Minimalism enhances your life by focusing on simplicity and eliminating excess, allowing you to prioritize what truly matters. This lifestyle reduces stress and increases clarity, fostering a sense of freedom and intentional living. Discover how embracing minimalism can transform your daily routine and mindset by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
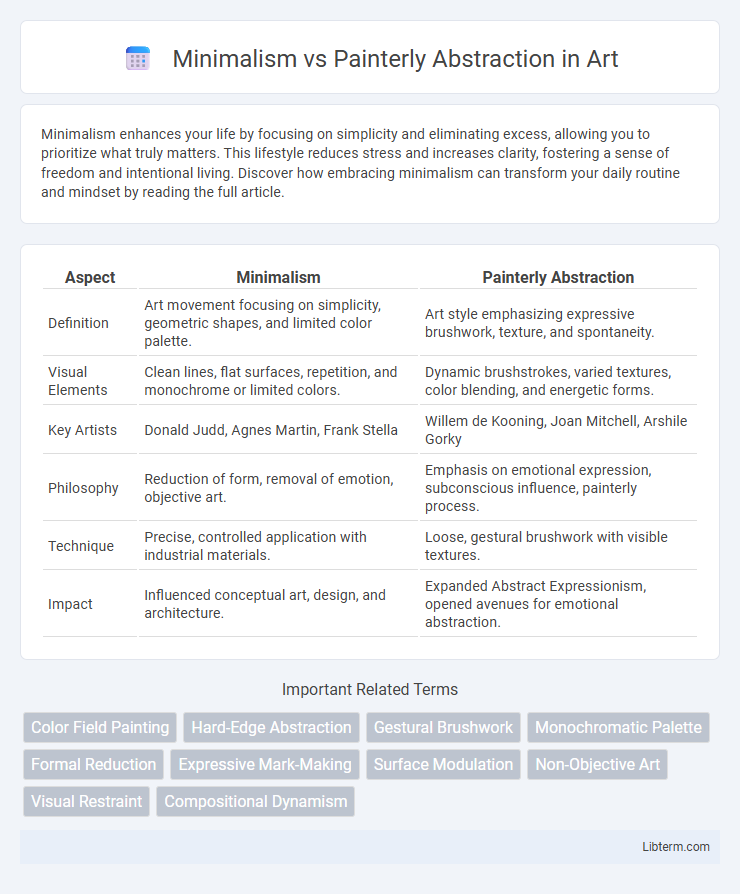
| Aspect | Minimalism | Painterly Abstraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art movement focusing on simplicity, geometric shapes, and limited color palette. | Art style emphasizing expressive brushwork, texture, and spontaneity. |
| Visual Elements | Clean lines, flat surfaces, repetition, and monochrome or limited colors. | Dynamic brushstrokes, varied textures, color blending, and energetic forms. |
| Key Artists | Donald Judd, Agnes Martin, Frank Stella | Willem de Kooning, Joan Mitchell, Arshile Gorky |
| Philosophy | Reduction of form, removal of emotion, objective art. | Emphasis on emotional expression, subconscious influence, painterly process. |
| Technique | Precise, controlled application with industrial materials. | Loose, gestural brushwork with visible textures. |
| Impact | Influenced conceptual art, design, and architecture. | Expanded Abstract Expressionism, opened avenues for emotional abstraction. |
Defining Minimalism: Simplicity and Clarity
Minimalism emphasizes simplicity and clarity through the use of clean lines, geometric shapes, and monochromatic palettes, stripping art to its essential elements. It rejects complexity and emotional expressiveness, aiming for an objective, refined aesthetic that highlights form and space. This approach contrasts sharply with Painterly Abstraction's emphasis on texture, spontaneity, and visible brushwork.
Understanding Painterly Abstraction: Expressive Gestures
Painterly Abstraction emphasizes expressive gestures through dynamic brushwork and spontaneous application of paint, creating textured surfaces that convey emotion and movement. This approach contrasts with Minimalism's focus on simplicity, geometric forms, and reduction of visual elements to eliminate personal expression. Understanding Painterly Abstraction requires analyzing how artists use brushstrokes as a language of emotion, where each gesture reflects the creator's subjective experience and energy.
