Acrylic medium enhances the texture, transparency, and drying time of acrylic paints, allowing artists to customize their work with greater precision and control. Your creativity benefits as you experiment with glazing, thick impasto, or smooth finishes tailored to your artistic vision. Explore the rest of the article to discover how different acrylic mediums can transform your painting techniques.
Table of Comparison
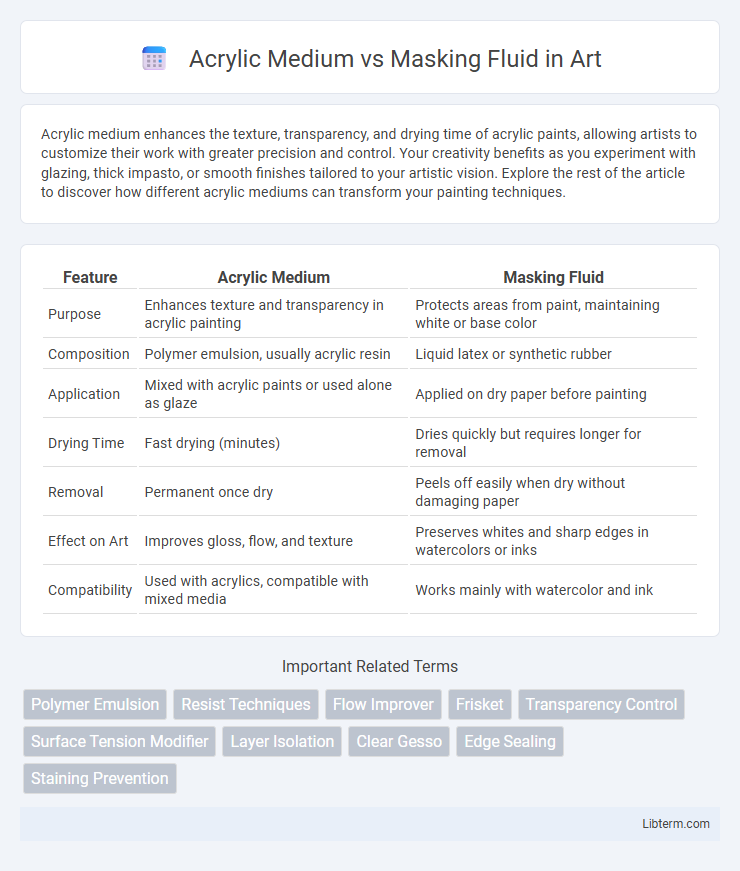
| Feature | Acrylic Medium | Masking Fluid |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances texture and transparency in acrylic painting | Protects areas from paint, maintaining white or base color |
| Composition | Polymer emulsion, usually acrylic resin | Liquid latex or synthetic rubber |
| Application | Mixed with acrylic paints or used alone as glaze | Applied on dry paper before painting |
| Drying Time | Fast drying (minutes) | Dries quickly but requires longer for removal |
| Removal | Permanent once dry | Peels off easily when dry without damaging paper |
| Effect on Art | Improves gloss, flow, and texture | Preserves whites and sharp edges in watercolors or inks |
| Compatibility | Used with acrylics, compatible with mixed media | Works mainly with watercolor and ink |
Understanding Acrylic Medium: Definition and Uses
Acrylic medium is a versatile additive in acrylic painting that modifies the texture, finish, and drying time of paint without altering its color intensity. It enhances adhesion, increases transparency, and allows artists to create varied effects such as glazing, thick impasto, or smooth blending. Common uses include extending paint, creating a glossy or matte finish, and improving flexibility to prevent cracking in acrylic artworks.
What is Masking Fluid? Key Features Explained
Masking fluid is a liquid latex or rubber-based substance used to protect areas of a canvas or paper from paint, allowing artists to preserve white spaces or underlying layers during the painting process. Key features include its quick drying time, flexibility when dry, and easy removal without damaging the surface beneath. Unlike acrylic medium, masking fluid is specifically designed for creating sharp edges and precise negative spaces in watercolor, acrylic, and mixed media artwork.
