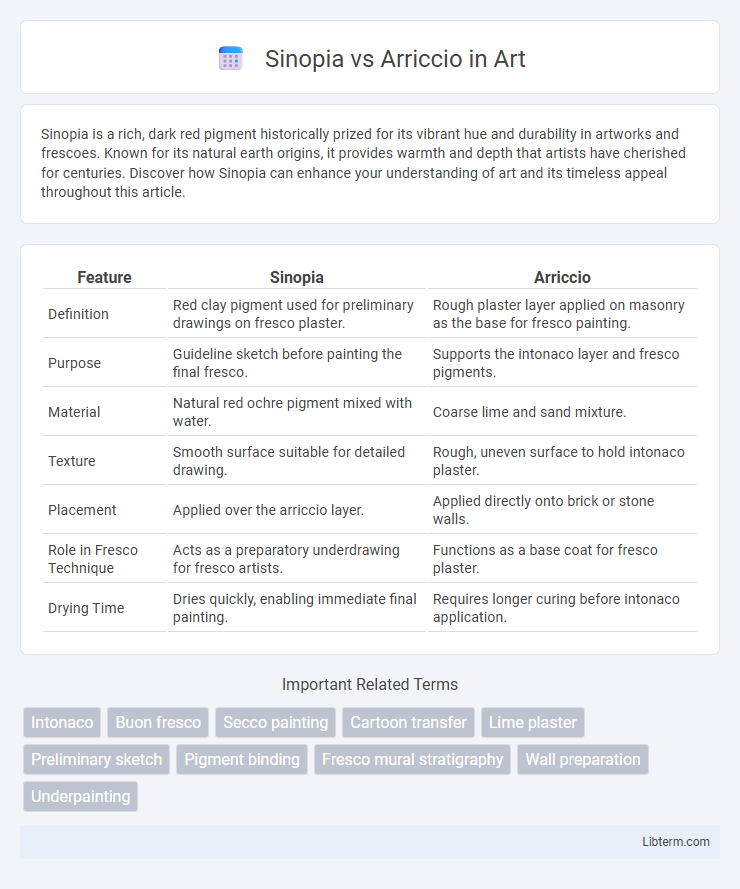
| Feature | Sinopia | Arriccio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Red clay pigment used for preliminary drawings on fresco plaster. | Rough plaster layer applied on masonry as the base for fresco painting. |
| Purpose | Guideline sketch before painting the final fresco. | Supports the intonaco layer and fresco pigments. |
| Material | Natural red ochre pigment mixed with water. | Coarse lime and sand mixture. |
| Texture | Smooth surface suitable for detailed drawing. | Rough, uneven surface to hold intonaco plaster. |
| Placement | Applied over the arriccio layer. | Applied directly onto brick or stone walls. |
| Role in Fresco Technique | Acts as a preparatory underdrawing for fresco artists. | Functions as a base coat for fresco plaster. |
| Drying Time | Dries quickly, enabling immediate final painting. | Requires longer curing before intonaco application. |
Introduction to Sinopia and Arriccio
Sinopia is a reddish-brown clay pigment traditionally used as the initial layer for fresco painting, providing a tonal base and primer on plaster surfaces. Arriccio refers to the rough undercoat of lime plaster applied to walls before the final, smooth intonaco layer, essential for fresco adhesion and durability. Both Sinopia and Arriccio serve foundational roles in fresco techniques, with Sinopia often sketched onto the Arriccio layer to guide the final artwork.
Historical Context of Sinopia and Arriccio
Sinopia and Arriccio are integral phases in the fresco painting technique, rooted deeply in Italian Renaissance artistry. Sinopia refers to the reddish-brown preparatory sketch made on the Arriccio, the rough first layer of plaster applied to walls. Historically, Sinopia allowed artists to outline designs precisely before adding pigment on the smooth Intonaco layer, reflecting a sophisticated method developed to enhance fresco durability and detail.
Definition and Purpose of Sinopia
Sinopia is a reddish-brown clay pigment used as an underdrawing layer in fresco painting, serving as a detailed guide for artists to outline compositions before applying Arriccio, the rough plaster base. The primary purpose of Sinopia is to provide a precise, durable sketch that ensures accuracy and proportion in the final artwork. Arriccio functions as the preparatory plaster layer onto which the Sinopia is applied, creating a stable surface for the subsequent painting layers.
Definition and Role of Arriccio
Arriccio is the rough undercoat layer of plaster applied on a wall before the final, smooth Sinopia layer in fresco painting. It serves as a base that provides texture and stability for the Sinopia, which carries the detailed sketch or outline for the artwork. This preparatory role of Arriccio ensures proper adhesion and durability of the fresco, making it essential for the fresco's structural integrity.
Techniques Used in Sinopia Preparation
Sinopia preparation involves sketching detailed preliminary drawings directly onto the arriccio layer, using natural red ochre pigments to outline compositions before applying final fresco layers. This traditional technique requires precise control of pigment application to ensure clarity and durability beneath the intonaco plaster. Sinopia lines serve as essential guides for fresco artists, blending artistic planning with structural preparation in mural painting.
The Application Process of Arriccio Layer
The application process of the Arriccio layer involves spreading a coarse plaster mixture composed of lime, sand, and sometimes small gravel onto the wall surface to create a rough base coat that ensures better adhesion for subsequent layers. This layer is typically applied with a trowel in a consistent thickness, followed by scoring or scratching to enhance the mechanical bond with the finer Sinopia layer. Proper curing times are essential to allow the Arriccio to set firmly, preventing cracks and ensuring structural integrity for the fresco painting process.
Differences Between Sinopia and Arriccio
Sinopia is a reddish-brown clay pigment used to create detailed preliminary sketches on a fresco surface, while arriccio is a rough undercoat layer of plaster applied to the wall before the final smooth intonaco layer. Sinopia serves as a guide for artists to map out their composition, whereas arriccio provides the foundational texture and absorbency needed for subsequent plaster layers. The key difference lies in their function: sinopia is a drawing medium on arriccio, which itself is a preparatory plaster layer.
Importance in Fresco Painting Techniques
Sinopia is the preliminary red ochre underdrawing applied directly onto the arriccio, the rough lime plaster base layer essential for fresco painting. The arriccio provides a durable, textured surface that absorbs the sinopia sketch, allowing artists to plan compositions precisely before applying the final intonaco layer. Mastery of both sinopia and arriccio ensures structural integrity and accurate transfer of detailed designs in traditional fresco techniques.
Preservation and Conservation Challenges
Sinopia, the preliminary red ochre sketches beneath frescoes, faces preservation challenges due to its delicate interface with plaster and vulnerability to environmental conditions such as humidity and temperature fluctuations. Arriccio, the rough plaster layer applied before the final fresco, requires careful conservation to prevent cracking and detachment that can compromise both the arriccio and the overlying artwork. Effective preservation strategies must address the inherent fragility of sinopia's pigment attachment and arriccio's structural stability to ensure the longevity of fresco techniques in cultural heritage sites.
Conclusion: Sinopia vs Arriccio in Mural Art
Sinopia serves as the detailed preliminary sketch directly on the plaster, guiding artists in mural composition with precise outlines and tonal variations. Arriccio, the rough undercoat plaster layer, provides the essential textured surface necessary for fresco adhesion and durability. In mural art, sinopia refines creative planning while arriccio ensures structural stability, making both indispensable for successful fresco execution.
Sinopia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com