Printmaking is a versatile art form that enables artists to create multiple copies of a single design using techniques such as woodcut, etching, and screen printing. It combines creativity with technical skill to produce unique textures and intricate details that are often difficult to achieve in other mediums. Explore the rest of this article to discover the fascinating history, methods, and contemporary applications of printmaking.
Table of Comparison
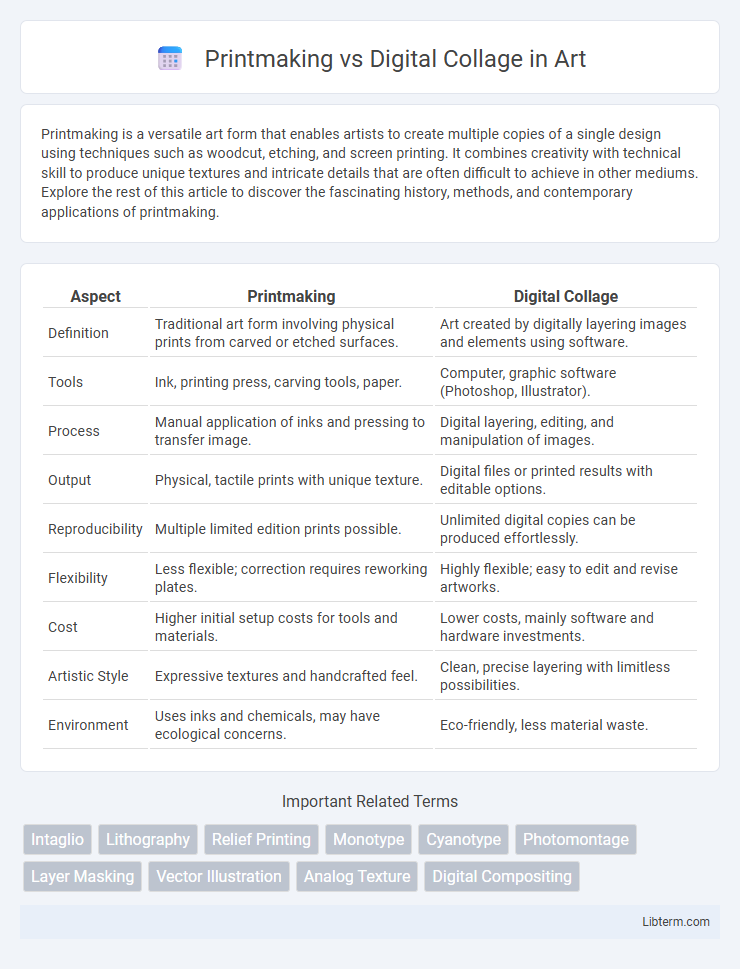
| Aspect | Printmaking | Digital Collage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional art form involving physical prints from carved or etched surfaces. | Art created by digitally layering images and elements using software. |
| Tools | Ink, printing press, carving tools, paper. | Computer, graphic software (Photoshop, Illustrator). |
| Process | Manual application of inks and pressing to transfer image. | Digital layering, editing, and manipulation of images. |
| Output | Physical, tactile prints with unique texture. | Digital files or printed results with editable options. |
| Reproducibility | Multiple limited edition prints possible. | Unlimited digital copies can be produced effortlessly. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; correction requires reworking plates. | Highly flexible; easy to edit and revise artworks. |
| Cost | Higher initial setup costs for tools and materials. | Lower costs, mainly software and hardware investments. |
| Artistic Style | Expressive textures and handcrafted feel. | Clean, precise layering with limitless possibilities. |
| Environment | Uses inks and chemicals, may have ecological concerns. | Eco-friendly, less material waste. |
Introduction to Printmaking and Digital Collage
Printmaking involves creating artworks by transferring ink from a matrix such as wood, metal, or stone onto paper, emphasizing techniques like etching, lithography, and screenprinting. Digital collage combines photographic elements, illustrations, and textures using software like Adobe Photoshop, allowing for flexible composition and easy manipulation of layers. Both methods offer unique creative possibilities, with printmaking rooted in tactile processes and digital collage leveraging modern technology for artistic exploration.