Historical Origins and Key Movements
Minimalism emerged in the 1960s as a reaction against the emotional intensity of Abstract Expressionism, emphasizing simplicity, geometric forms, and reduced color palettes rooted in artists like Donald Judd and Agnes Martin. Painterly Abstraction traces its origins to early 20th-century modernism, with movements such as Abstract Expressionism and artists like Willem de Kooning prioritizing expressive brushwork and dynamic compositions. The key movements in Minimalism include the Post-Minimalist developments of the 1970s, while Painterly Abstraction evolved through various phases of gestural and lyrical abstraction.
Notable Artists in Minimalism and Painterly Abstraction
Minimalism features artists like Donald Judd, Frank Stella, and Agnes Martin, who emphasize simplicity, geometric forms, and monochromatic palettes. Painterly Abstraction highlights figures such as Willem de Kooning, Hans Hofmann, and Joan Mitchell, known for expressive brushstrokes, dynamic compositions, and rich textures. Both movements contrast in technique and philosophy, with Minimalism focusing on reduction and Painterly Abstraction celebrating gestural, spontaneous mark-making.
Philosophical Underpinnings: Intent and Interpretation
Minimalism emphasizes reduction to essential forms and materials, reflecting a philosophy of objectivity and viewer contemplation without emotional distraction. Painterly Abstraction embraces expressive brushwork and emotional depth, rooted in existential ideas about individual experience and subjective interpretation. These contrasting philosophies shape both artistic intent and audience engagement, with Minimalism inviting impersonal clarity and Painterly Abstraction provoking personal response.
Visual Language: Form, Color, and Texture
Minimalism employs simple geometric forms, limited color palettes, and smooth, untextured surfaces to emphasize purity and objectivity in visual language. Painterly Abstraction favors dynamic forms, vibrant and varied colors, and rich textures created through expressive brushstrokes to convey emotion and spontaneity. The contrast between Minimalism's restrained, precise aesthetic and Painterly Abstraction's energetic, textured approach highlights differing artistic intentions in form, color, and texture.
Viewer Engagement: Emotional Impact vs Intellectual Response
Minimalism emphasizes simplicity and geometric forms to provoke an intellectual response by encouraging viewers to contemplate space, structure, and materiality without emotional distraction. Painterly Abstraction relies on expressive brushwork, vibrant colors, and dynamic compositions to evoke strong emotional engagement, inviting viewers to experience mood and personal interpretation. The viewer's interaction with Minimalism is cerebral and reflective, while Painterly Abstraction fosters a visceral, sensory connection through emotional intensity.
Techniques and Materials Used
Minimalism emphasizes simplicity through the use of uniform, often industrial materials like metal, glass, and monochromatic paint applied with precision to create clean, geometric forms. Painterly Abstraction employs expressive brushstrokes, rich textures, and varied pigment layering on canvas or textured surfaces to evoke emotion and dynamic movement. Techniques in Minimalism minimize visible gesture, while Painterly Abstraction highlights the artist's physical interaction with materials through spontaneous, energetic application.
Minimalism vs Painterly Abstraction in Contemporary Art
Minimalism in contemporary art emphasizes simplicity, geometric forms, and the reduction of visual elements to create a sense of order and purity, often using monochromatic palettes and industrial materials. Painterly Abstraction, by contrast, celebrates expressive brushwork, texture, and vibrant colors to evoke emotional depth and dynamic movement within the canvas. The debate between these styles centers on the tension between objectivity and subjectivity in art, where Minimalism prioritizes structure and precision while Painterly Abstraction highlights spontaneity and sensory experience.
Collecting and Displaying: Market Trends and Valuation
Minimalism and Painterly Abstraction exhibit distinct market trends, with Minimalism often commanding higher valuations due to its clean lines and conceptual clarity appealing to contemporary collectors focused on spatial harmony. Painterly Abstraction attracts collectors who value emotional expression and dynamic brushwork, leading to fluctuating prices influenced by artist reputation and historical significance. Both styles demonstrate strong market demand, but Minimalism's streamlined aesthetic aligns with modern interior design trends, driving consistent growth in collection and display preferences.
Minimalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com