Composition Comparison: Acrylic Medium vs Masking Fluid
Acrylic medium is composed primarily of acrylic polymer emulsion, offering flexibility and durability when mixed with acrylic paints, while masking fluid consists of a liquid latex formula designed to create temporary resist barriers on paper. The acrylic medium enhances paint adhesion and texture by forming a strong, clear film, whereas masking fluid provides a removable layer that peels off easily after drying to preserve underlying surfaces. These compositional differences determine their distinct roles in painting techniques, with acrylic mediums integrating into paint layers and masking fluids serving as protective masks.
Applications in Art: When to Use Each Product
Acrylic medium is ideal for enhancing texture, transparency, and flexibility in paintings, making it perfect for layering and glazing techniques in acrylic artwork. Masking fluid is best suited for preserving white spaces or detailed highlights by creating resist areas before applying watercolor or ink washes. Use acrylic medium to modify paint consistency and finish, while masking fluid excels at protecting areas during wet-on-wet applications or intricate detailing.
Techniques Achievable with Acrylic Medium
Acrylic medium enables versatile techniques such as glazing, impasto, and texture creation, enhancing the depth and complexity of acrylic paintings. It allows artists to modify paint consistency, increase transparency, and create smooth blends or thick, textured effects that dry quickly and are durable. Unlike masking fluid, which is primarily used for masking areas in watercolor, acrylic medium expands creative possibilities by improving adhesion and flexibility in acrylic artwork.
Techniques Achievable with Masking Fluid
Masking fluid enables precise preservation of white or light areas in watercolor and acrylic paintings, allowing artists to create sharp edges, fine details, and complex layering effects without color bleeding. It is ideal for techniques such as creating intricate patterns, highlighting textures, and achieving negative painting effects by protecting underlying surfaces during washes. Once dried, masking fluid can be peeled off cleanly, uncovering untouched paper or canvas that enhances contrast and depth in the artwork.
Compatibility with Different Paints and Surfaces
Acrylic medium is highly compatible with a wide range of paints, including acrylics, oils, and watercolors, and adheres well to various surfaces like canvas, wood, and paper without altering the paint's texture. Masking fluid works best with water-based paints such as watercolors but can peel off easily on delicate or porous surfaces, limiting its use on textured canvases or oils. Choosing between acrylic medium and masking fluid depends on the paint type and surface, as acrylic medium offers more versatility across media, whereas masking fluid provides precise resist for watercolors on smooth papers.
Removal and Clean-Up: Acrylic Medium vs Masking Fluid
Acrylic Medium typically cleans up easily with water before it dries, allowing for smooth removal using a damp cloth or brush, while dried acrylic medium can require gentle scraping or rewetting to remove without damaging the surface. Masking Fluid, on the other hand, is designed to peel off easily once fully dry, often in a rubbery film that can be lifted without leaving residue; however, if left on too long or applied too thickly, it may become more difficult to remove and potentially damage delicate paper fibers. Effective removal of acrylic medium relies on timely cleaning, whereas masking fluid removal depends on proper curing and careful peeling to preserve underlying artwork.
Effects on Art Quality and Longevity
Acrylic medium enhances paint adhesion, flexibility, and vibrancy, contributing to improved art quality and durability by preventing cracking and fading over time. Masking fluid preserves underlying paper areas by creating a removable barrier, which maintains sharp contrasts and protects white space but may cause surface texture alterations and potential paper damage if overused. Combining both mediums strategically can optimize the longevity and visual impact of mixed-media artworks.
Choosing the Right Product for Your Artistic Goals
Acrylic medium enhances paint flexibility, texture, and drying time, making it ideal for blending and layering techniques in acrylic painting, while masking fluid protects areas from paint, preserving the underlying surface for crisp, clean highlights. Selecting the right product depends on your artistic goals: use acrylic medium to modify paint consistency and finish, and choose masking fluid when you need to maintain precise, unpainted sections during complex compositions. Understanding the distinct properties and applications of each ensures effective use in achieving desired visual effects and texture control in your artwork.
Acrylic Medium Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com