Historical Background of Printmaking
Printmaking dates back to ancient civilizations such as China and Egypt, where artists first used relief and intaglio techniques to reproduce images on paper and fabric. The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century revolutionized printmaking, enabling mass production of texts and artworks, and establishing it as a significant artistic medium. Throughout history, printmaking evolved through methods like woodcut, etching, and lithography, influencing both fine art and commercial printing before the rise of digital collage in the late 20th century.
Evolution of Digital Collage Art
The evolution of digital collage art has transformed traditional printmaking by integrating advanced software tools that enable complex layering, manipulation, and seamless blending of images. This digital medium allows artists to explore infinite creative possibilities with precision and speed, surpassing the tactile limitations of printmaking methods such as etching or lithography. The rise of digital platforms and graphic design technologies continues to push the boundaries of collage, making it a dynamic form adaptable to contemporary visual narratives.
Tools and Materials: Traditional vs Digital
Printmaking relies on traditional tools and materials such as carving tools, ink, brayers, and printing presses, often using paper or fabric as the substrate. Digital collage utilizes software like Adobe Photoshop or Procreate, leveraging digital brushes, layers, and textures without physical media. The tactile nature of printmaking contrasts with the flexibility and undo features of digital collage, affecting workflow and creative possibilities.
Creative Process Comparison
Printmaking involves a tactile, hands-on creative process that requires mastering techniques like etching, screen printing, or lithography, which demand precision and layering of inks to produce detailed textures and depth. Digital collage leverages software tools and digital assets, allowing for rapid experimentation with layering, blending, and resizing images, offering greater flexibility and ease in manipulation without the constraints of physical materials. Both methods emphasize composition and visual storytelling, but printmaking anchors creativity in materiality and craftsmanship, while digital collage prioritizes versatility and infinite revisions.
Aesthetic Differences in Final Artwork
Printmaking produces textured, tactile surfaces with rich ink layering and organic imperfections that highlight craftsmanship, contrasting with digital collage's crisp edges and seamless blending enabled by software tools. The inherent process of printmaking often results in unique variations with each print, while digital collages maintain consistent visual elements across multiple reproductions. Aesthetic differences also emerge in color depth and saturation, where printmaking offers subtle tonal shifts from physical pigments, compared to the vibrant, precise color control found in digital compositions.
Accessibility and Learning Curve
Printmaking often requires specialized equipment like presses and inks, making initial setup costly and less accessible for beginners. Digital collage benefits from widely available software and tools, allowing users to experiment with minimal investment and a gentler learning curve. Mastery in printmaking demands hands-on skills and understanding of physical materials, whereas digital collage emphasizes familiarity with graphic design programs and digital manipulation techniques.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Printmaking often involves hazardous inks, solvents, and paper waste that can negatively impact the environment, whereas digital collage minimizes material consumption and waste by utilizing virtual tools. The carbon footprint of digital art primarily stems from electricity use in devices and data storage, which can be reduced with renewable energy sources. Sustainable practices in printmaking include using eco-friendly inks and recycled papers, but digital collage offers a more inherently low-impact alternative for environmentally conscious artists.
Market Trends: Collecting and Selling
Printmaking continues to attract collectors with its tangible texture and limited editions, driving demand in traditional art markets and galleries. Digital collage gains momentum for its versatility and accessibility, appealing to younger audiences and online platforms through NFTs and digital marketplaces. Both mediums reflect evolving collector behaviors, with printmaking emphasizing scarcity and craftsmanship while digital collage leverages innovation and global reach.
Choosing the Right Medium for Your Art
Printmaking offers tactile textures and unique editioned works ideal for artists seeking traditional craftsmanship and physical depth, while digital collage provides unlimited flexibility with layering, manipulation, and quick revisions suited for contemporary, multimedia art forms. Consider the desired final presentation and audience interaction: printmaking excels in gallery settings and collectors valuing originality, whereas digital collage thrives in digital platforms and commercial design. Assess your workflow preferences, budget constraints, and technical skills to select a medium that aligns with your creative vision and professional goals.
Printmaking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com